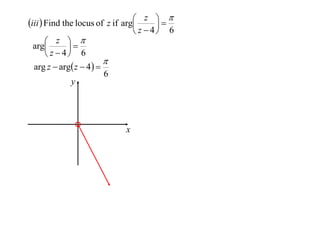
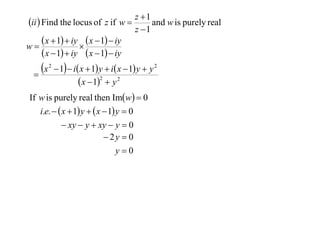The document discusses finding the locus of complex numbers ω or z given some condition on ω or z. It provides examples of determining the locus when:
1) ω is purely real or purely imaginary, which results in the locus being lines.
2) The argument of a linear function of z equals an angle θ, which results in the locus being an arc of a circle.
3) An example is worked through where the locus is a circle with center (1,0) and radius 1/2.
4) Another example finds the locus of z if w is purely real, which results in the locus being the x-axis where y=0.