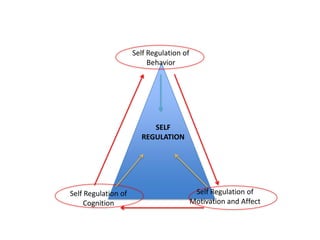
This document discusses self-regulation and its importance for academic achievement. It defines self-regulation as an integrated learning process involving the development of constructive behaviors that affect one's learning. Self-regulation involves regulating behavior, cognition, and motivation/affect. Regarding behavior, the document outlines strategies for structuring one's environment, using faculty/peers, and taking advantage of academic resources. For cognition, it notes controlling learning strategies improves performance. Finally, for motivation/affect, it emphasizes controlling beliefs and goals to adapt to course demands.