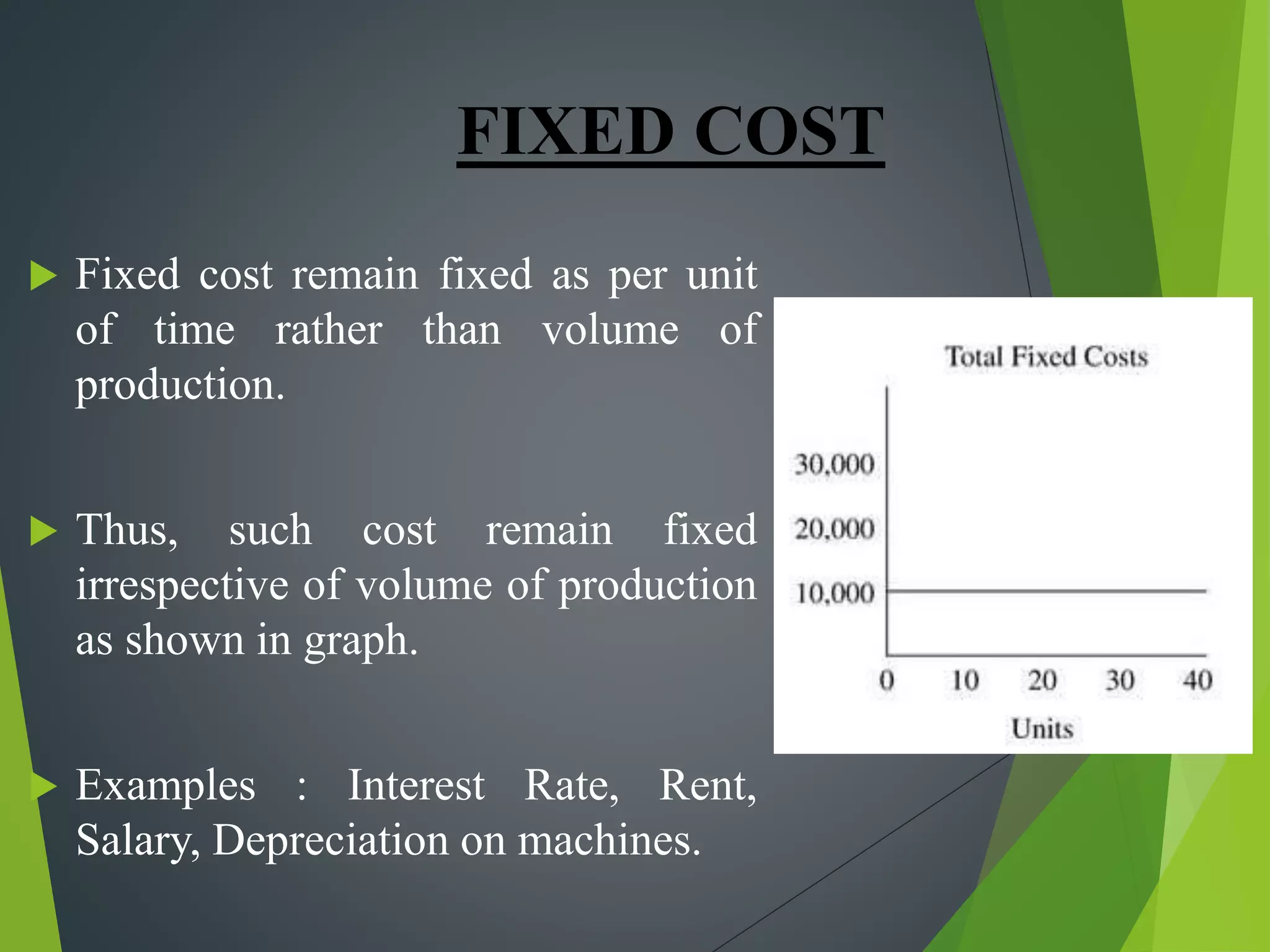
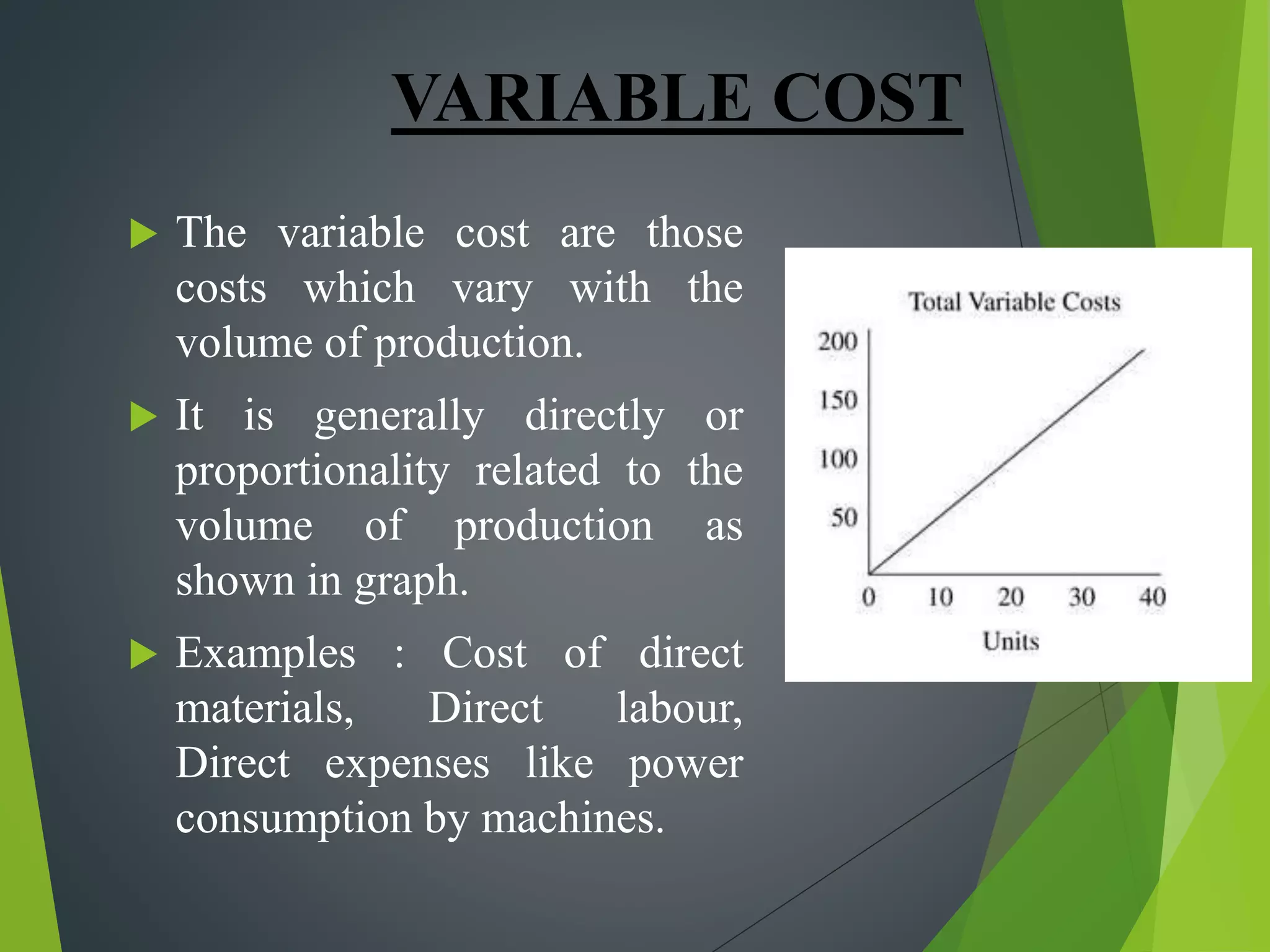
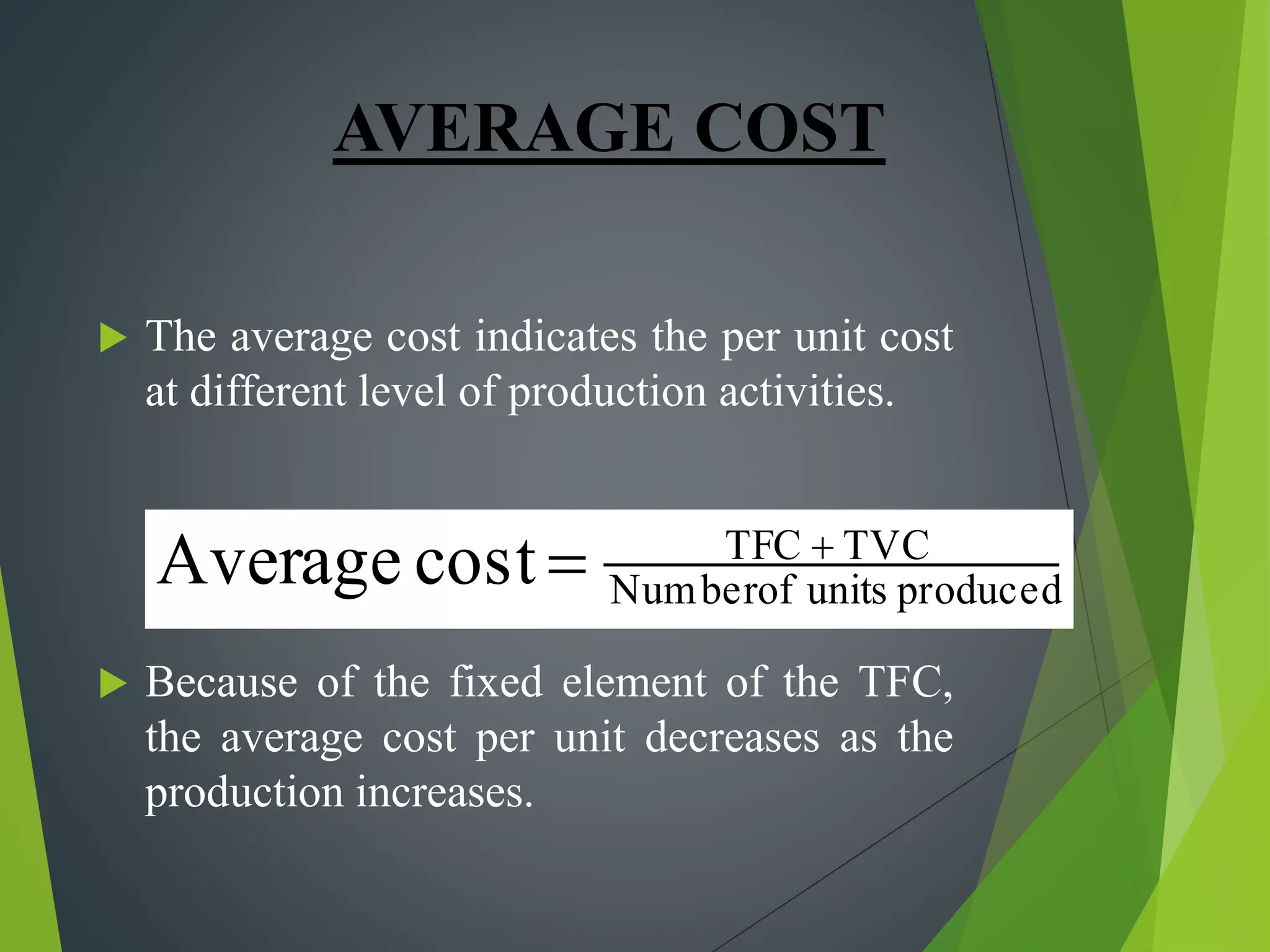
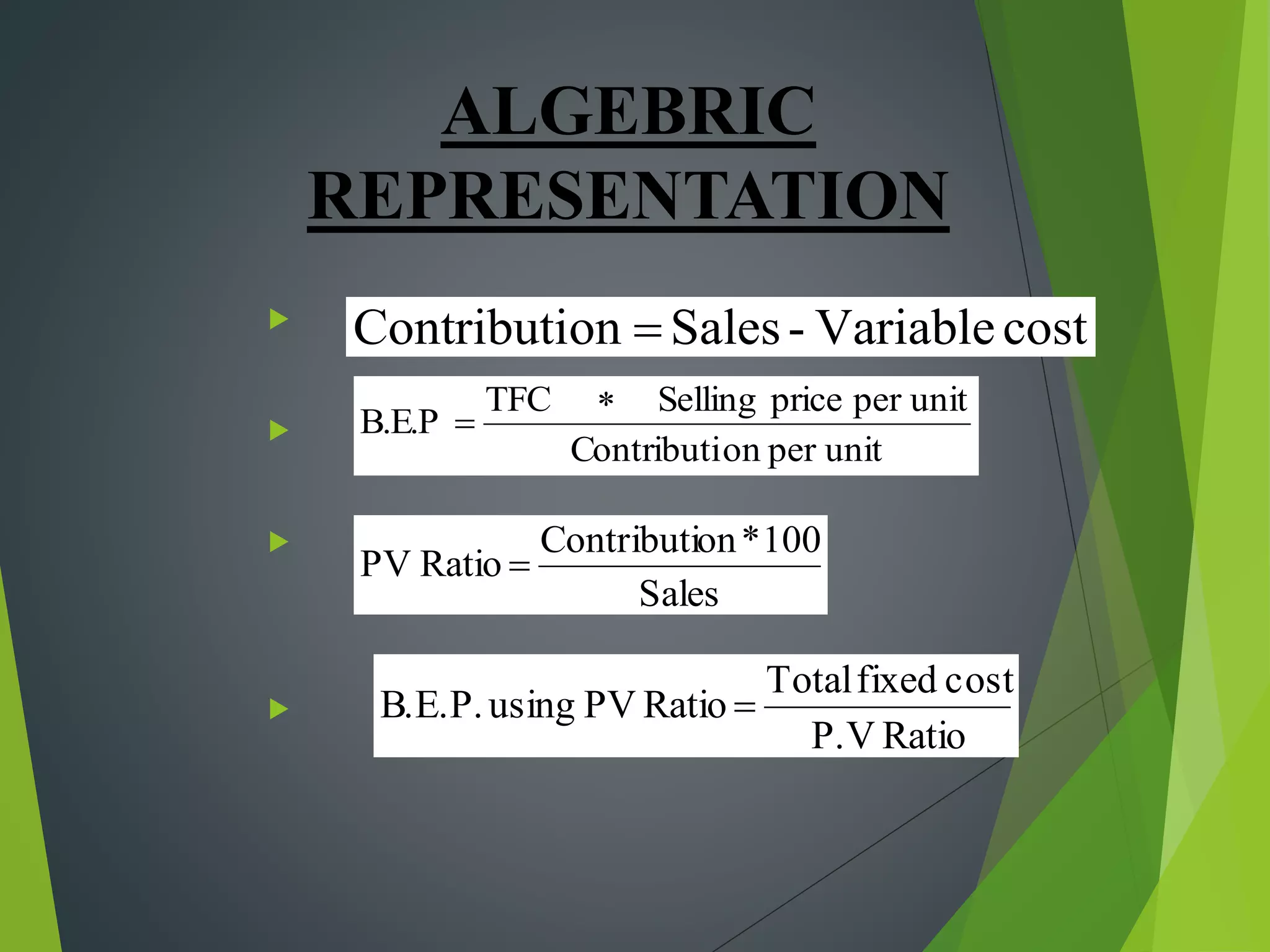
