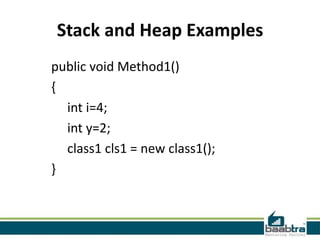
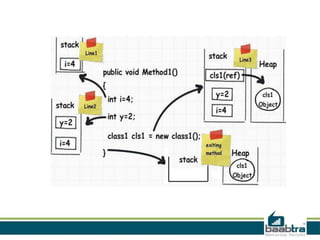
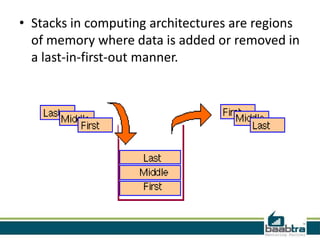
This document discusses the differences between the stack and the heap in computing memory. The stack is a temporary storage area where function variables are stored. Data is added or removed in a last-in, first-out manner. The stack has a fixed size and data is automatically deleted when a function exits. The heap is used for dynamic memory allocation and data remains until manually deleted. The stack is faster than the heap for memory allocation due to its structure. Examples are given showing how variables are allocated on the stack or heap.





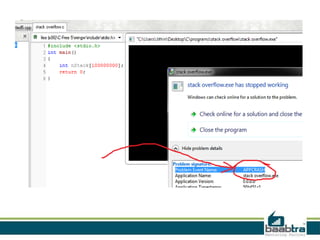
![• Example For Stack overflow
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int nStack[100000000];
return 0;
}
• This program that causes a stack overflow.
• If you run this the program will crash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stckndheap-121127063920-phpapp02/85/Stack-and-heap-7-320.jpg)