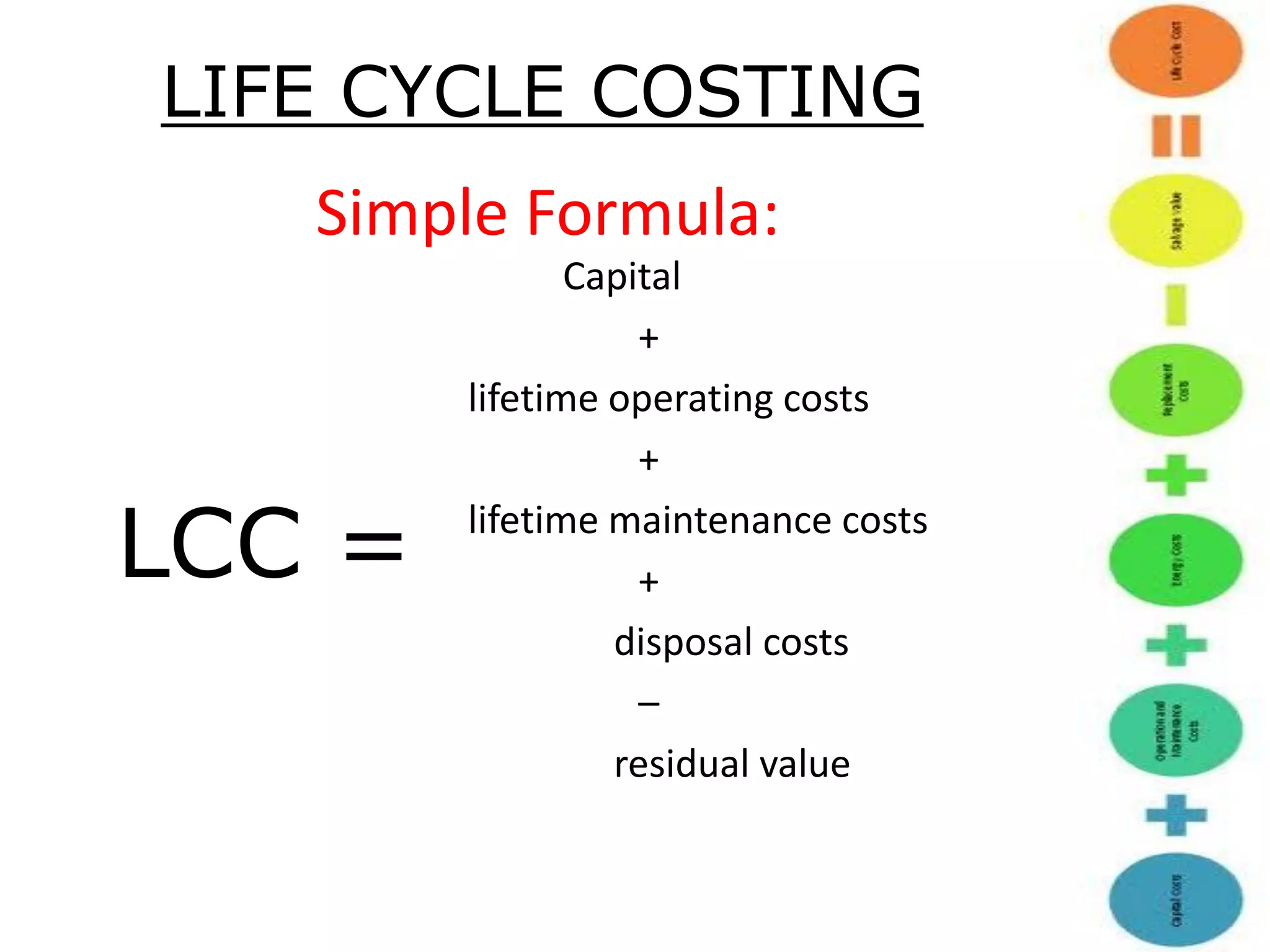
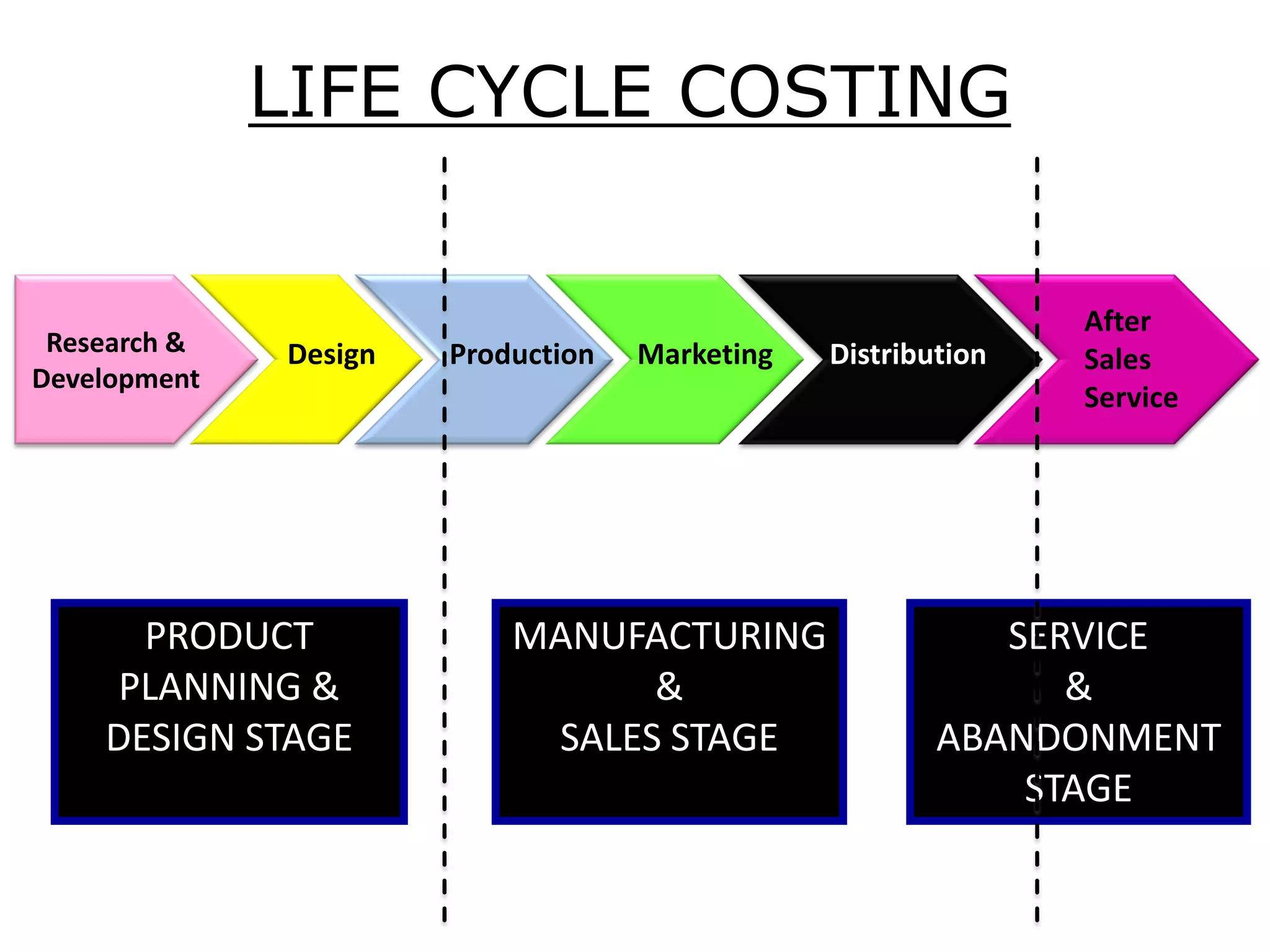
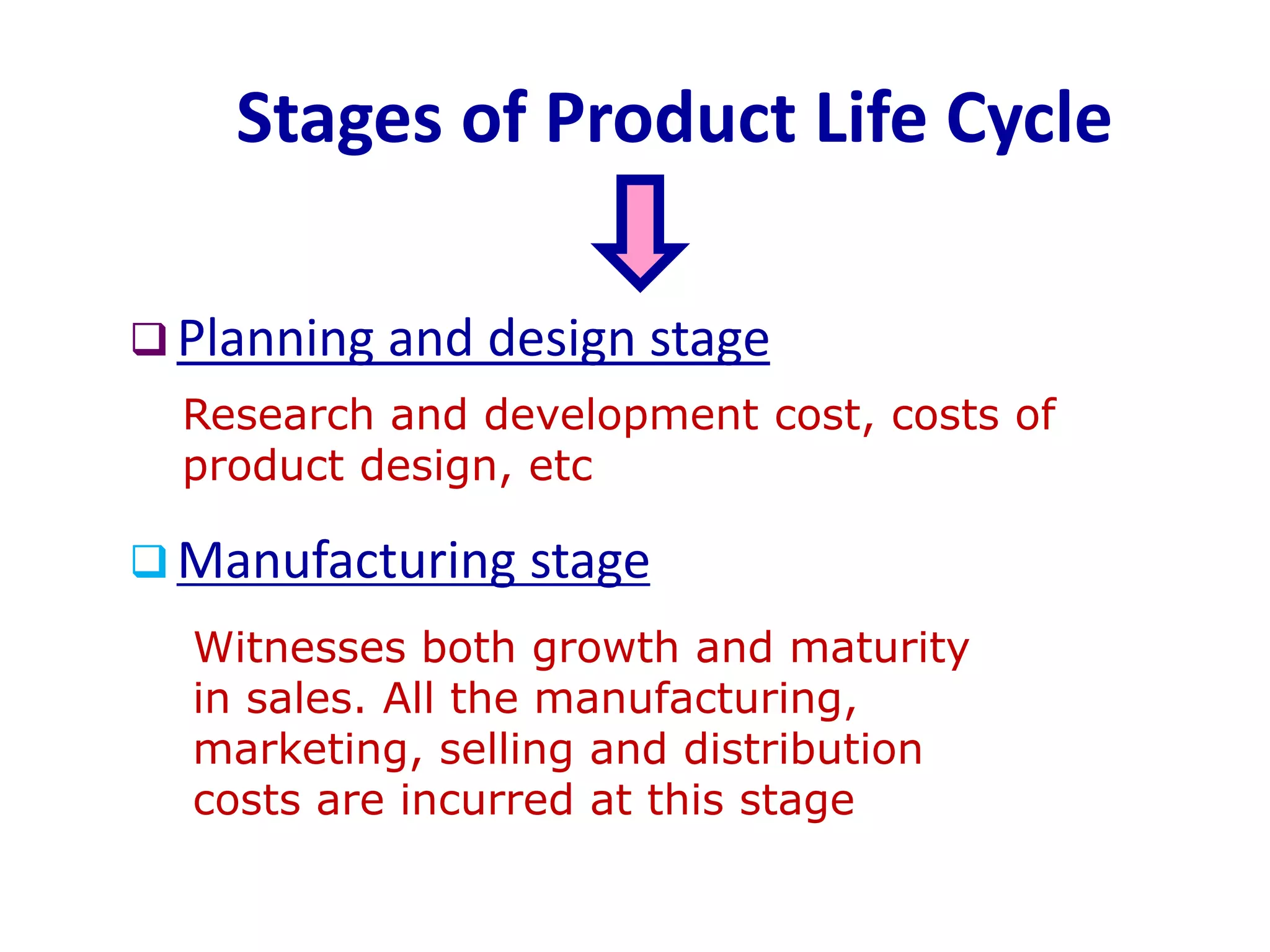
