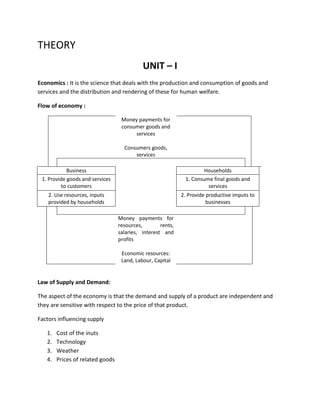
This document outlines the key concepts and formulas covered in the Engineering Economics and Cost Analysis course. It discusses topics like profit calculation, break-even analysis, time value of money formulas, capital investment evaluation methods, depreciation techniques, replacement analysis, and public project evaluation. The course aims to teach students methods to make economic decisions that minimize costs and maximize benefits for business organizations.