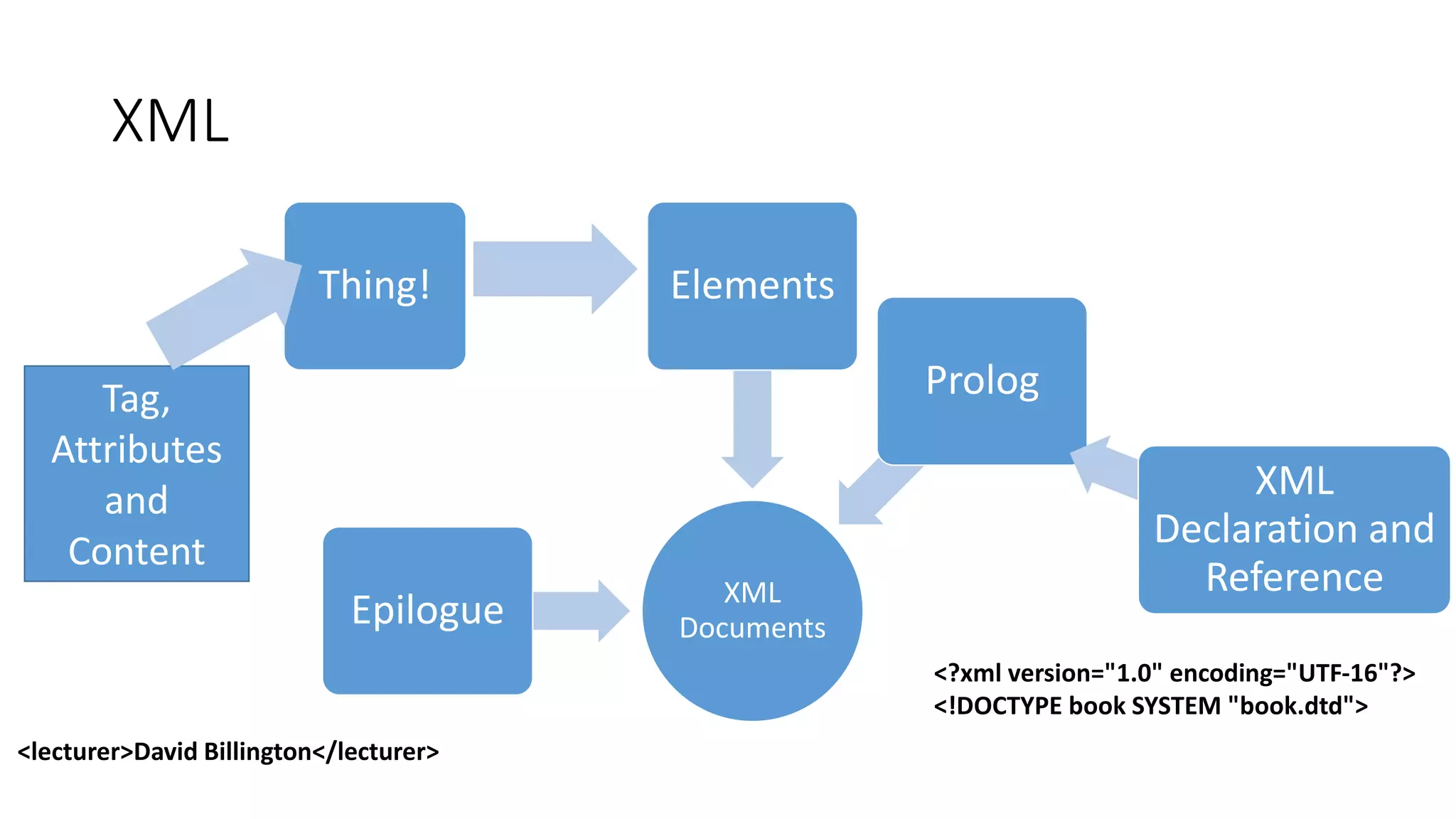
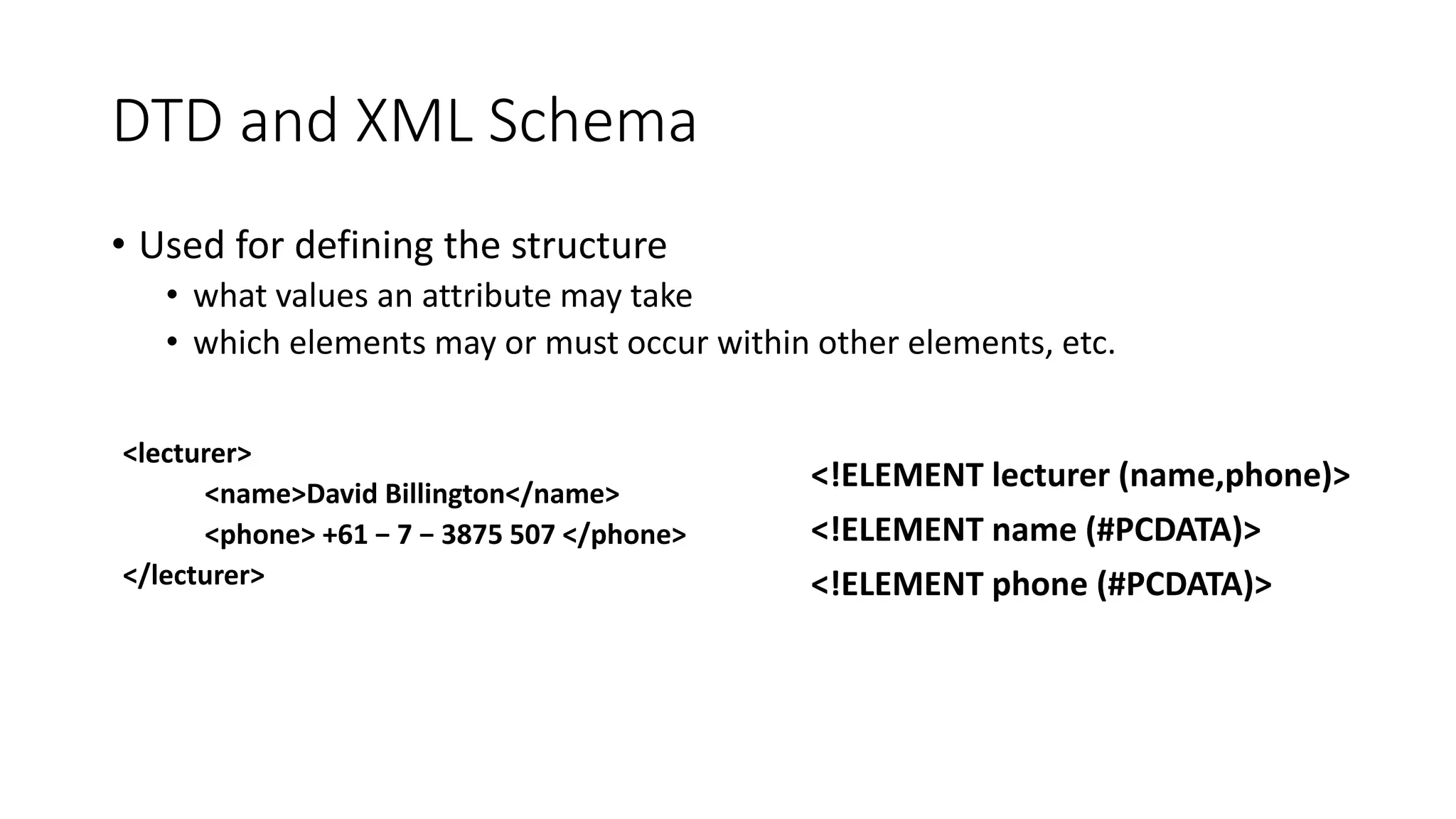
