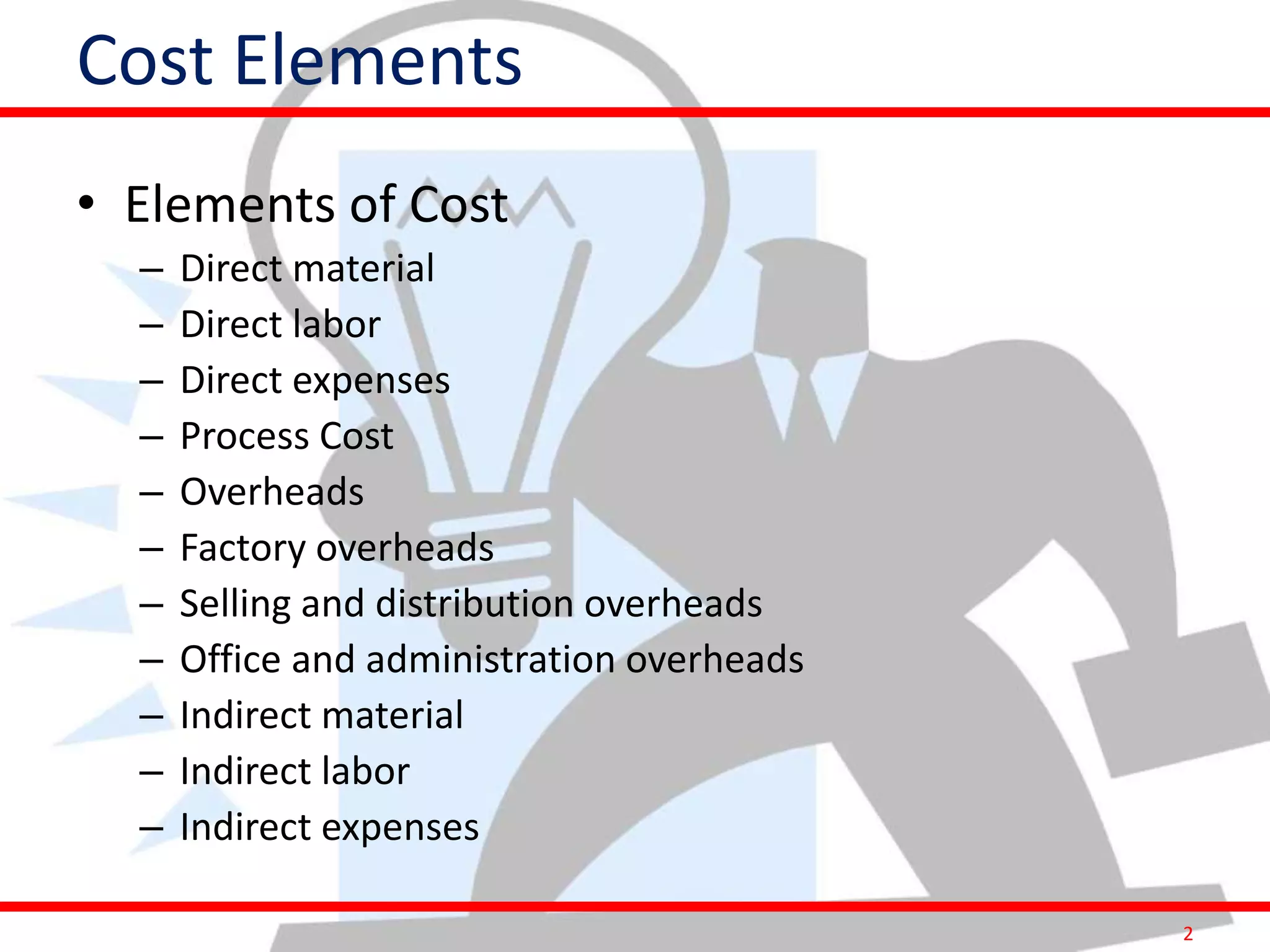
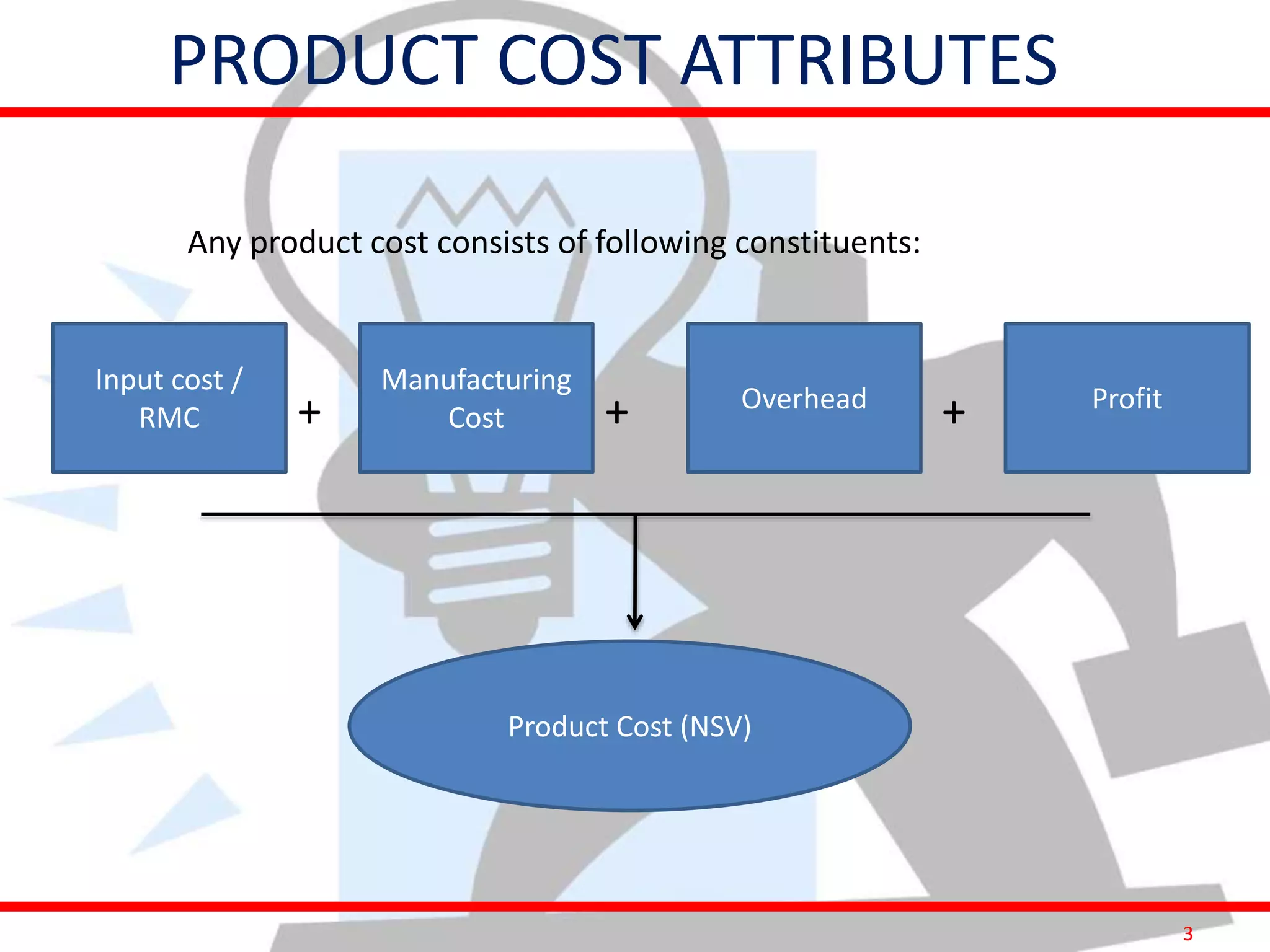
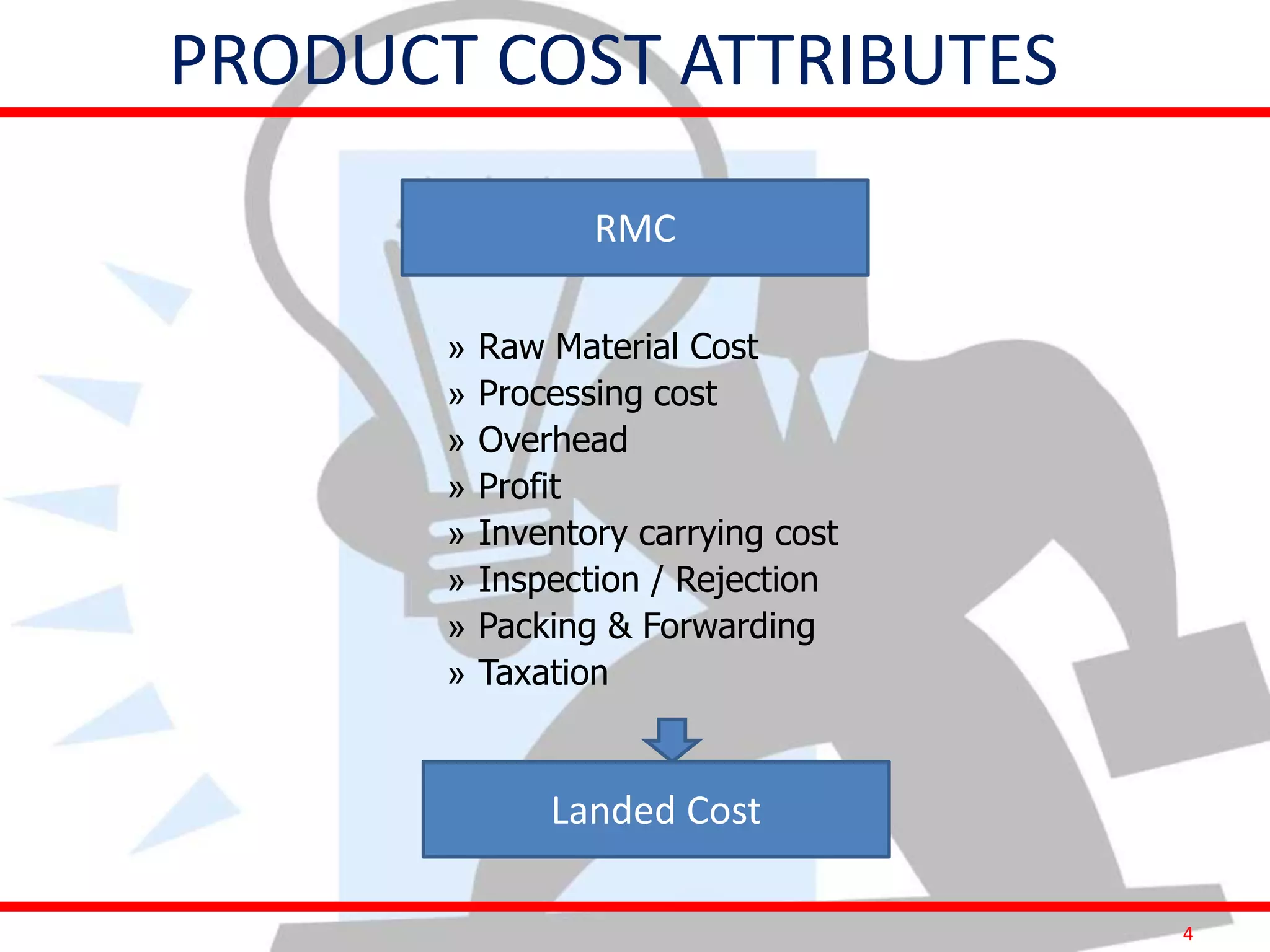
