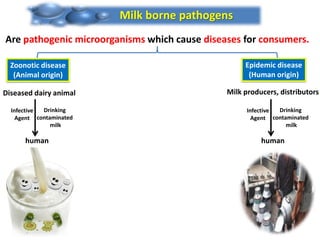
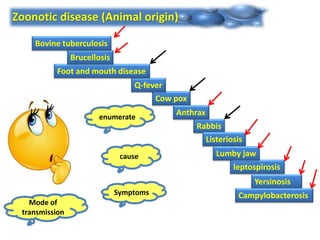
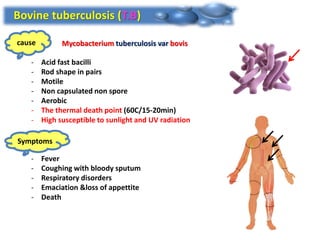
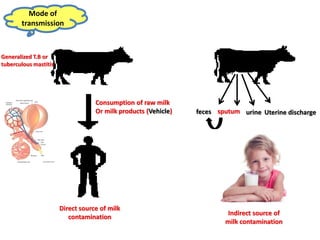
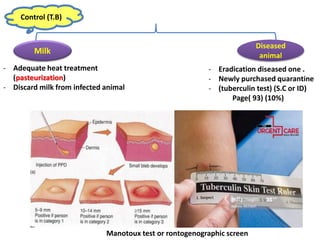
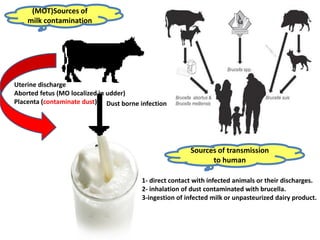
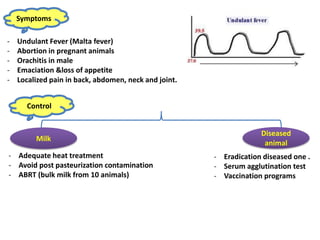
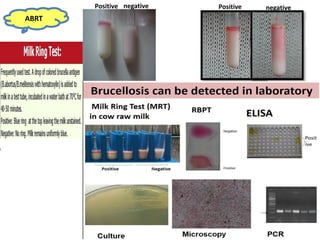
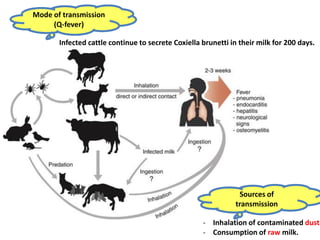
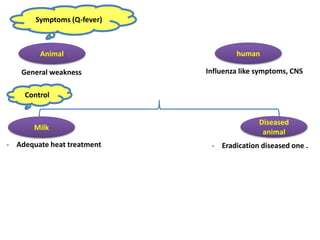
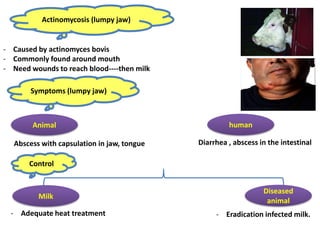
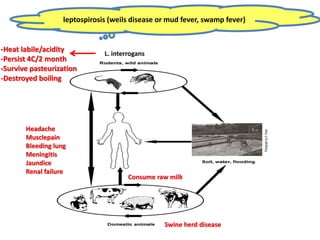
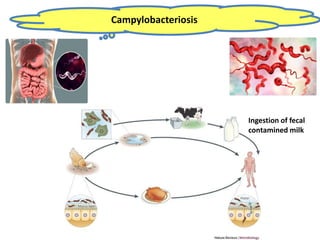
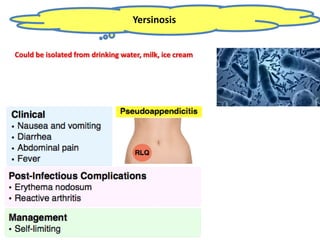
Dr. Dina A. B. Awad discusses milk-borne pathogens, including various zoonotic diseases that can infect humans through contaminated milk and dairy products. The document outlines the causes, symptoms, transmission modes, and control measures for several diseases such as bovine tuberculosis, brucellosis, Q-fever, and leptospirosis. Effective control strategies include adequate heat treatment, eradication of infected animals, and prevention of post-pasteurization contamination.