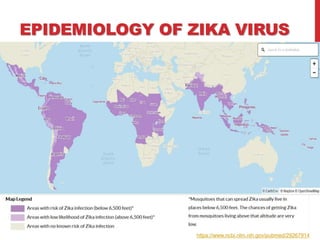
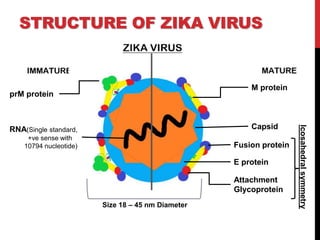
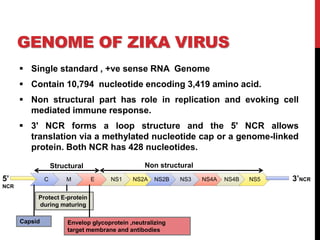
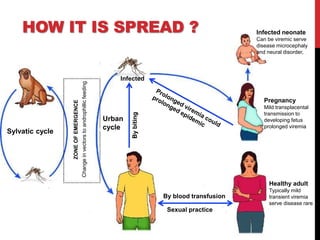
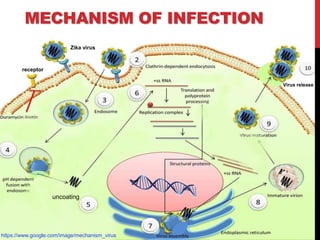
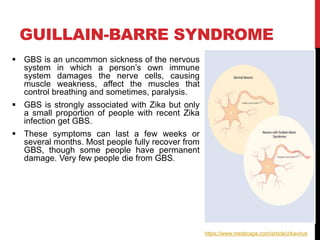
Zika virus was first discovered in Uganda in 1947 and has since spread to many countries. It is transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes and can cause microcephaly in fetuses if the mother is infected during pregnancy. While most Zika infections cause only mild symptoms, it poses a serious threat during pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects. Diagnostic tests for Zika look for viral RNA or IgM antibodies. There is no vaccine or specific treatment, so prevention focuses on controlling mosquito populations and protecting against bites.