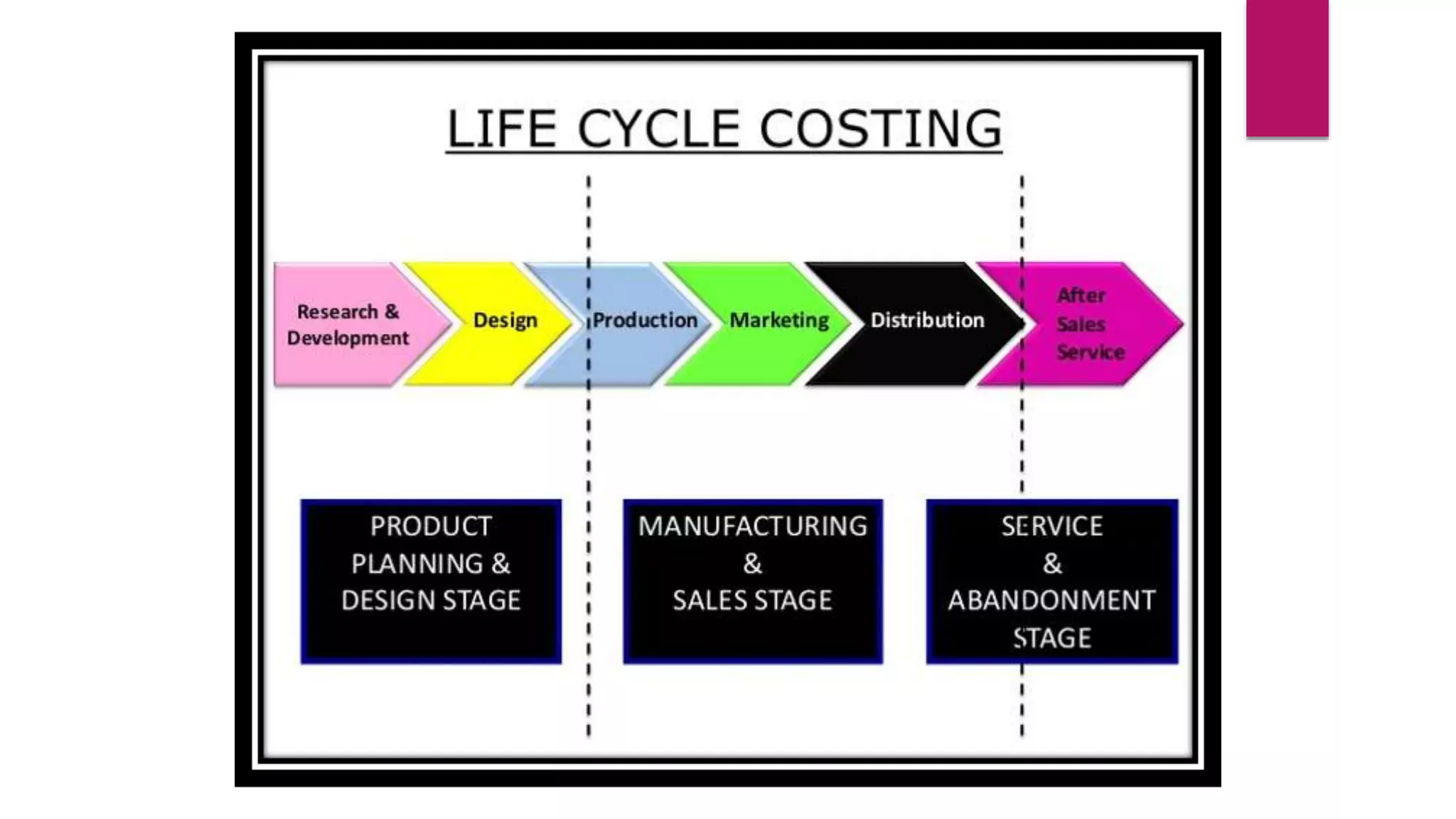
This document discusses product life cycle costing, which involves accumulating the costs of a product over its entire lifespan from inception to abandonment. It notes the typical stages of a product life cycle as introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Lifecycle costing considers costs from research and development, design, manufacturing, marketing, distribution, and disposal. It helps management evaluate product profitability over the long-term and make decisions around new product development, pricing, and capital budgeting. Lifecycle costing provides a framework for considering total costs incurred at each stage of a product's life.