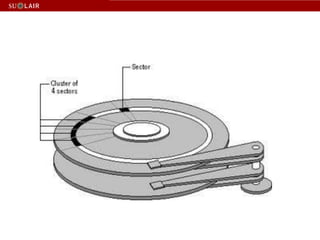
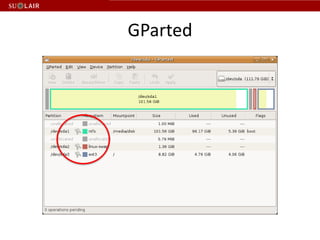
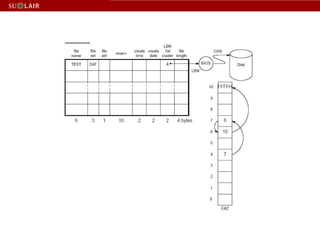
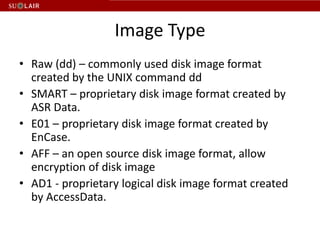
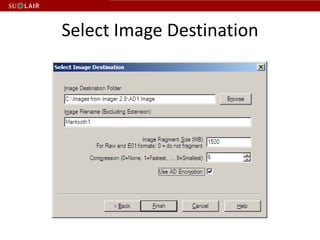
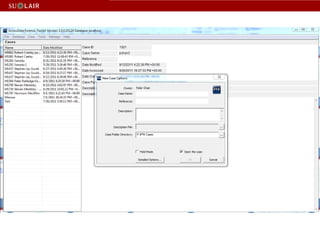
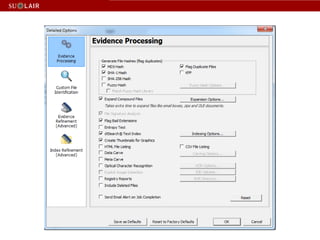
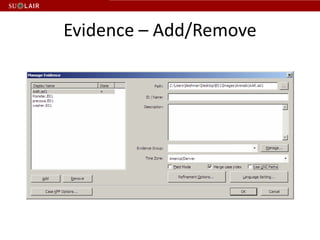
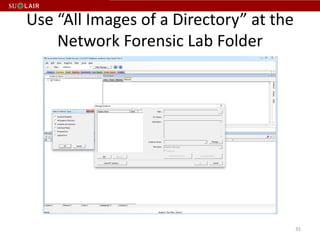
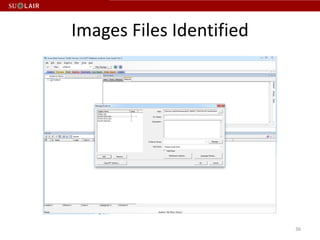
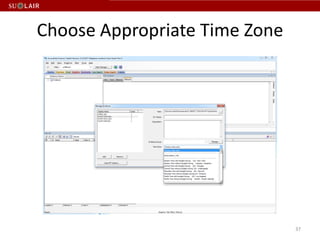
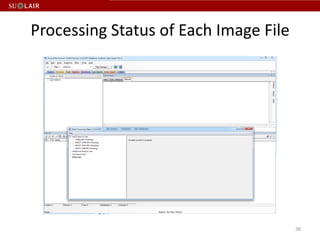
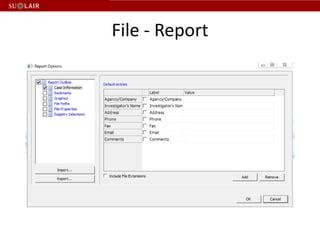
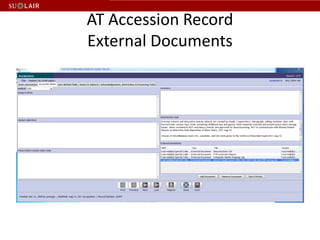
This document outlines the steps for imaging and processing born-digital materials, including: running virus checks, creating disk/logical images using FTK Imager, partitioning disks, identifying file systems, capturing images to evidence folders with case numbers, processing images in AccessData FTK including hashing and indexing files, and generating a collection summary report. The workflow is intended to thoroughly capture and document born-digital content for long-term preservation and access.