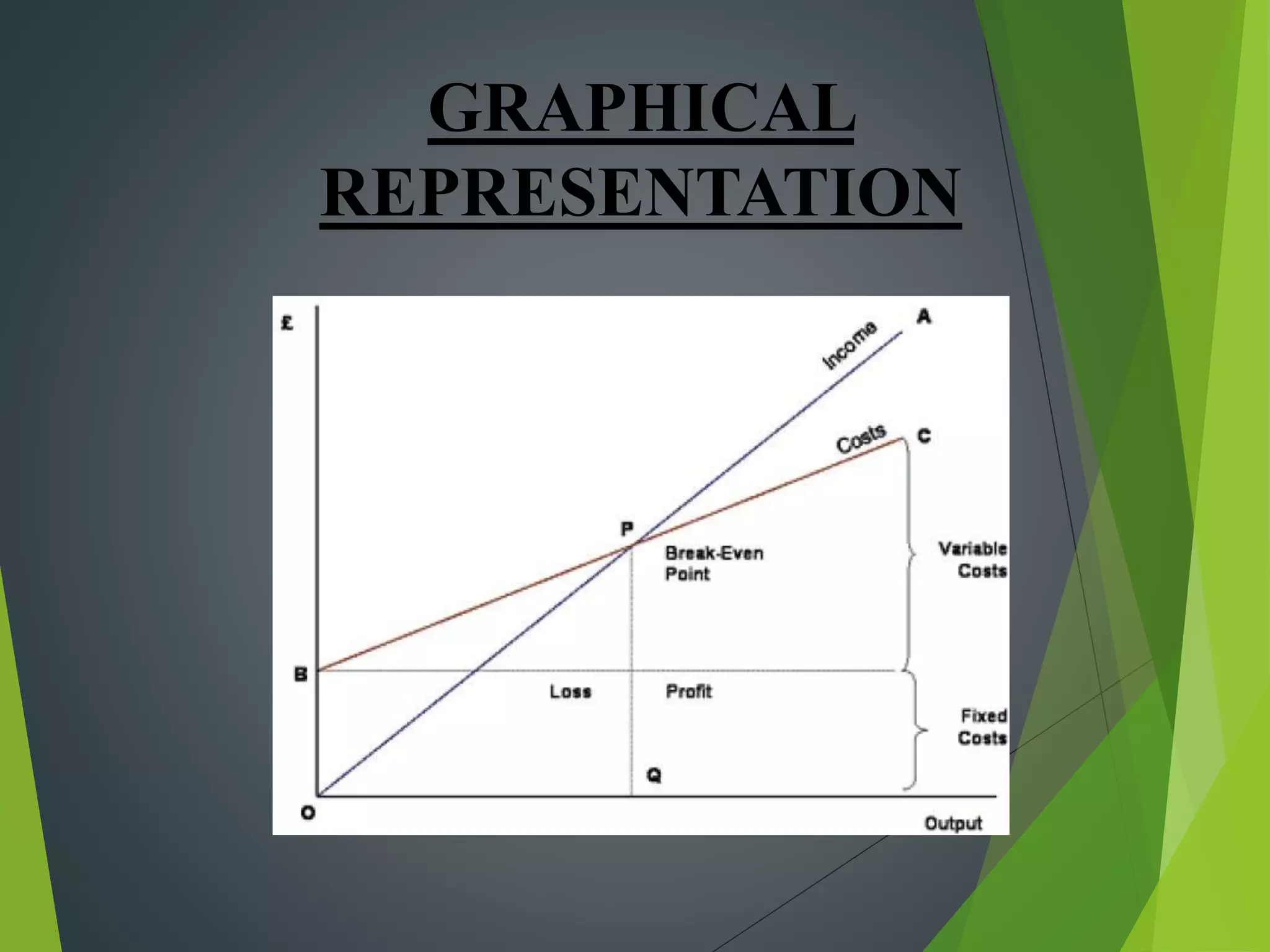
This document discusses cost concepts and break even analysis. It defines different types of costs such as fixed costs, variable costs, total costs, average costs and marginal costs. It then provides an example break even analysis of GM Motors, noting their total fixed costs, variable costs and average revenue. It summarizes GM's early history and founding, their current revenues, employee numbers and projected break even point. Finally, it outlines some of GM's marketing strategies used to target different customer segments.