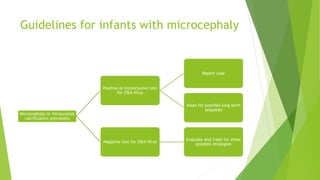
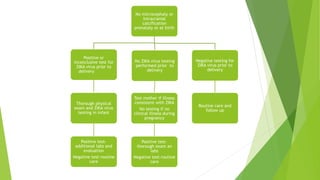
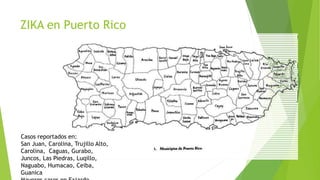
This document provides information about the Zika virus. It discusses that Zika is a mosquito-borne flavivirus transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes. While most cases are asymptomatic, symptomatic cases involve fever, rash, joint pain, and red eyes. There is no vaccine or treatment. The virus can be transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy and has been linked to microcephaly in newborns. Testing and guidelines are outlined for pregnant women, infants, and preventing transmission. An administrative order in Puerto Rico mandates screening and care for pregnant women due to Zika outbreaks on the island.