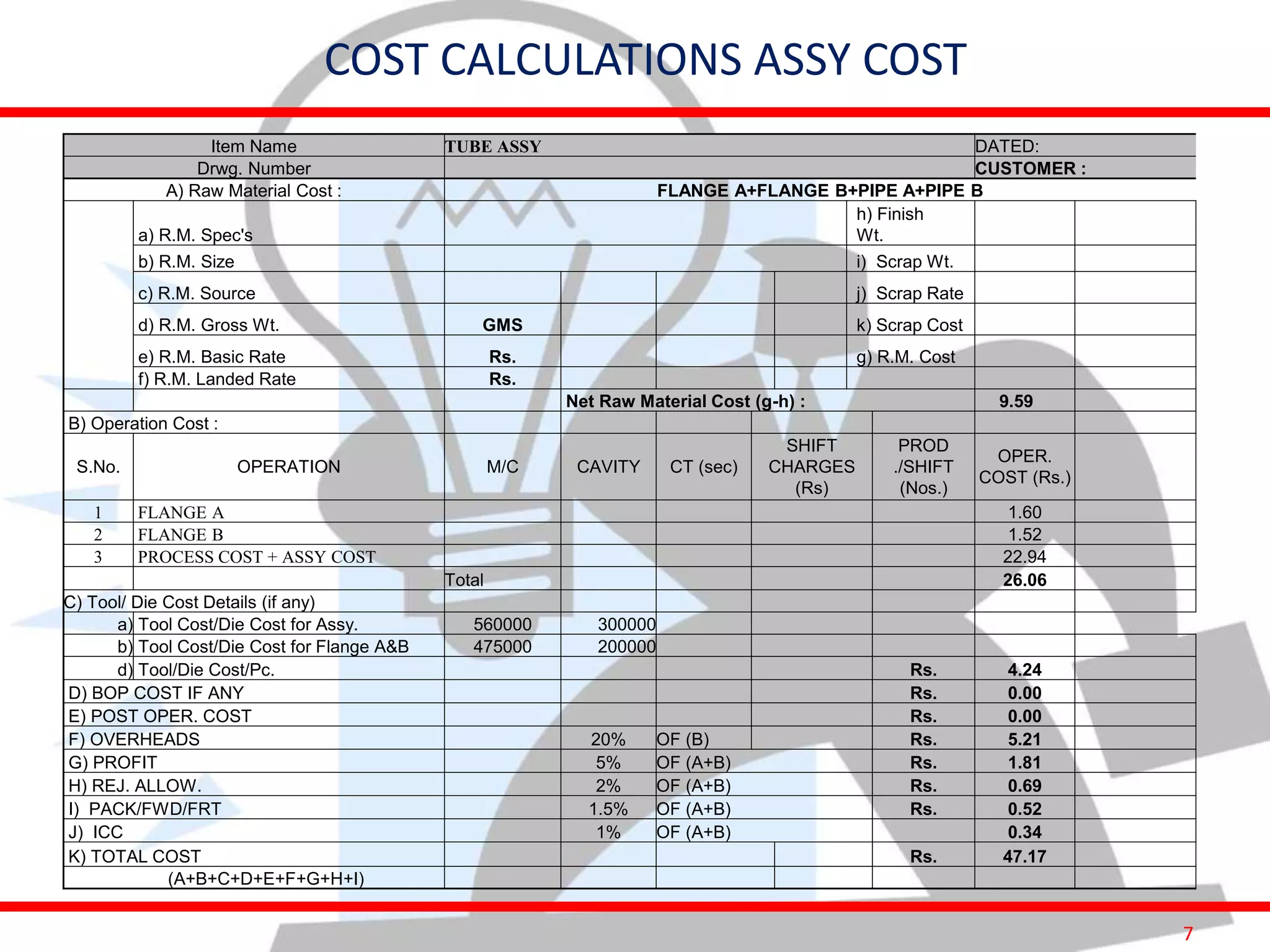
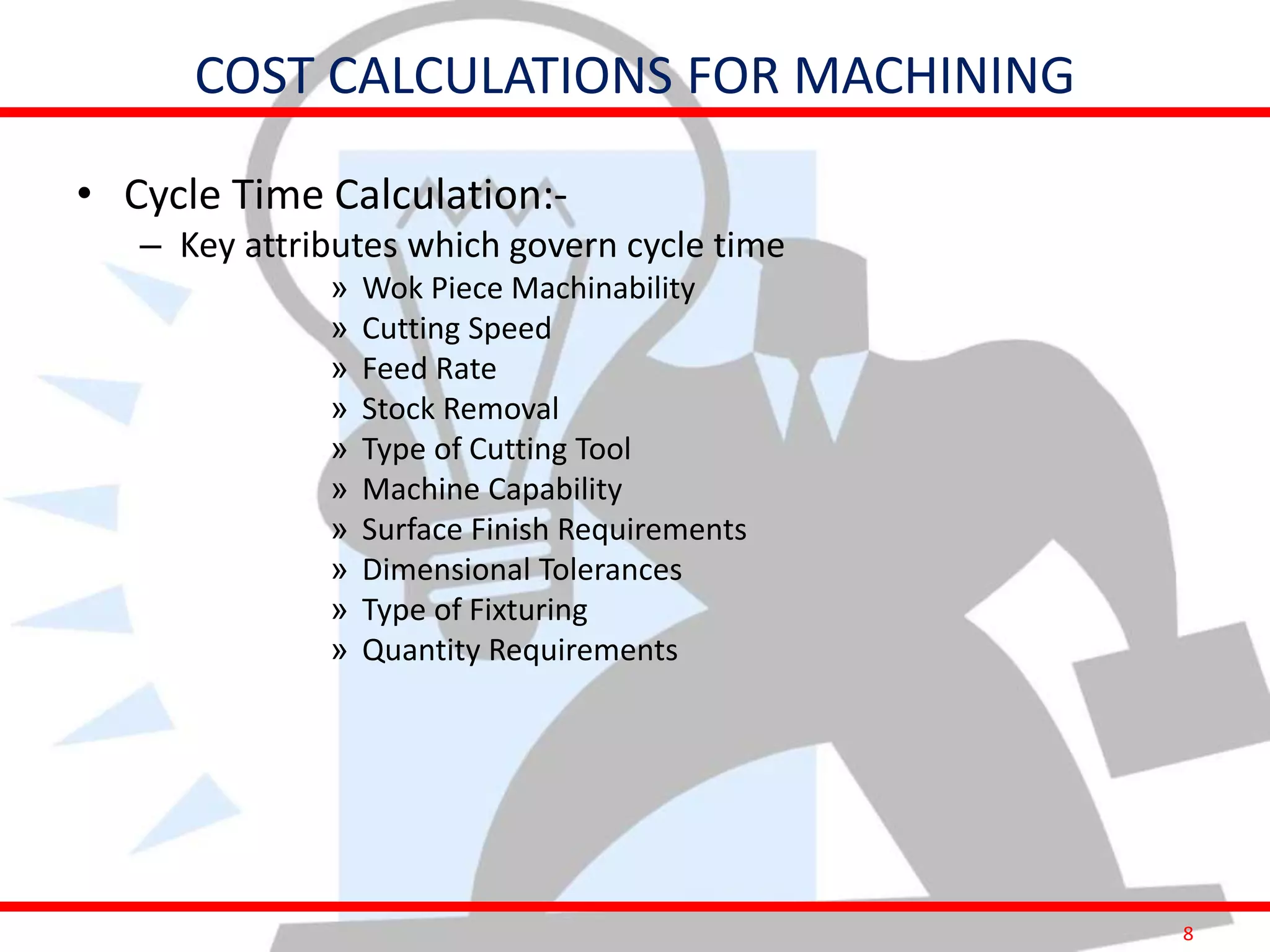
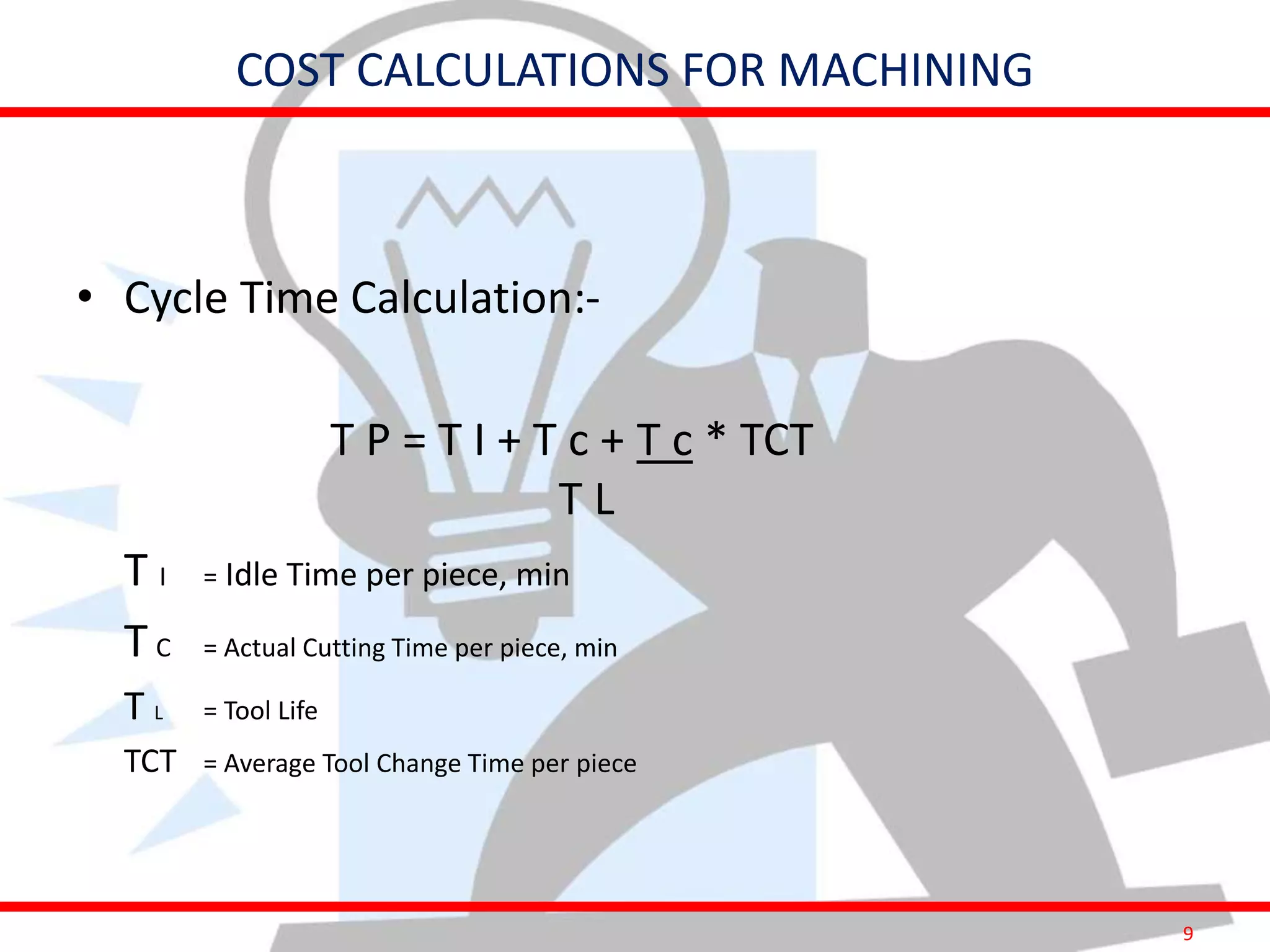
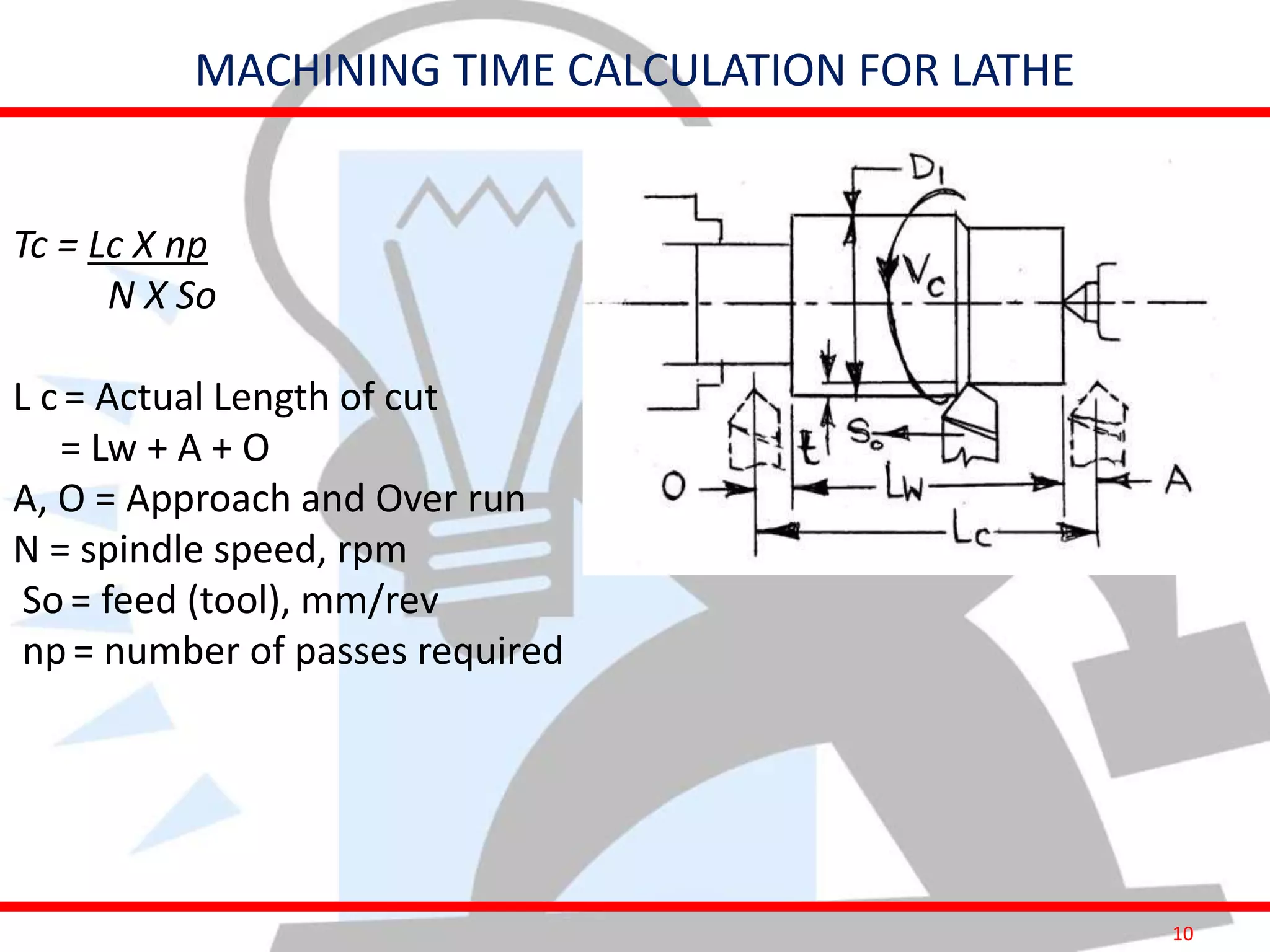
