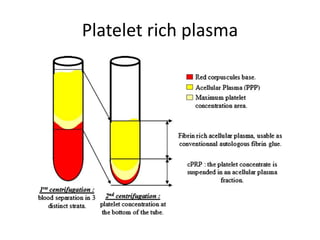
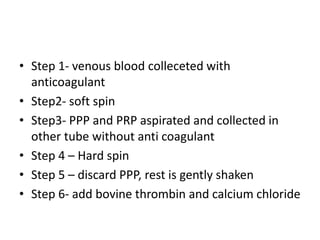
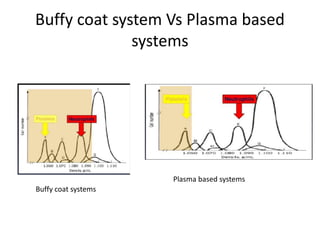
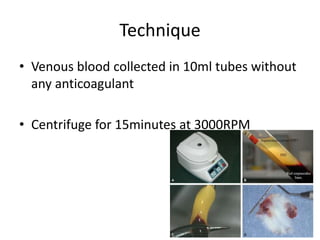
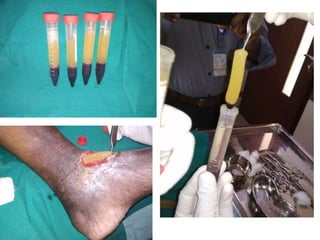
This document discusses platelet concentrates and their role in wound healing. It describes techniques for obtaining platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) through blood centrifugation. PRP and PRF contain growth factors that are released from platelet granules and promote wound healing through angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and recruitment of cells. The document outlines the clinical applications of PRP and PRF in various surgical procedures and injuries to enhance healing. It also reviews the advantages and limitations of different platelet concentrate collection methods.