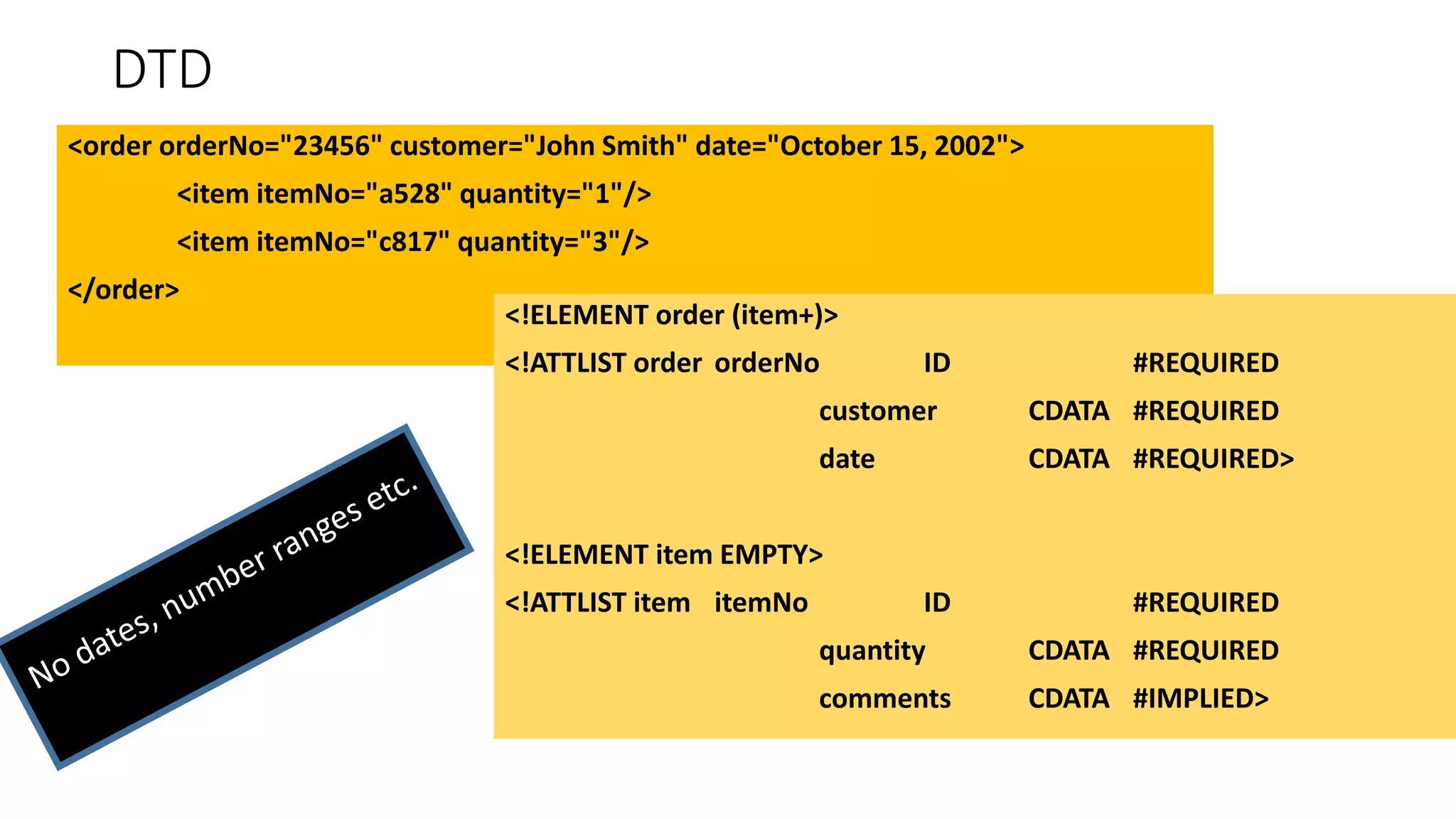
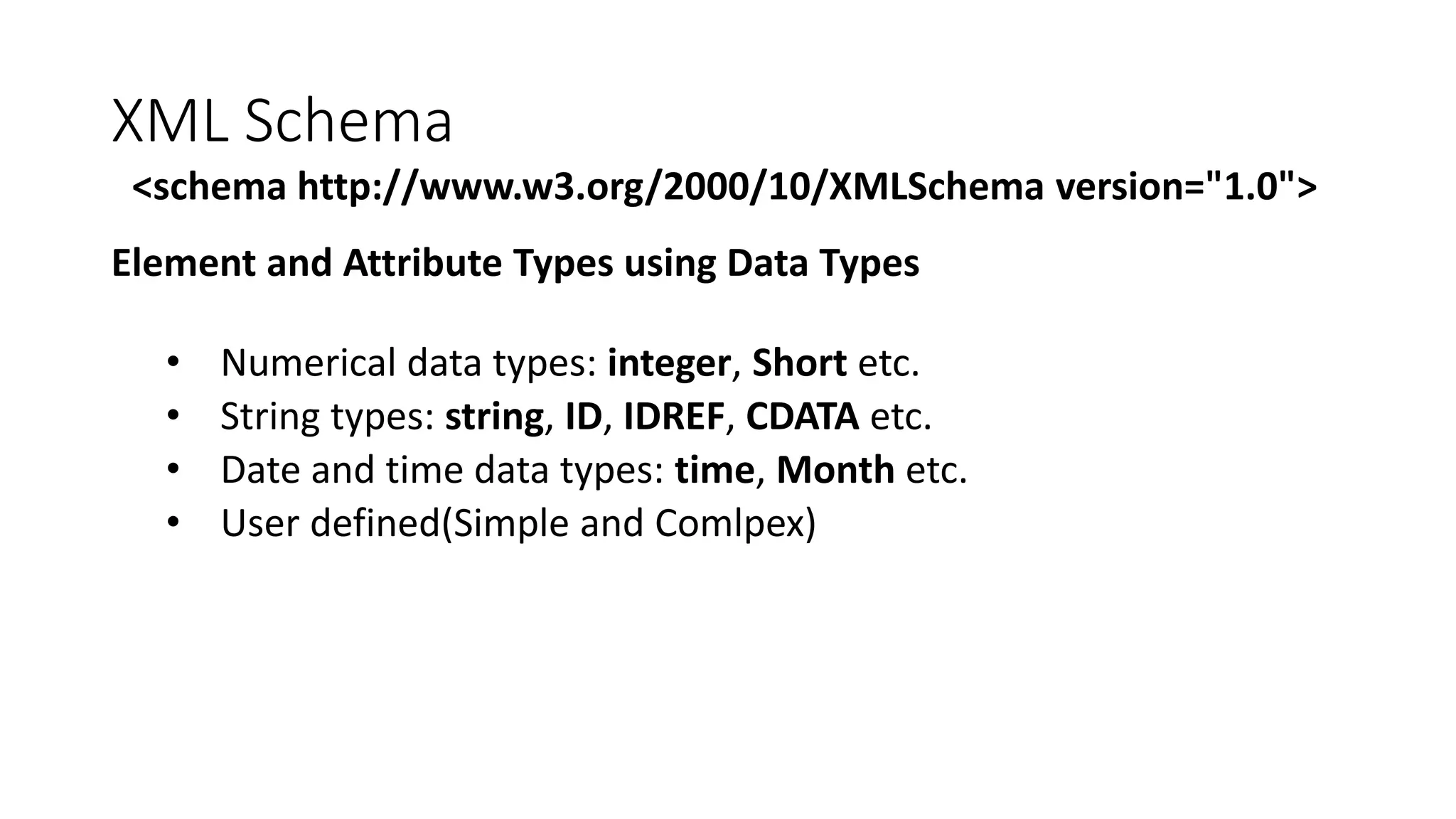
