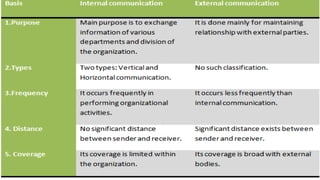
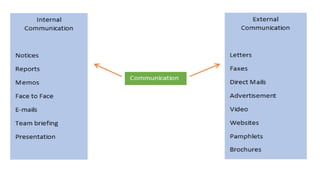
This document discusses the differences between formal and informal writing styles. It notes that informal writing is suitable for everyday communication with friends and family, while formal writing is used for business and official purposes. The main characteristics of informal writing are a personal tone, simple structure, use of contractions and abbreviations, and showing emotion. Formal writing takes a more objective, third-person approach with complex structure, full words, and aims for clarity and structure in arguments. The choice between formal and informal depends on the audience and medium.