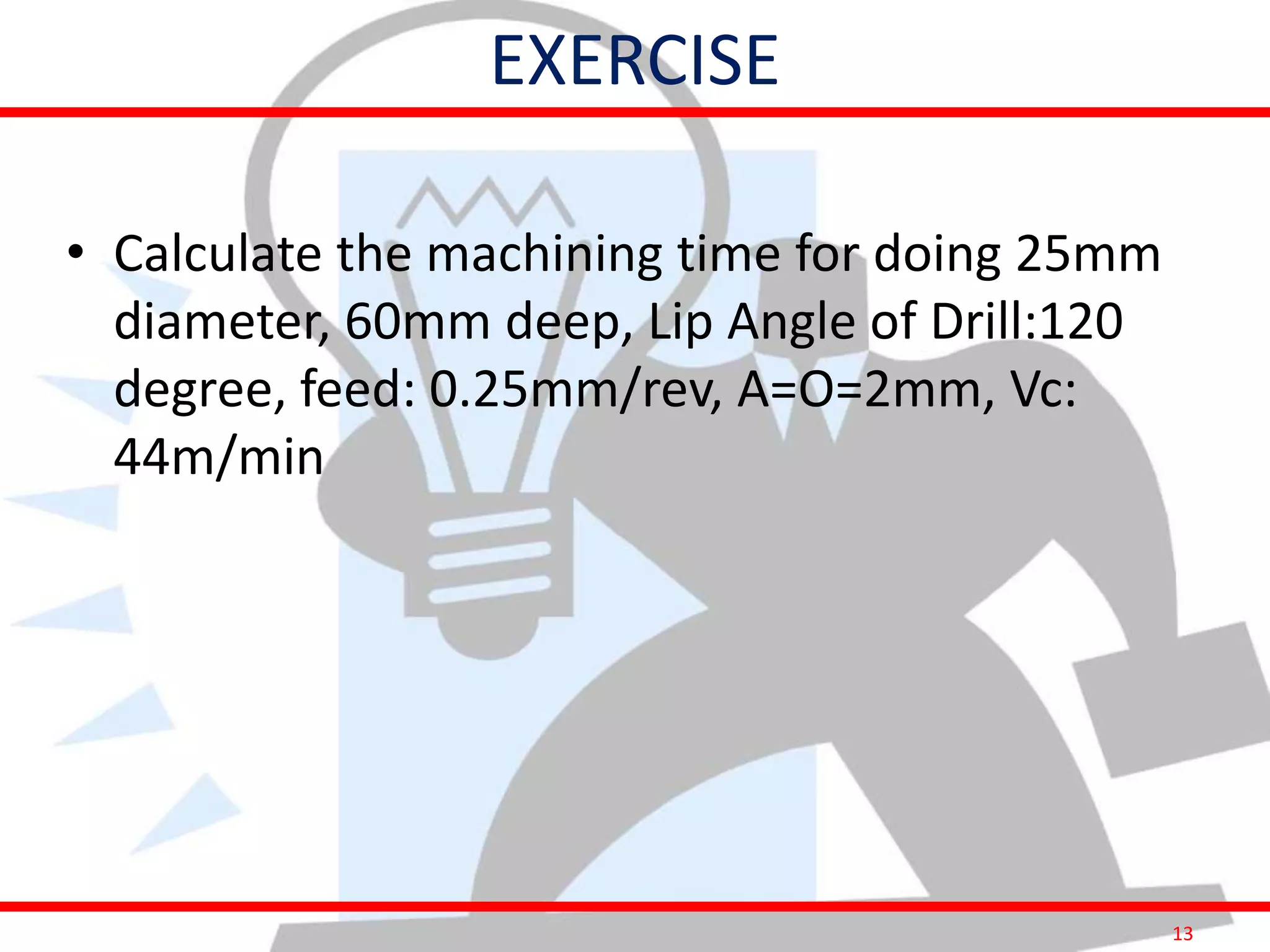
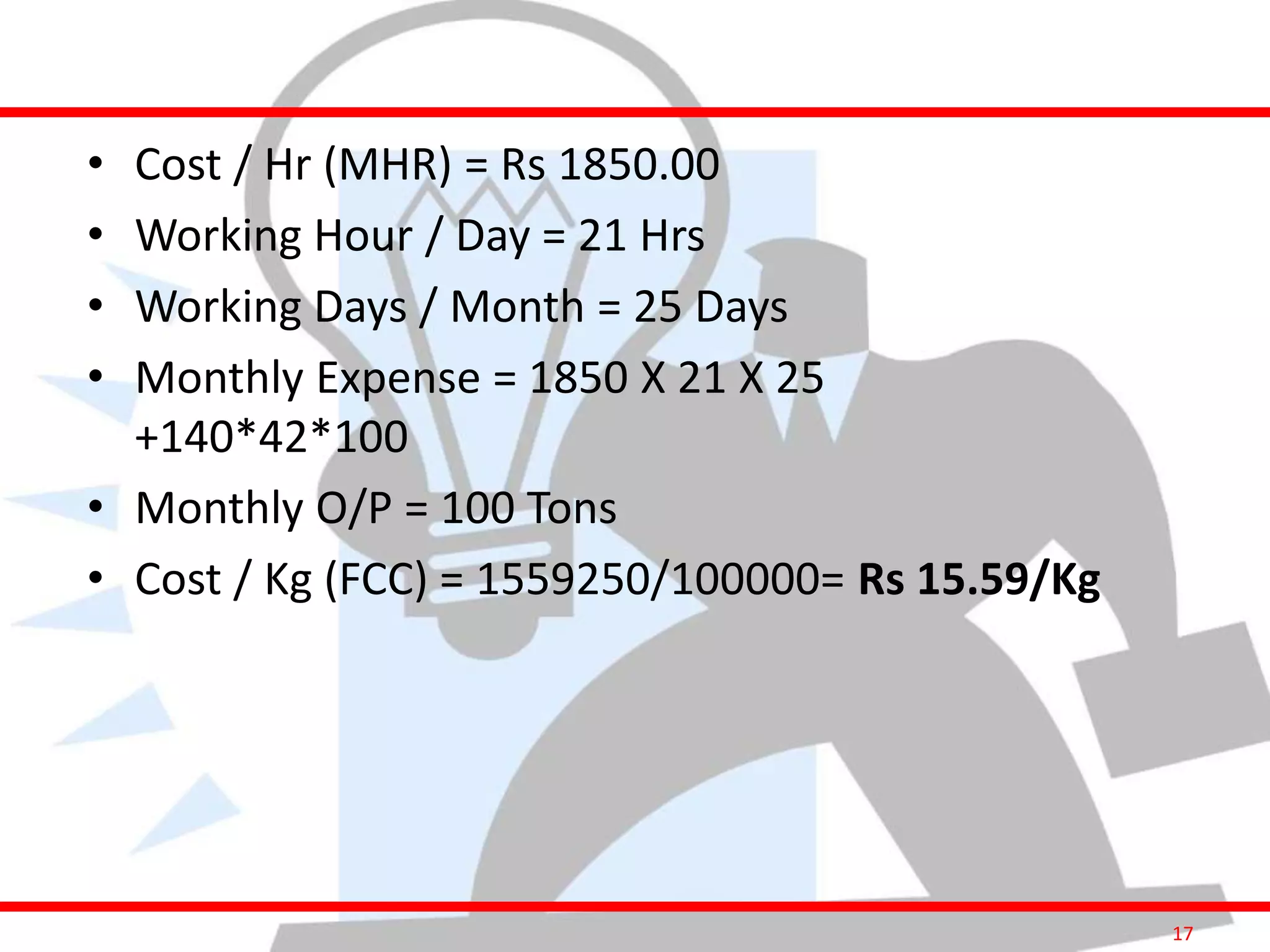
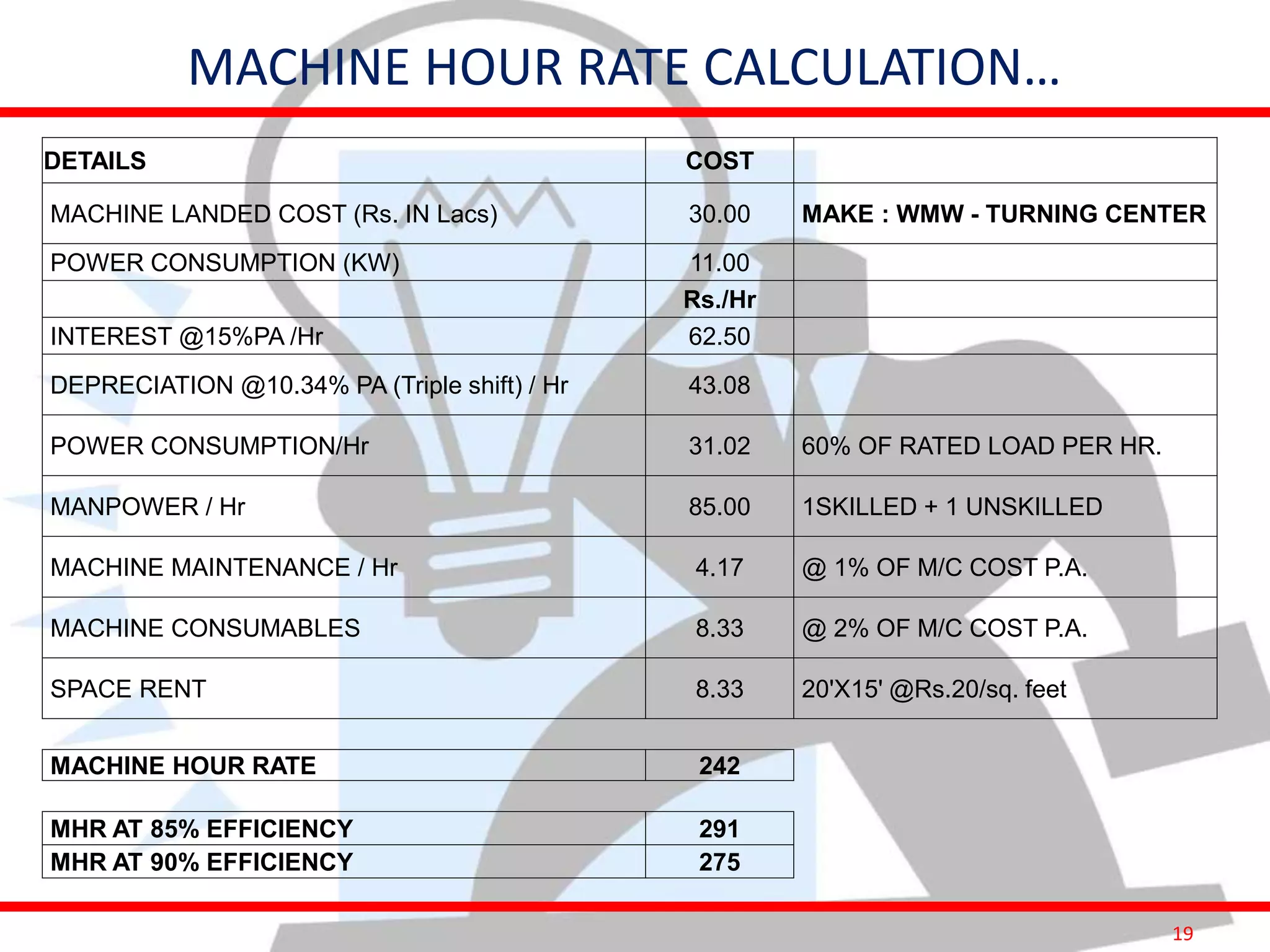