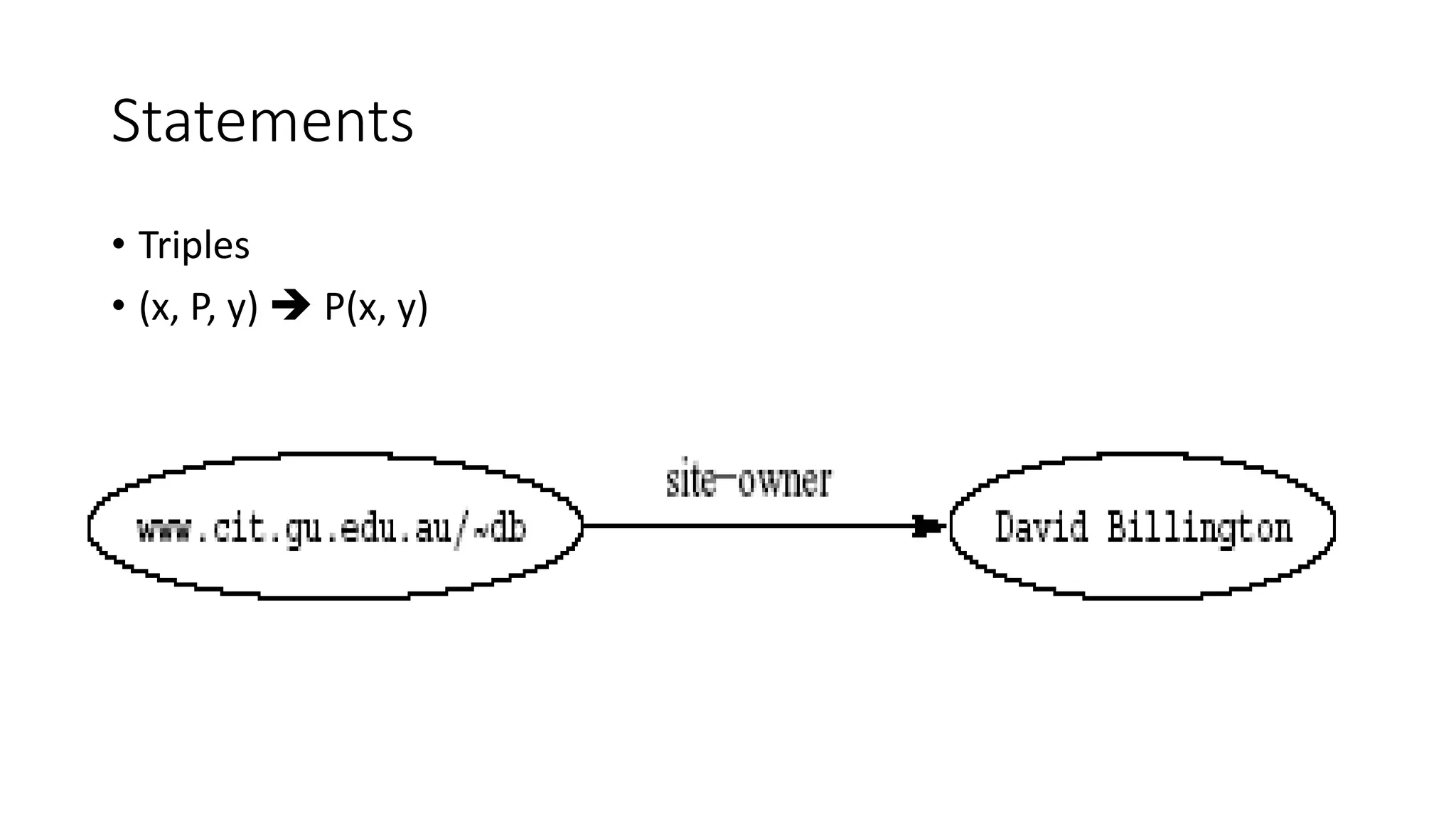
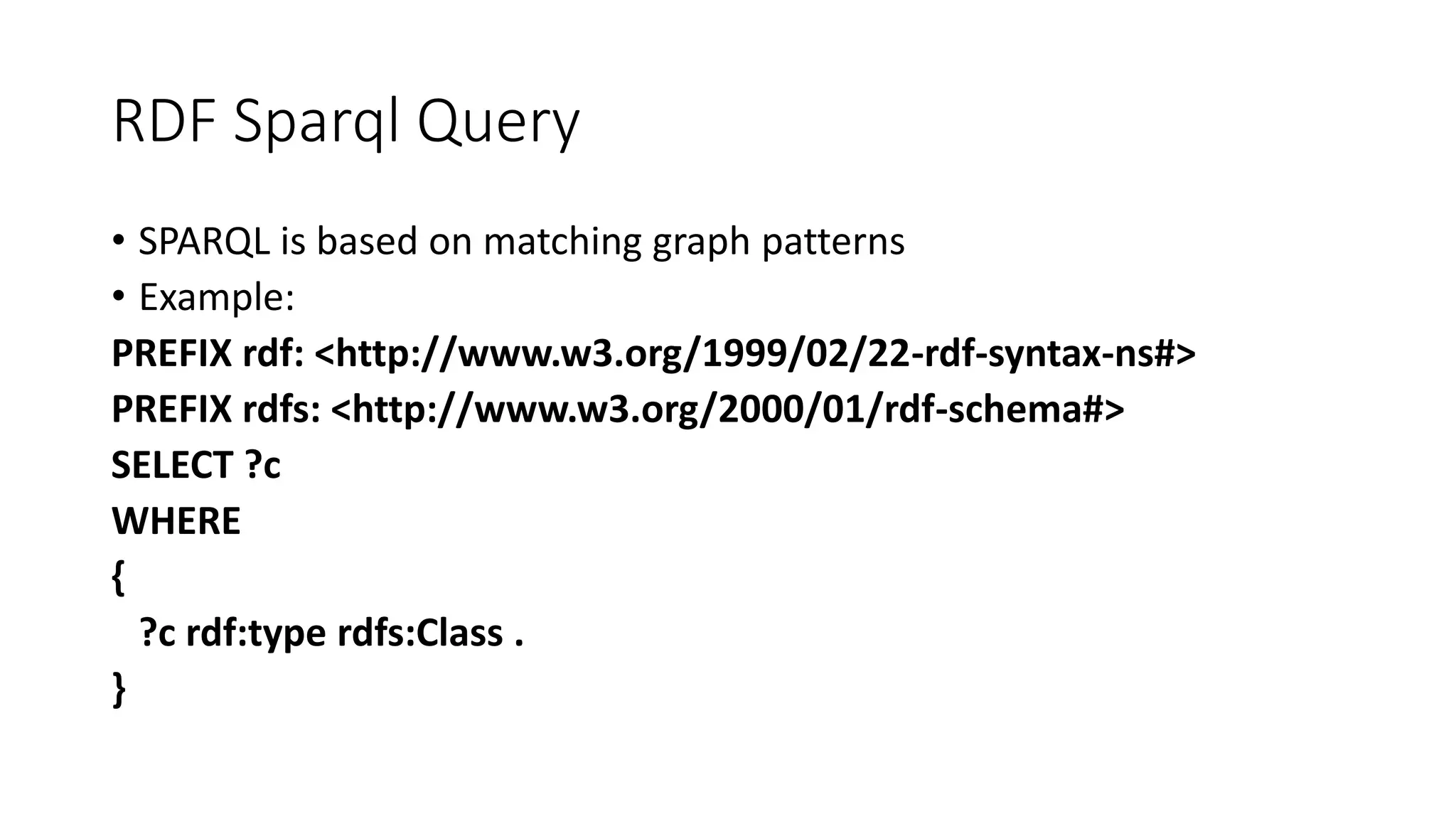
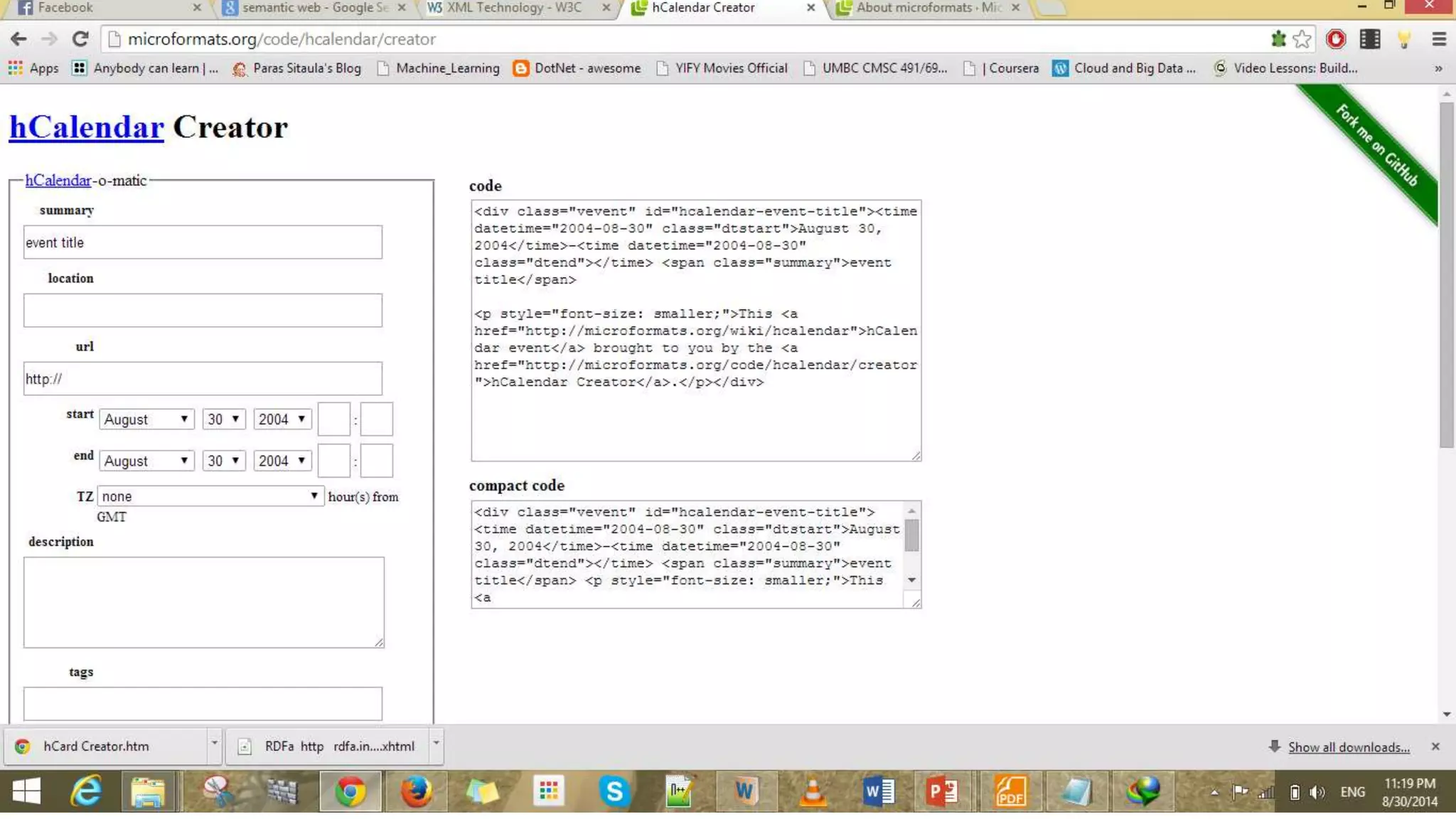
