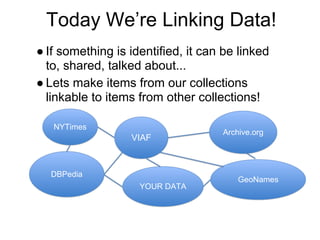
The document introduces linked data and microdata, emphasizing the importance of linking identifiable data to enhance sharing and collaboration across various collections. It discusses the transition from traditional data models to a graph-based model using Resource Description Framework (RDF) and triples, which describe relationships between entities. It also mentions standards for data semantics, vocabularies, and tools like SPARQL for querying RDF datasets.