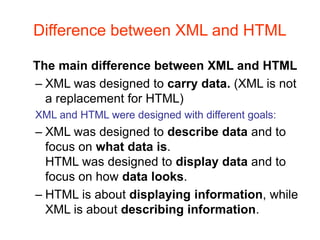
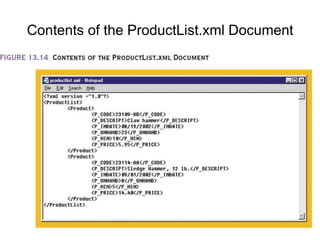
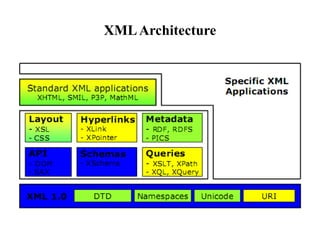
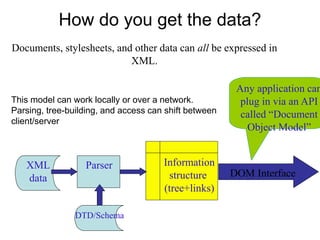
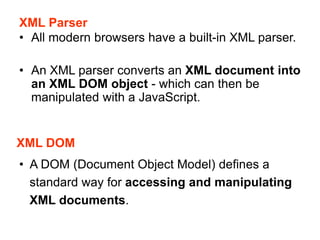
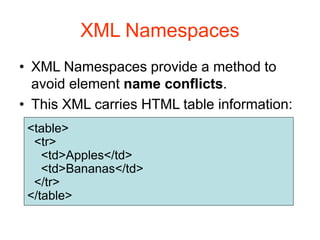
XML is a markup language similar to HTML but designed for carrying data rather than displaying it. It allows users to define their own elements and tags. XML documents use tags to describe and structure information and can be displayed using CSS or transformed using XSL. Key benefits of XML include its ability to describe hierarchical data, separate data from presentation, and enable data sharing across different systems.






























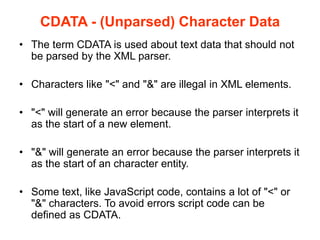
![• Everything inside a CDATA section is ignored by
the parser.
• A CDATA section starts with "<![CDATA[" and
ends with "]]>":
<script>
<![CDATA[
function matchwo(a,b)
{
if (a < b && a < 0) then
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
]]>
</script>
In this example, everything inside
the CDATA section is ignored by the
parser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-xmlfundamentals-191125035233/85/1-xml-fundamentals-42-320.jpg)
