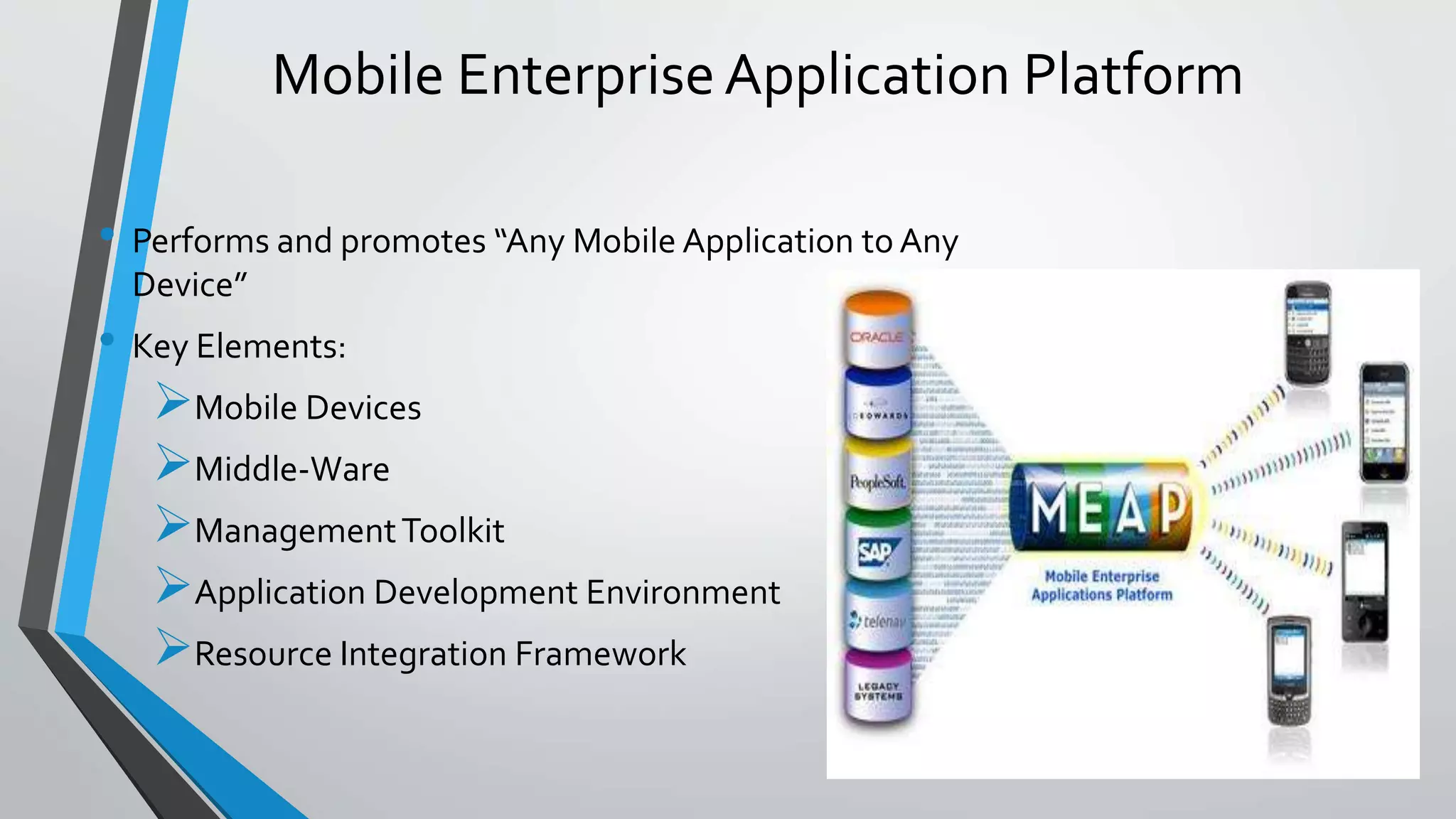
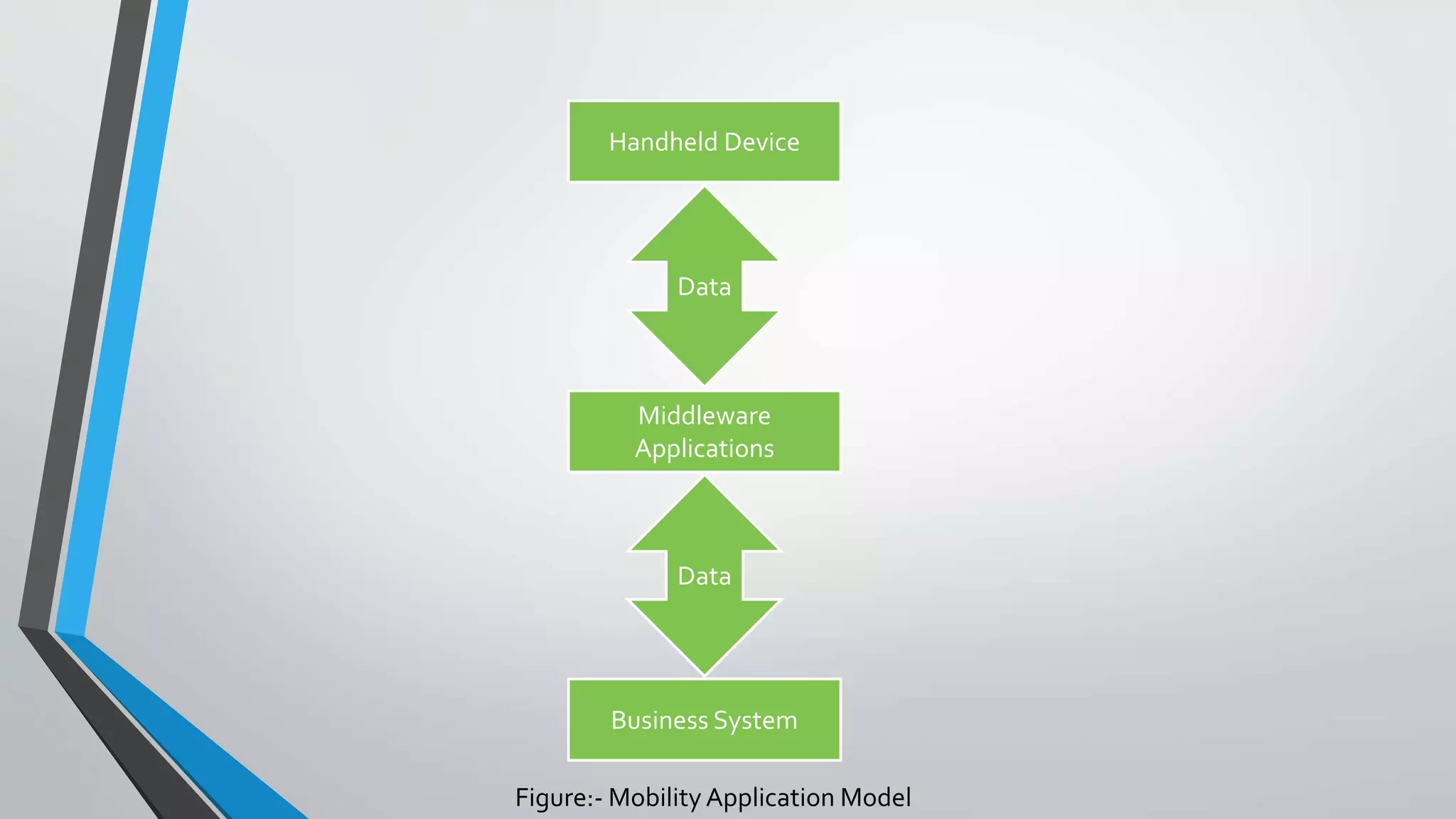
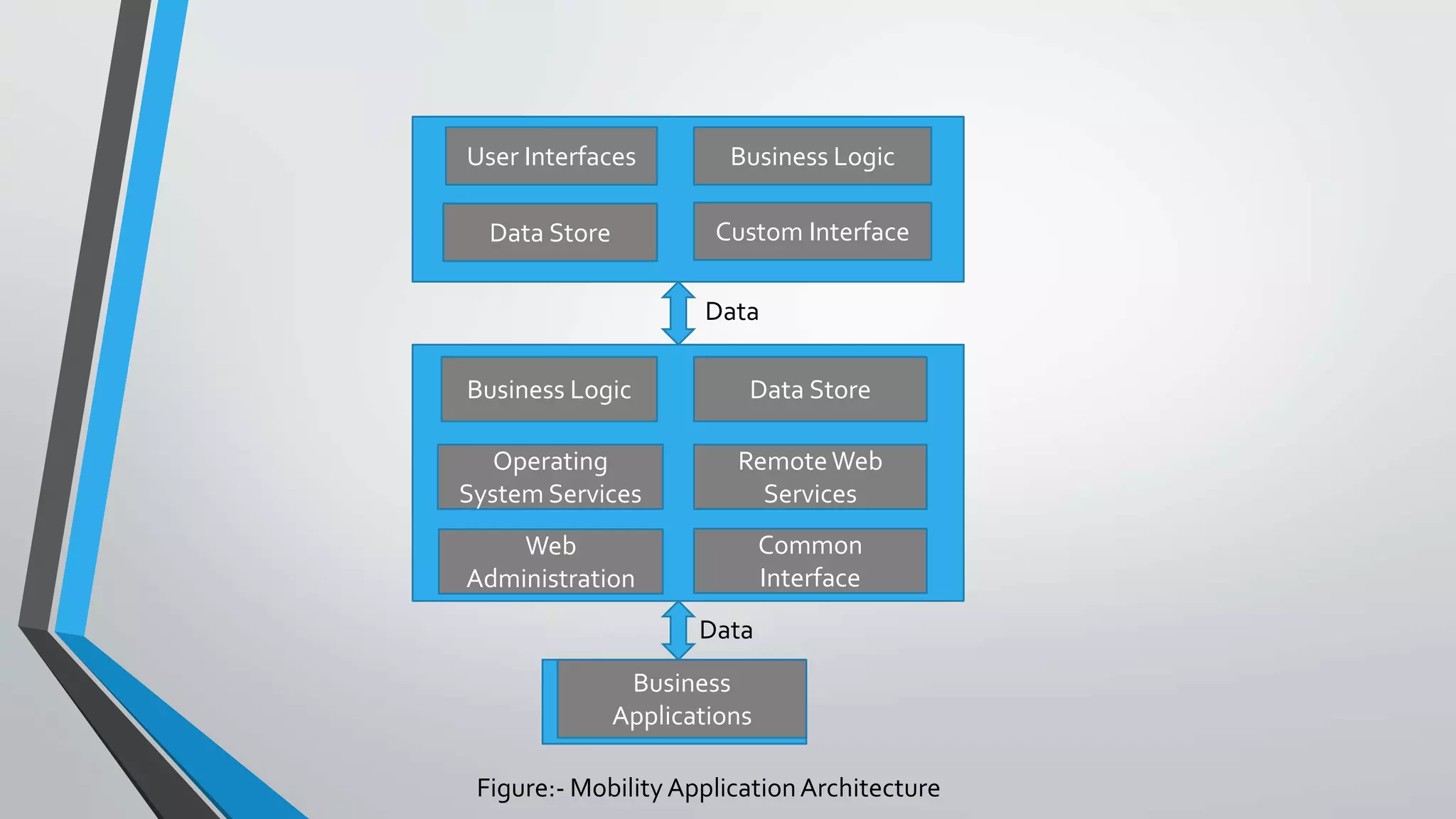
The document discusses cloud mobility and mobile enterprise application platforms. It describes how bringing your own device (BYOD) allows users flexibility and increases productivity. It also outlines some business problems with mobilizing systems, like separating processes, security, integration, and supporting different devices and infrastructure. The document then explains that mobile enterprise application platforms allow "any app to any device" and discusses key elements like middleware, management tools, and application development environments.