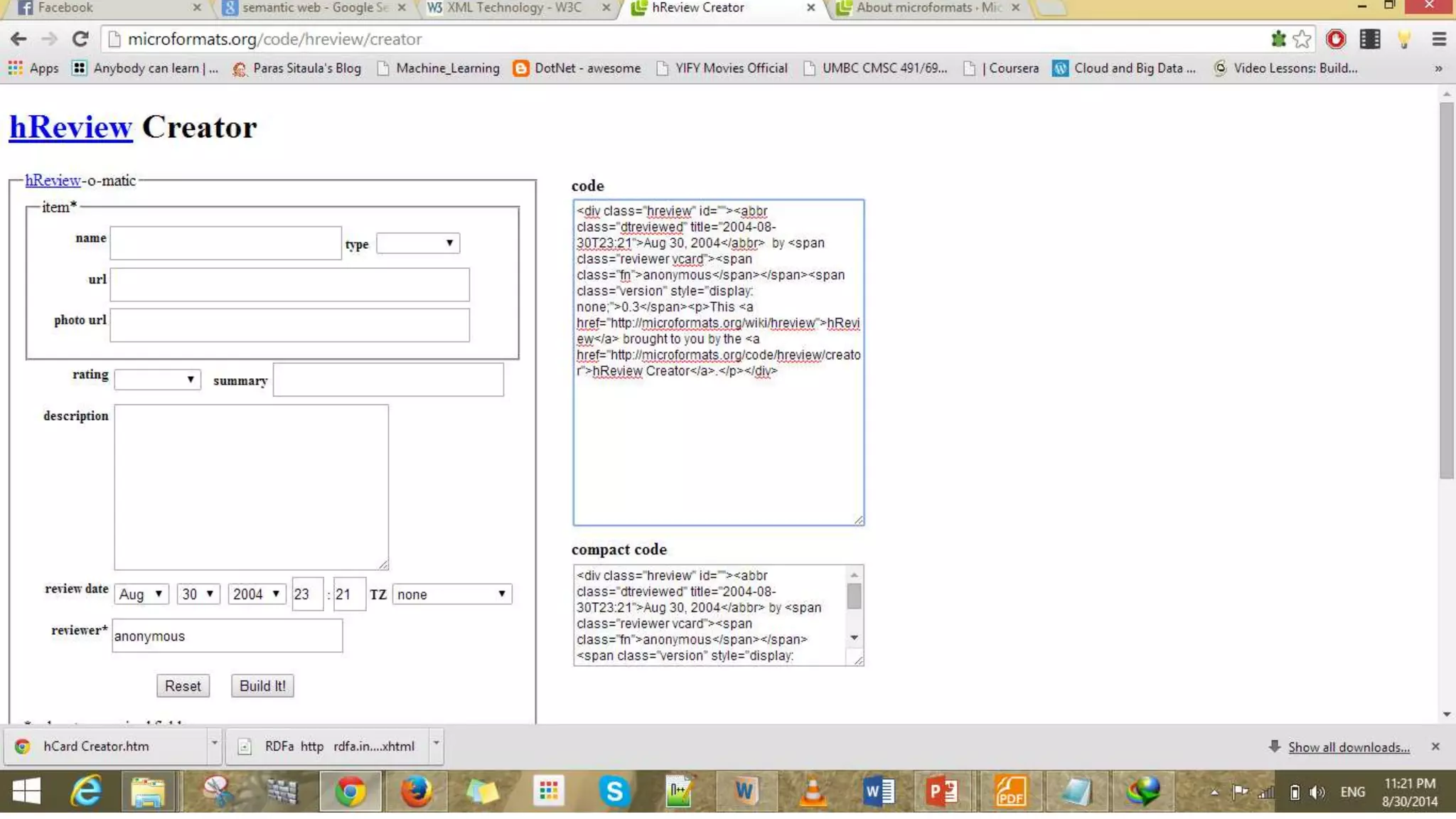
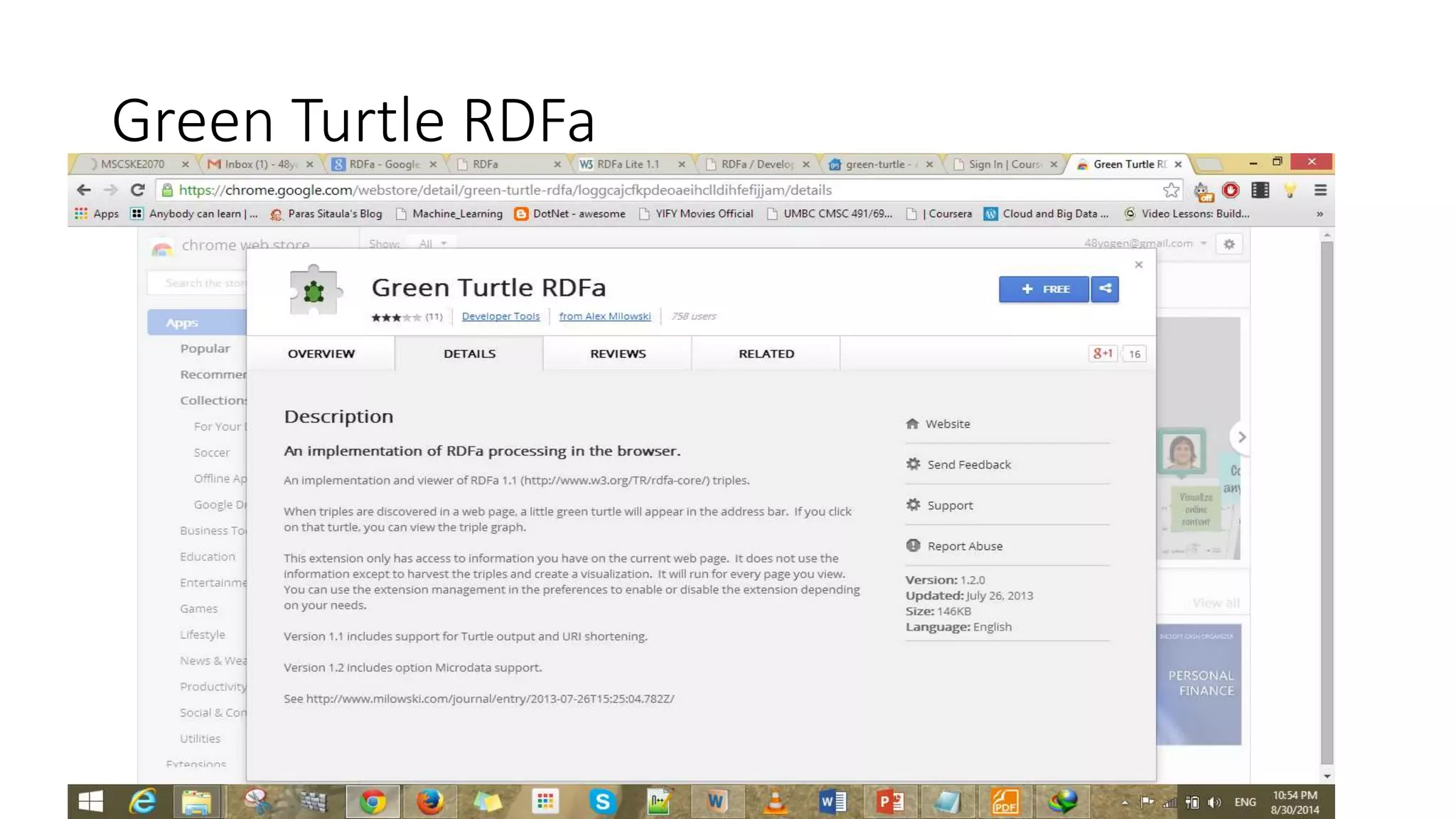
