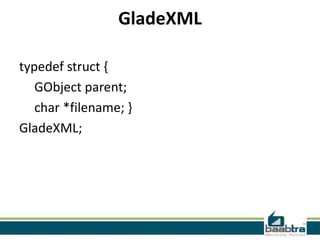
This document provides an overview of XML including:
- XML stands for Extensible Markup Language and is used to carry data, not display it. Tags are user-defined.
- An XML example shows a simple note with predefined tags.
- XML schemas define valid elements, attributes, structure and data types for XML documents.
- XML documents form a tree structure with elements nested within a root element. Syntax rules ensure documents are well-formed.
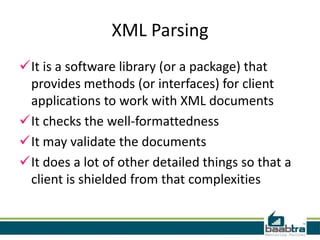
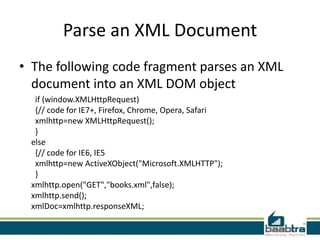
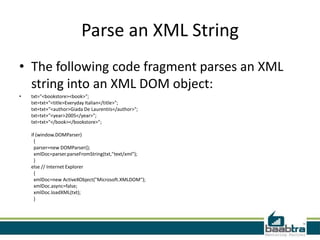
- XML parsers like SAX and DOM are used to read and build a model of an XML document programmatically.