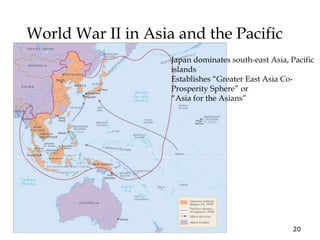
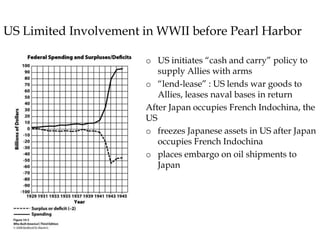
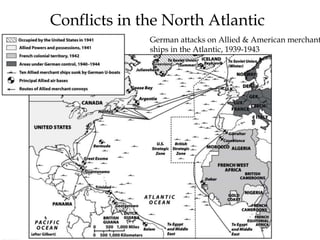
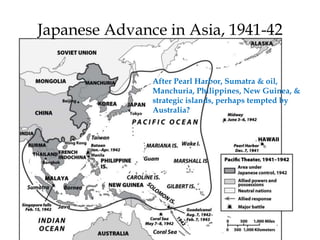
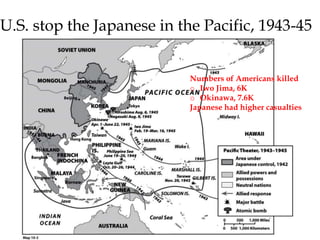
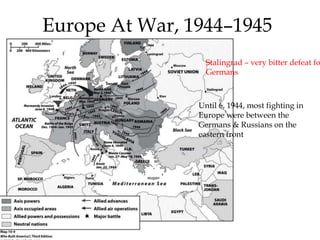
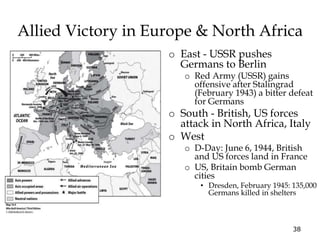
The document provides an overview of key events and outcomes of WWII:
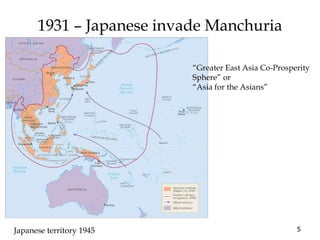
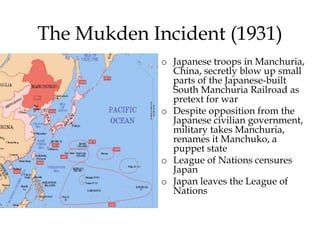
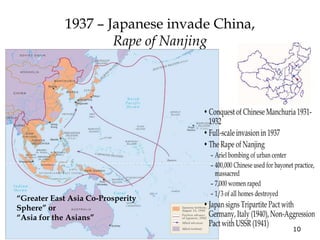
1) WWII started in Asia in 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria and escalated globally over the next decade as Germany, Italy and Japan expanded their territories aggressively through military force.
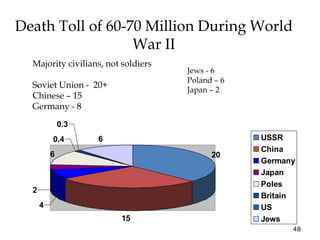
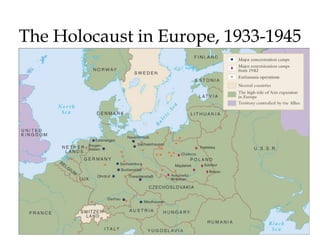
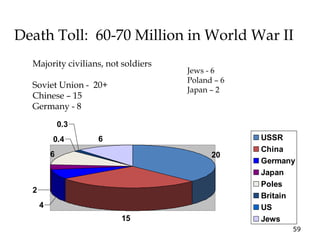
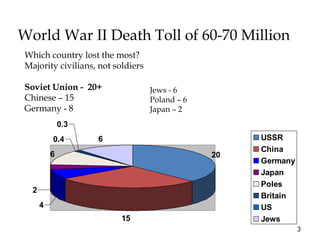
2) The war resulted in 60-70 million deaths, the majority being civilians in the USSR, China, Germany and Poland. It also led to the Holocaust and genocide of 6 million Jews.
3) While bringing unprecedented peace to Europe through organizations like the UN, WWII also set the stage for the Cold War between Western allies and the Soviet Union that persisted globally after the war.





























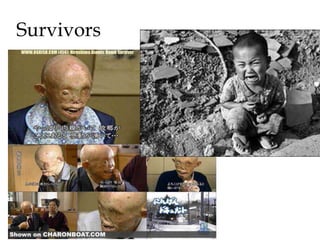

![“Why do you have to end the war twice?”
“To me, actually, the important event was not the first bomb, but the
second…[w]hen they announced the second bomb…, that came as a
shock to me. I said, ‘But the war is over.’ In fact, the headlines at
that time were ‘Japanese Surrender.’ and then bang, there was the
bomb in Nagasaki. And that hit me like a glass of cold water
thrown at you. I suddenly said, ‘Now, wait a second. What for?’ I
mean, great, we ended the war – but why do you have to end the
war twice?’…
Bernard Feld,
graduate student,
Manhattan Project, a U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Atomic Bomb
Research & Development
The Reminiscences of Bernard Feld, Columbia Oral History Research Office, Columbia University, 1980, 19-20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture8-wwiicaptainamericathefinalsolution-141028170037-conversion-gate02/85/Lecture-8-World-War-II-Captain-America-and-the-Final-Solution-45-320.jpg)