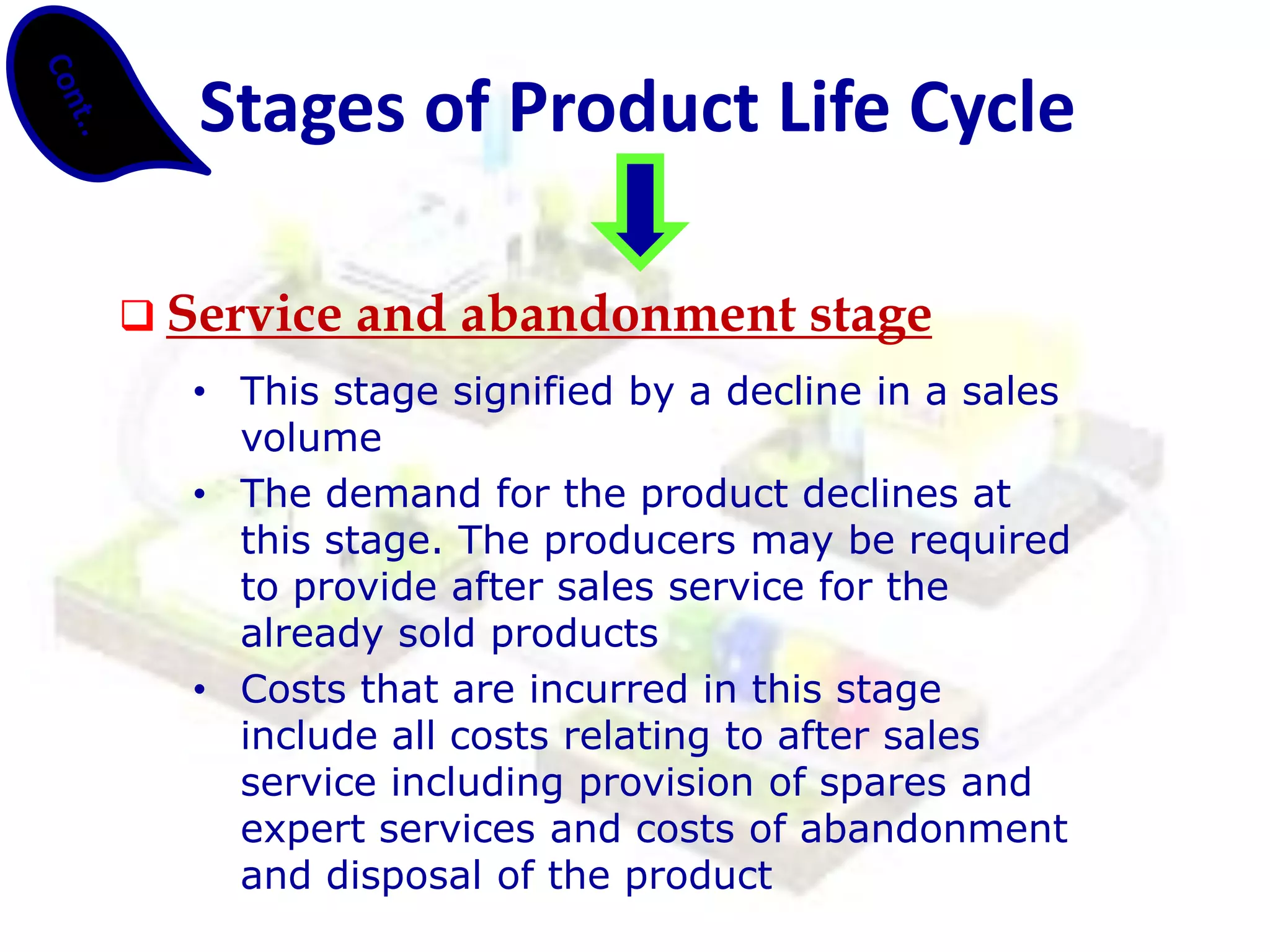
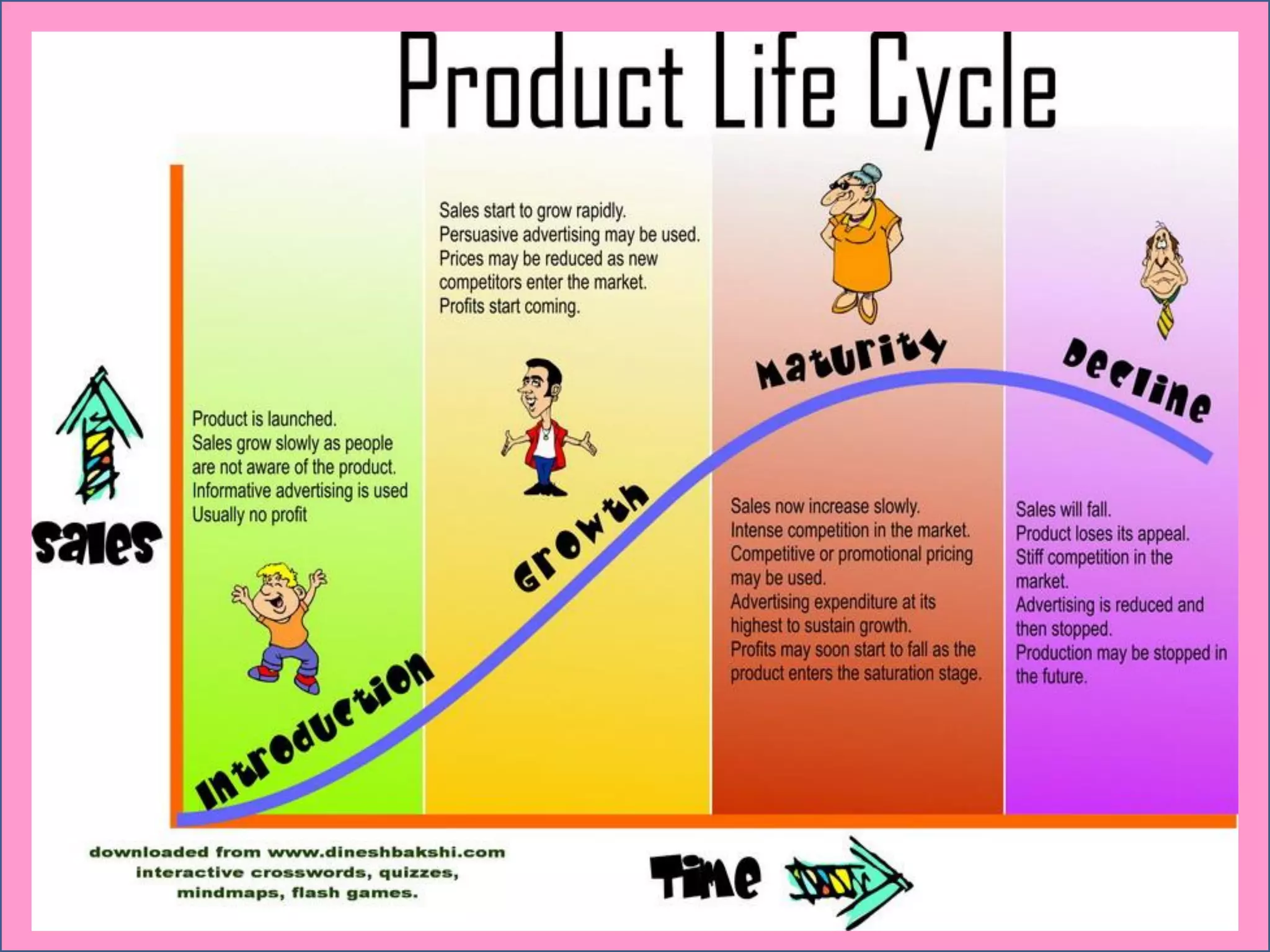
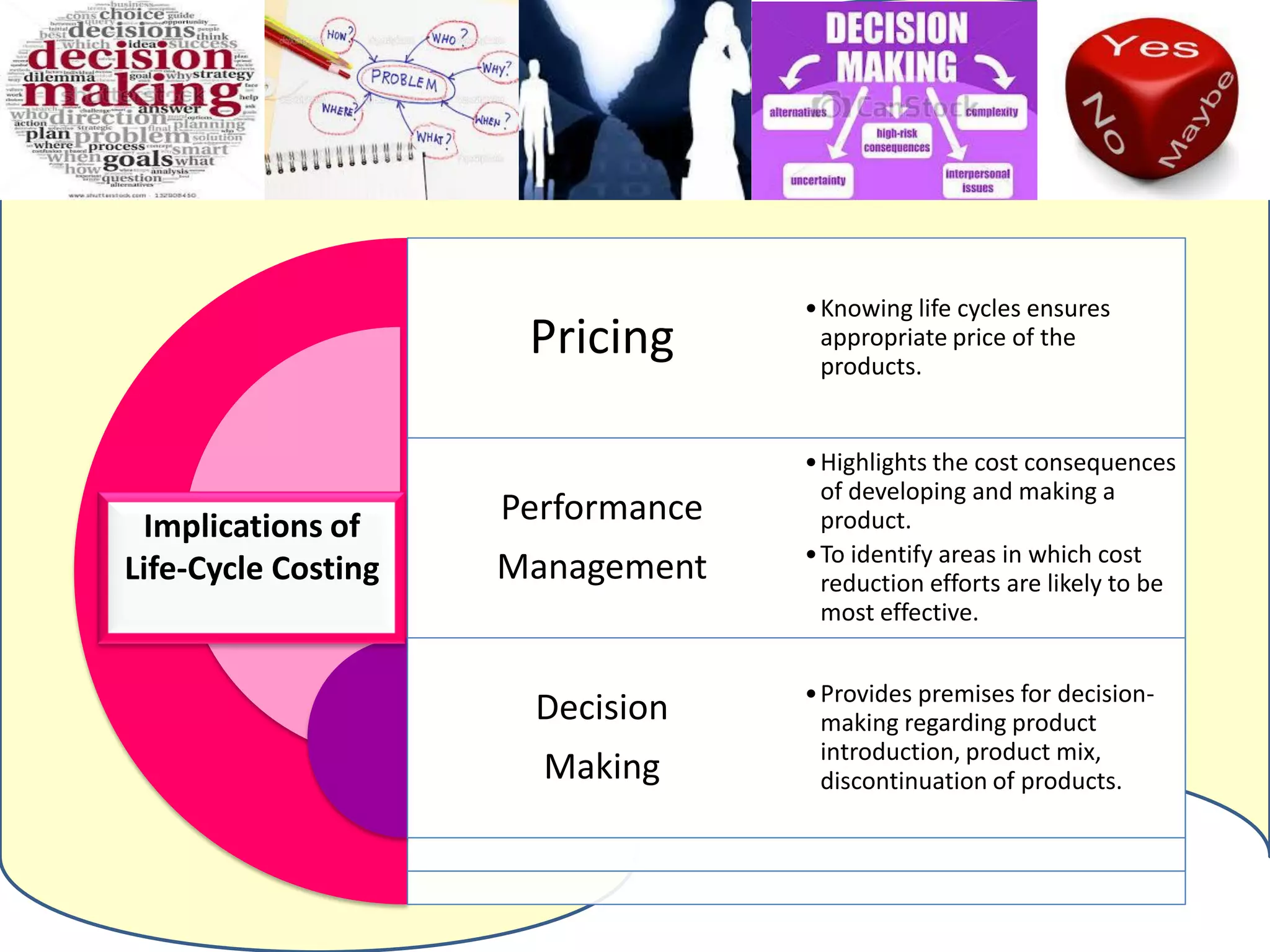
Life cycle costing is defined as the total cost of owning an asset over its entire life, from acquisition through operations and maintenance to disposal. It considers all costs associated with a product or asset over multiple stages - planning and design, manufacturing and sales, and service and abandonment. Calculating life cycle costs helps management understand cost consequences, identify areas for cost reduction, and make better decisions around product development, pricing, and discontinuation.