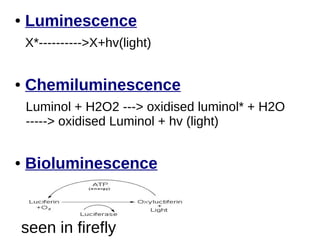
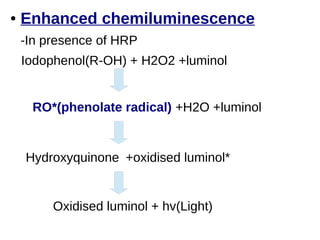
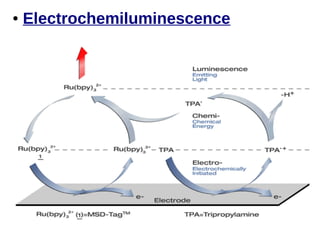
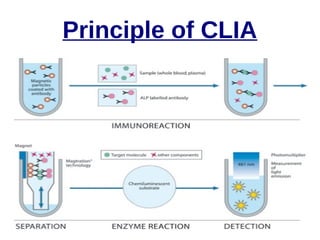
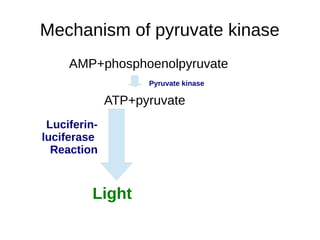
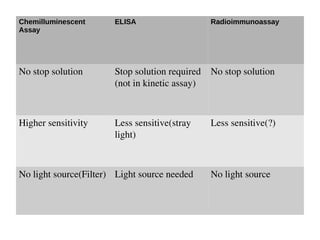
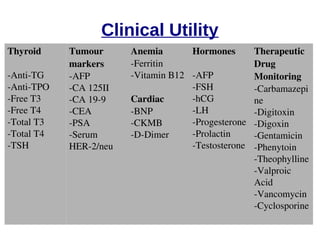
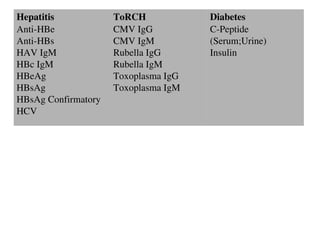
This document discusses the principles and clinical applications of chemiluminescent assays. Chemiluminescence involves the emission of light from a chemical reaction and can be enhanced through the use of enzymes like horseradish peroxidase. Chemiluminescent assays are commonly used for immunoassays and have higher sensitivity than ELISA or radioimmunoassays. The document outlines the mechanisms and substrates involved in chemiluminescence and lists many clinical applications for measuring markers of thyroid function, tumor progression, anemia, cardiac function, hormone levels, therapeutic drug monitoring, hepatitis, and diabetes.