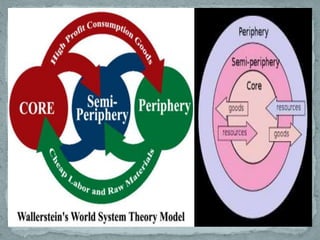
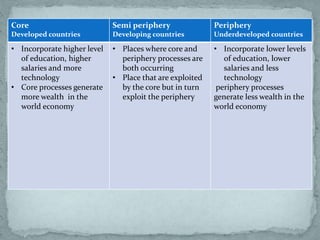
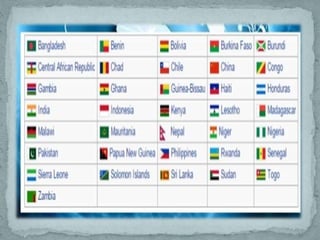
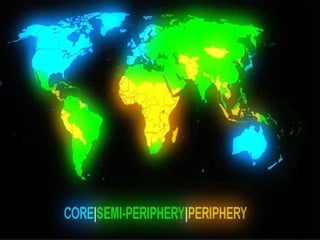
World system theory, developed by Immanuel Wallerstein, proposes that the global economy consists of a core, semi-periphery, and periphery. The core countries engage in banking, manufacturing, and technology and exploit peripheral countries for raw materials and labor. Peripheral countries have weak governments and economies and are dependent on core countries. Semi-peripheral countries share some characteristics of both, exploiting peripheries while also being exploited by cores. The theory emphasizes global economic inequality between these zones.