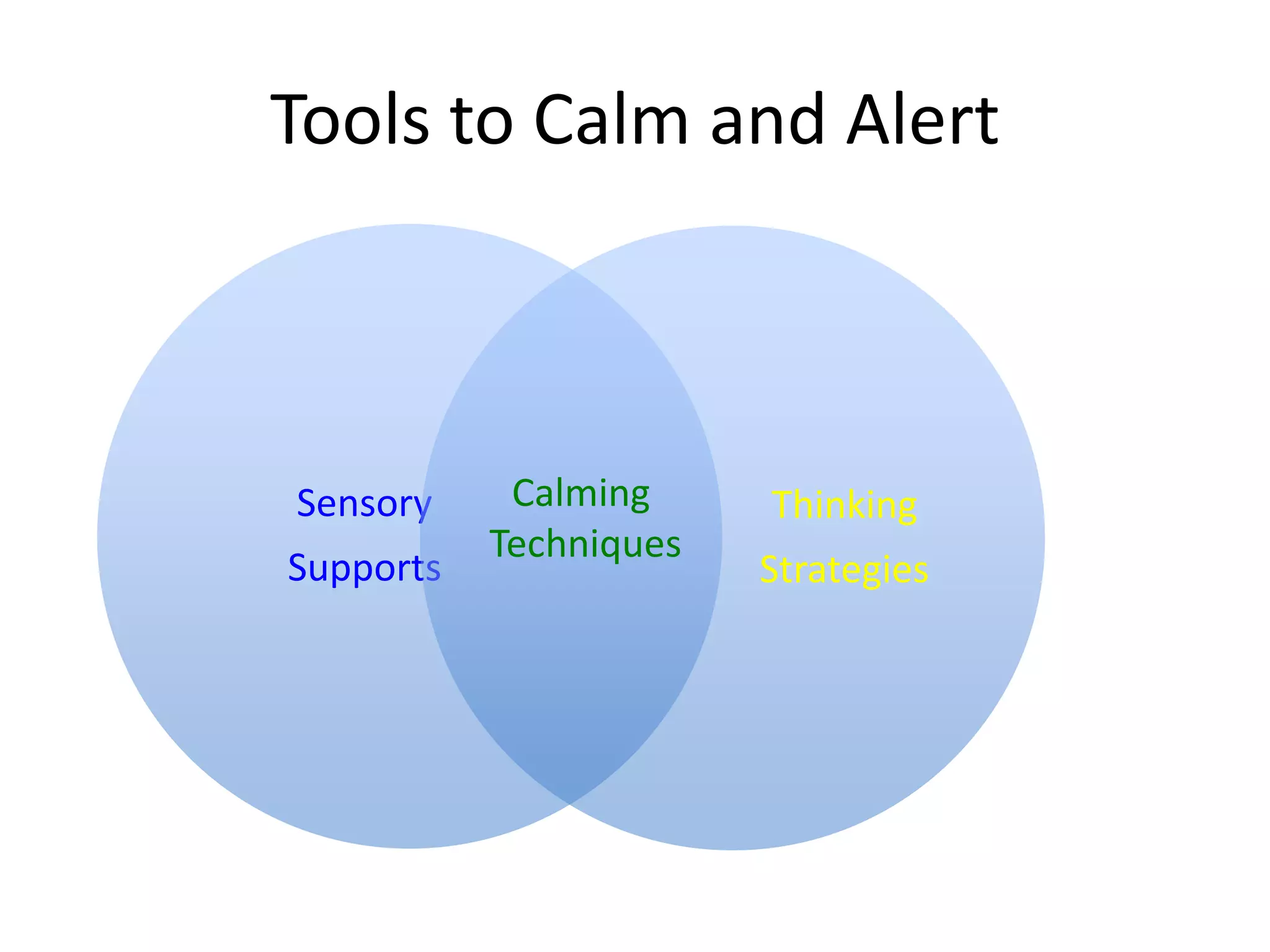
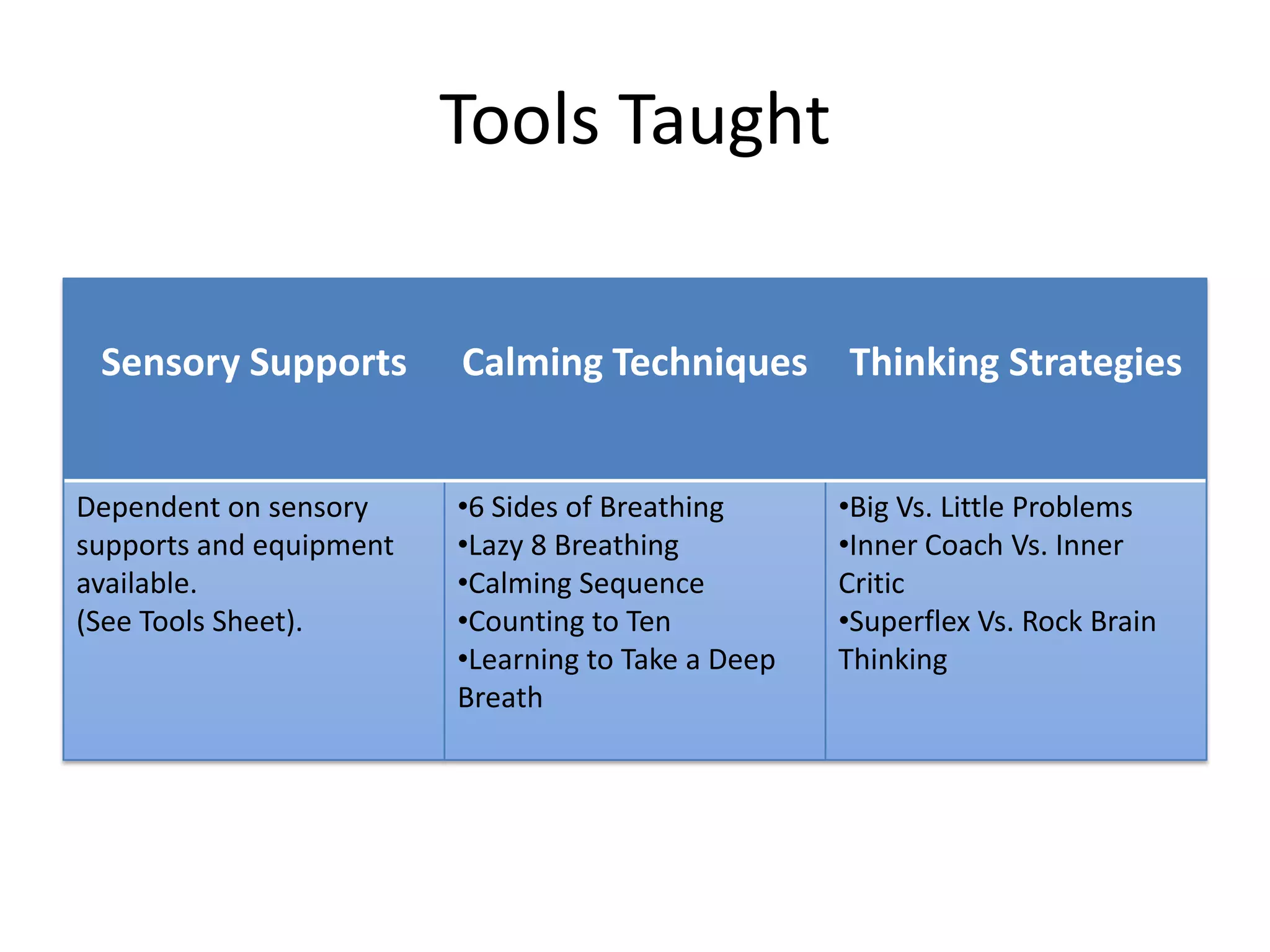
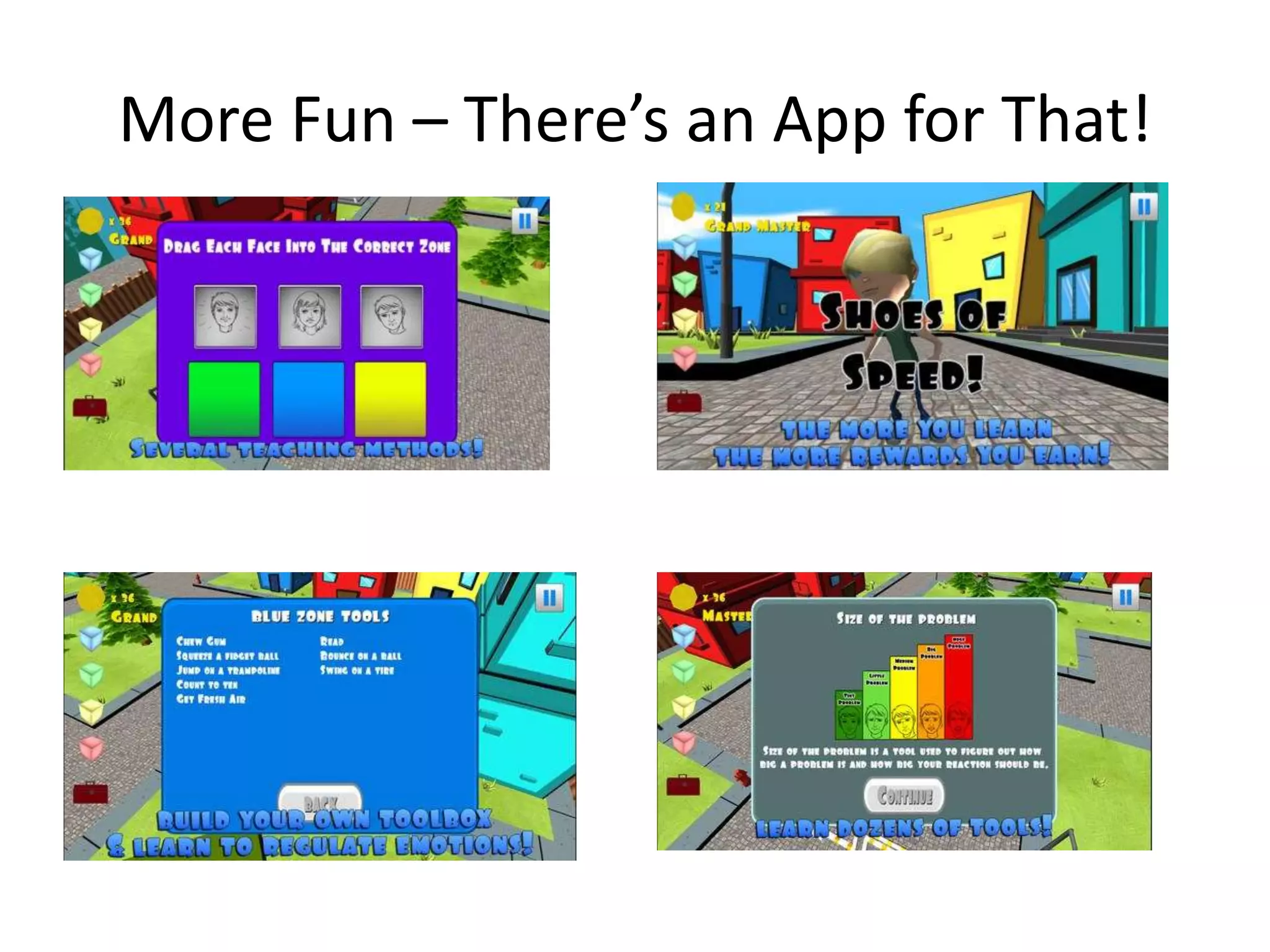
The document describes the Zones of Regulation curriculum, which teaches students to identify and regulate their emotions. It discusses the four zones - blue, green, yellow, and red - and explains what emotions correspond to each zone. The curriculum includes lessons to help students recognize emotions in themselves and others. Implementing this program may help students spend more time actively engaged in learning by improving their ability to self-regulate emotions.