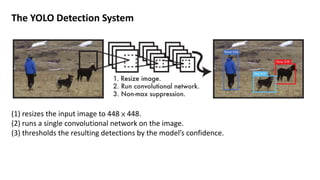
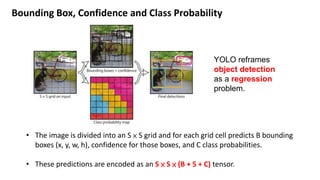
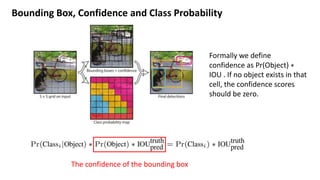
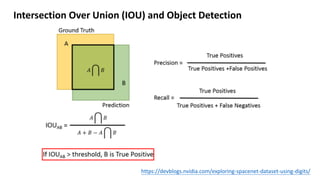
(1) YOLO frames object detection as a single regression problem to predict bounding boxes and class probabilities directly from full images in one step. (2) It resizes images as input to a convolutional network that outputs a grid of predictions with bounding box coordinates, confidence, and class probabilities. (3) YOLO achieves real-time speeds while maintaining high average precision compared to other detection systems, with most errors coming from inaccurate localization rather than predicting background or other classes.