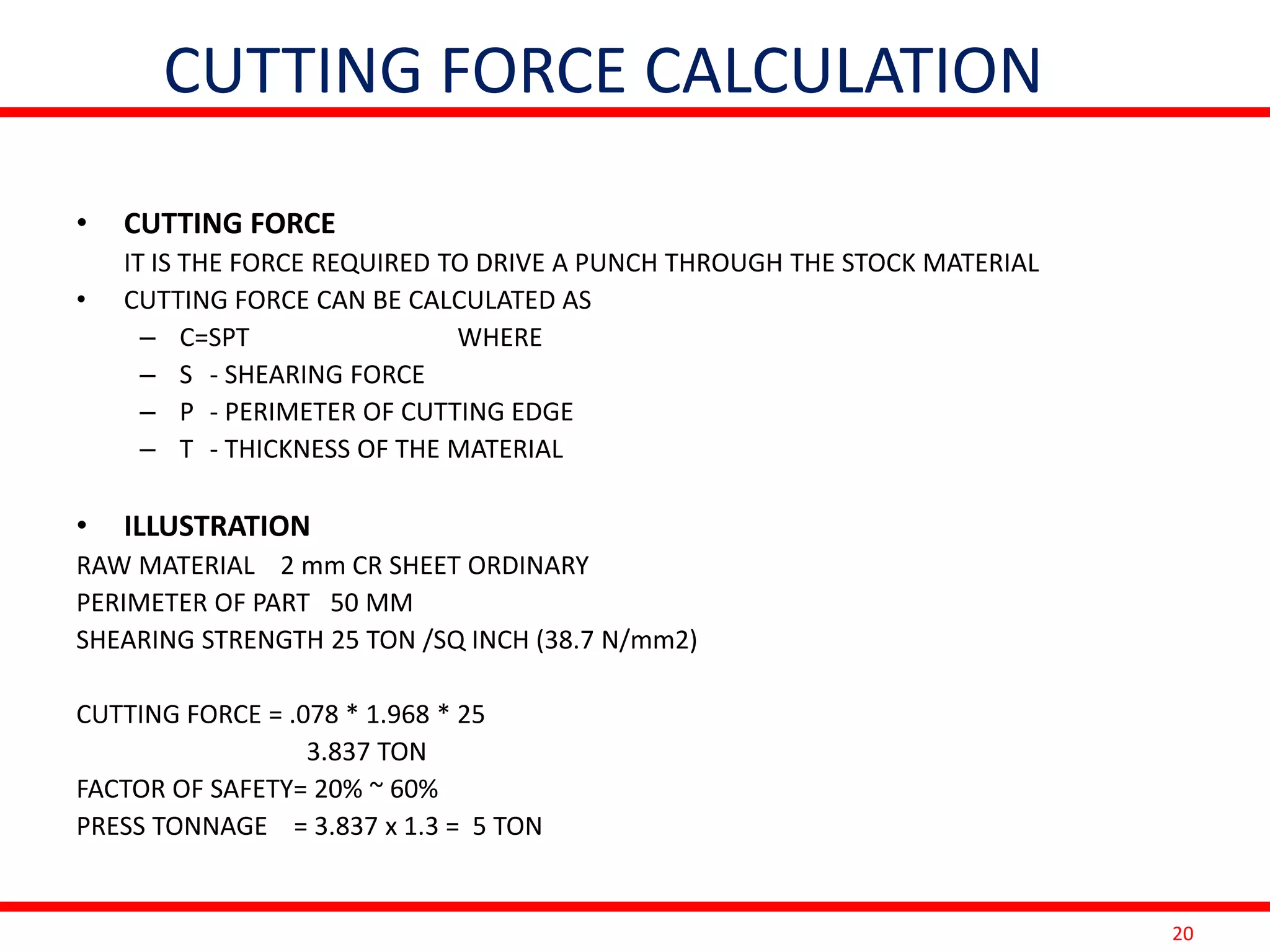
This document provides information on costing and cost calculations for manufacturing processes. It discusses the need for zero-based costing to understand cost contributions and identify cost reduction opportunities. It then outlines various cost elements like direct material, labor, expenses, and overheads. The document also provides examples of calculating costs for specific manufacturing processes like machining, drilling, milling, and forging conversion. Machine hour rates are calculated considering machine depreciation, power, labor, and other expenses. Cutting forces for sheet metal cutting are also explained.