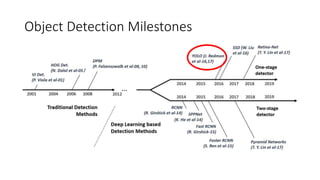
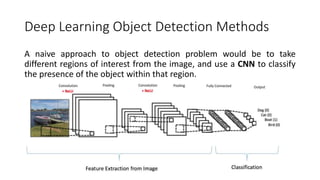
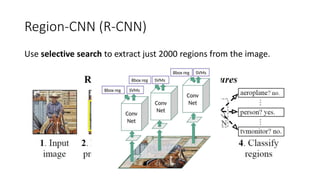
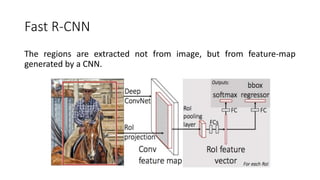
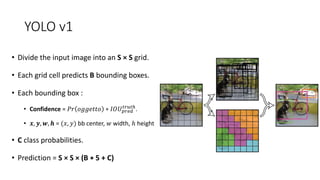
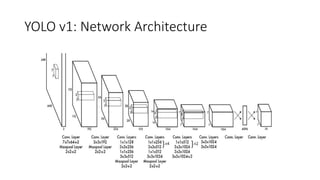
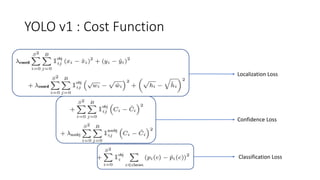
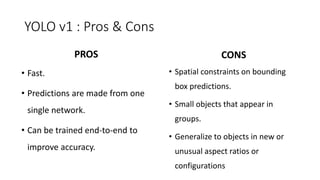
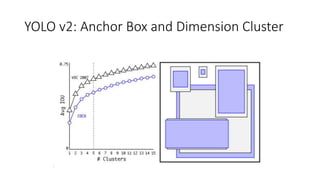
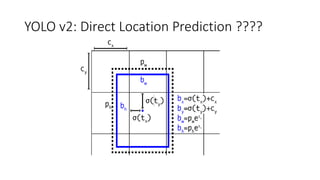
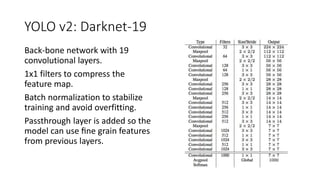
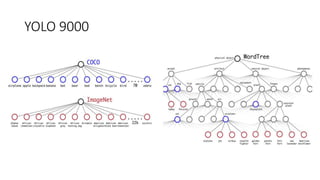
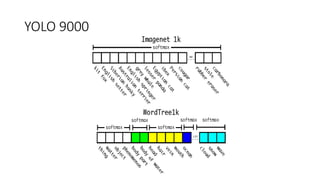
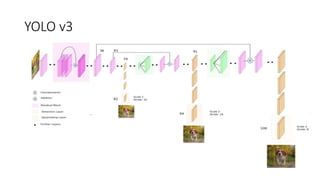
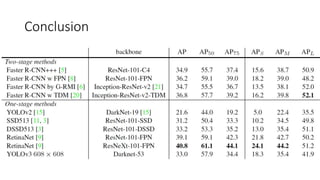
YOLO releases are one-stage object detection models that predict bounding boxes and class probabilities in an image using a single neural network. YOLO v1 divides the image into a grid and predicts bounding boxes and confidence scores for each grid cell. YOLO v2 improves on v1 with anchor boxes, batch normalization, and a Darknet-19 backbone network. YOLO v3 uses a Darknet-53 backbone, multi-scale feature maps, and a logistic classifier to achieve better accuracy. The YOLO models aim to perform real-time object detection with high accuracy while remaining fast and unified end-to-end models.