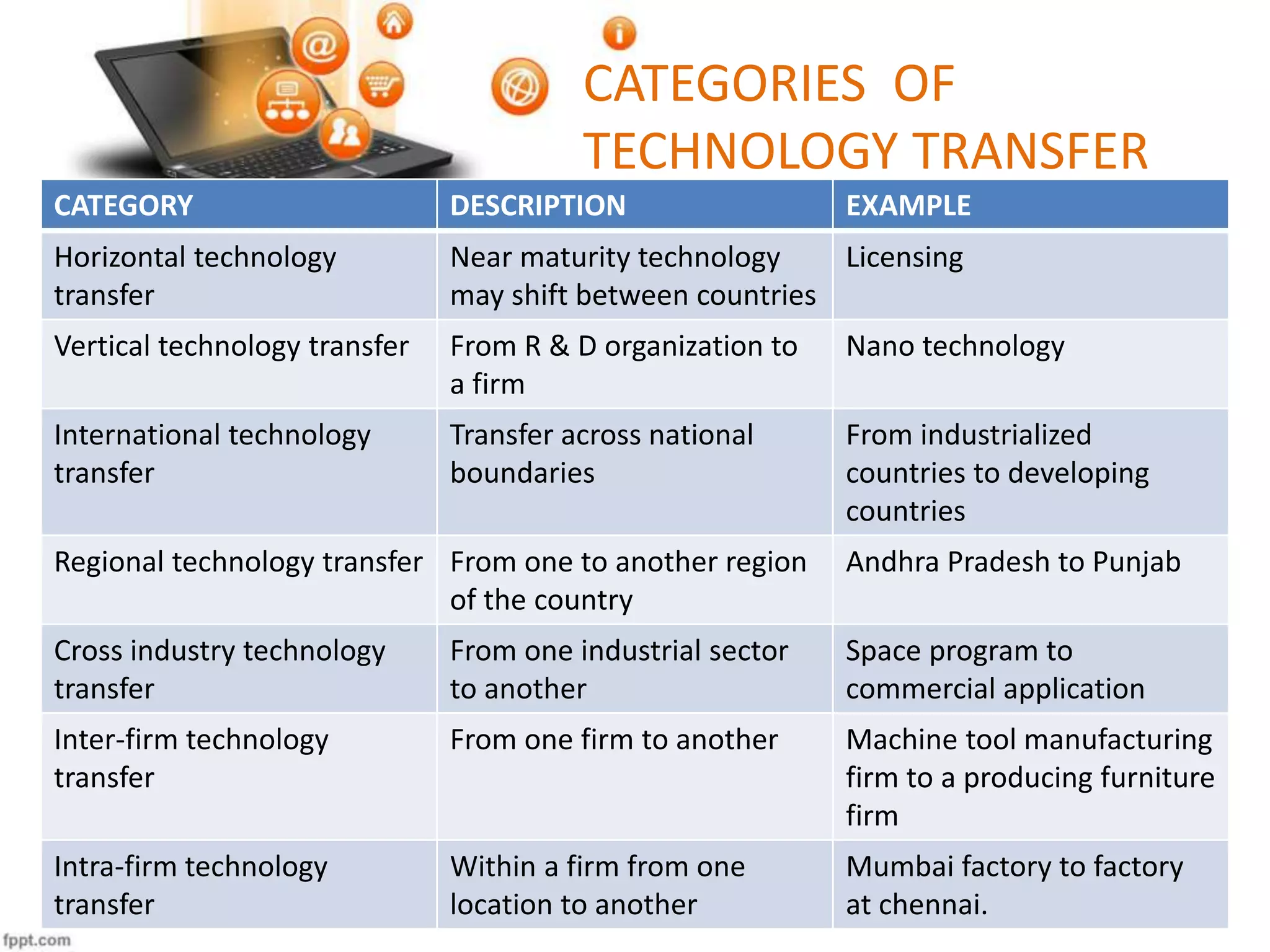
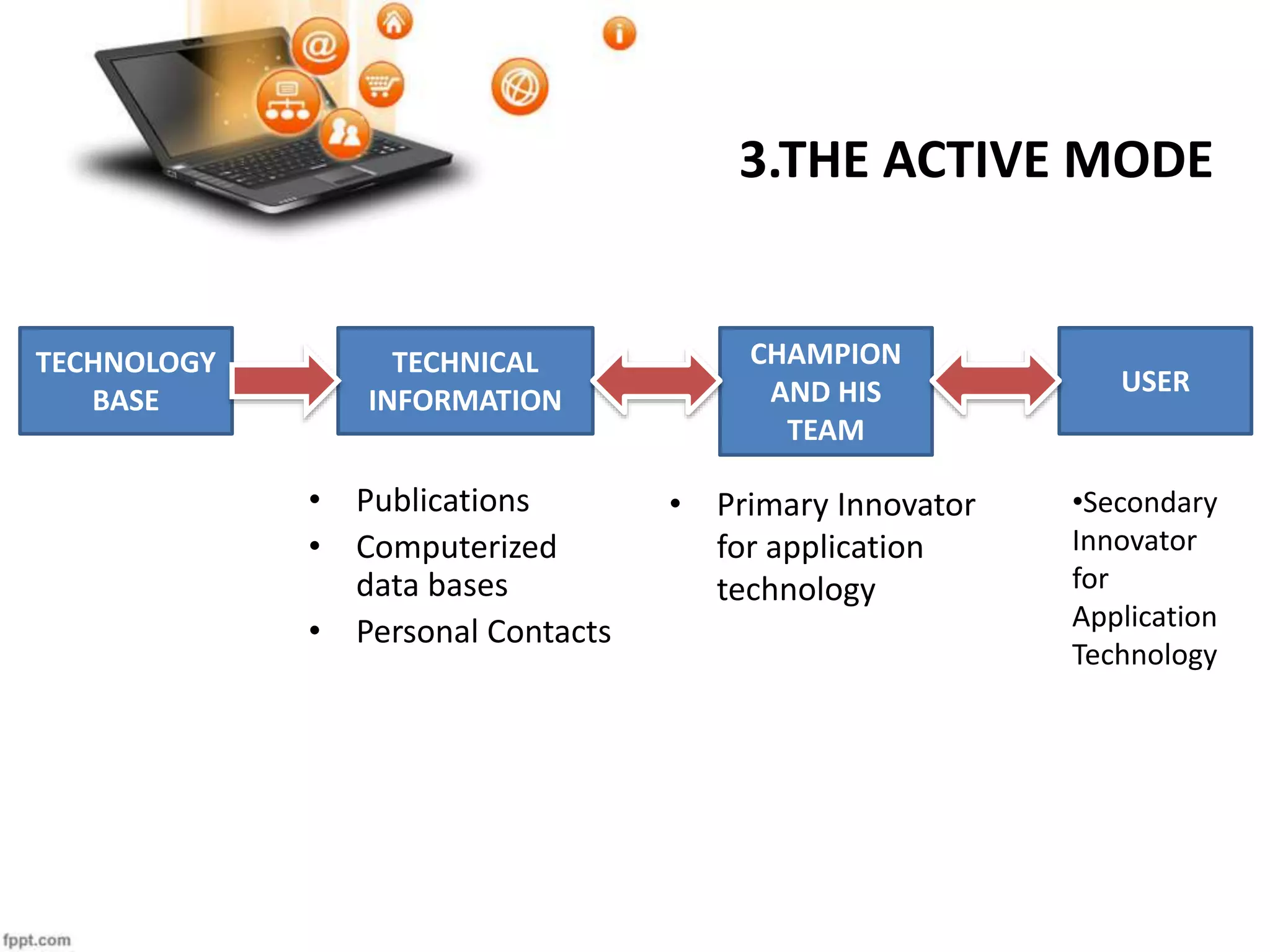
Technology transfer is the process of transferring technology from one organization to another. The document discusses technology transfer, providing definitions and describing different categories, models, modes, routes, and cases of technology transfer. Specifically, it examines technology transfer between Volvo Cars and Geely in China, and between Volkswagen and Chinese automaker FAW, describing the motivations and challenges involved in transferring automotive manufacturing technologies between companies in different countries and industries.