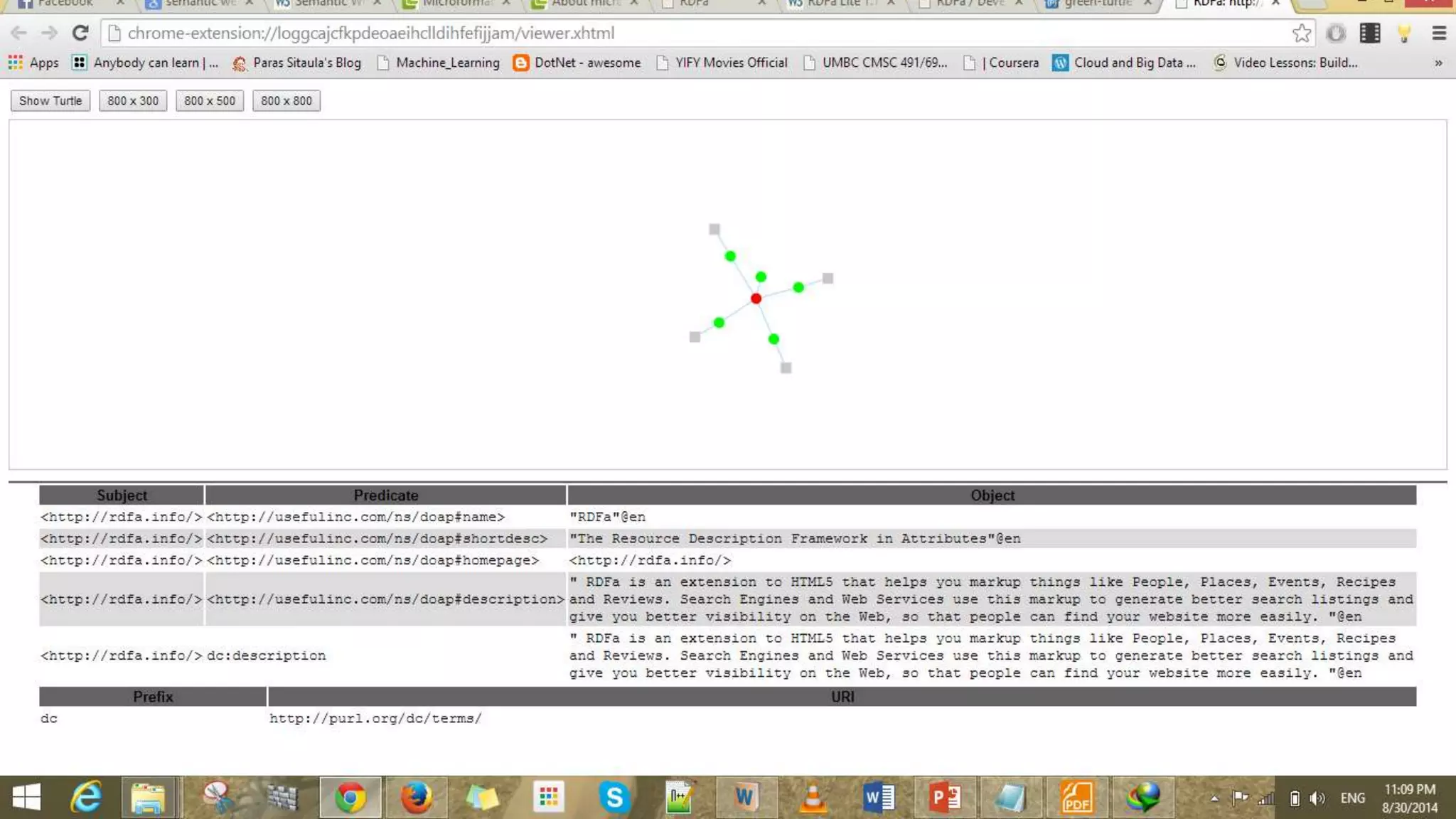
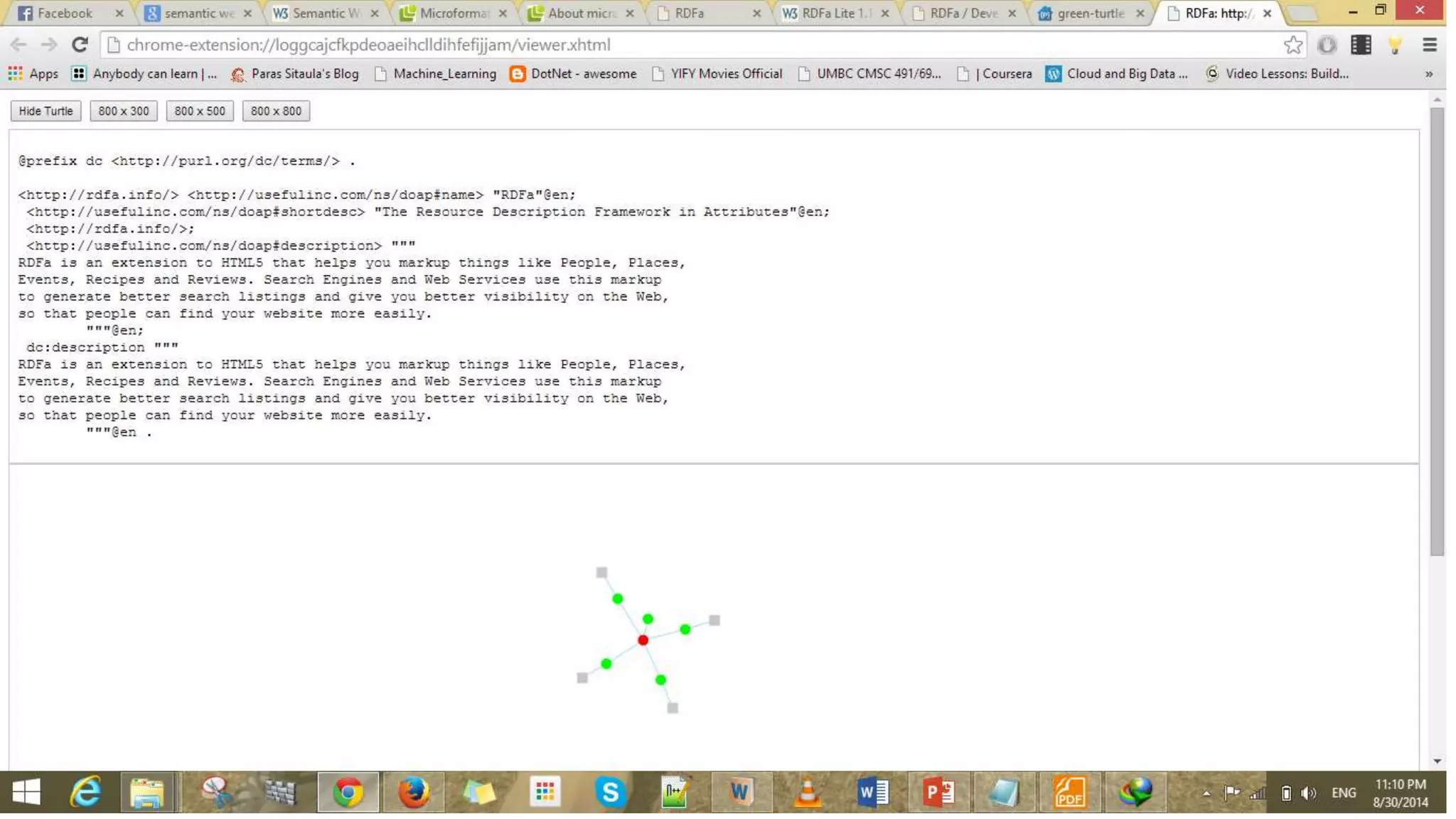
This document provides an overview of information representation standards including XML, DTD, XML Schema, RDF, RDF Schema, and related technologies. It describes the basic structures and components of these standards for representing structured data and semantics on the web.