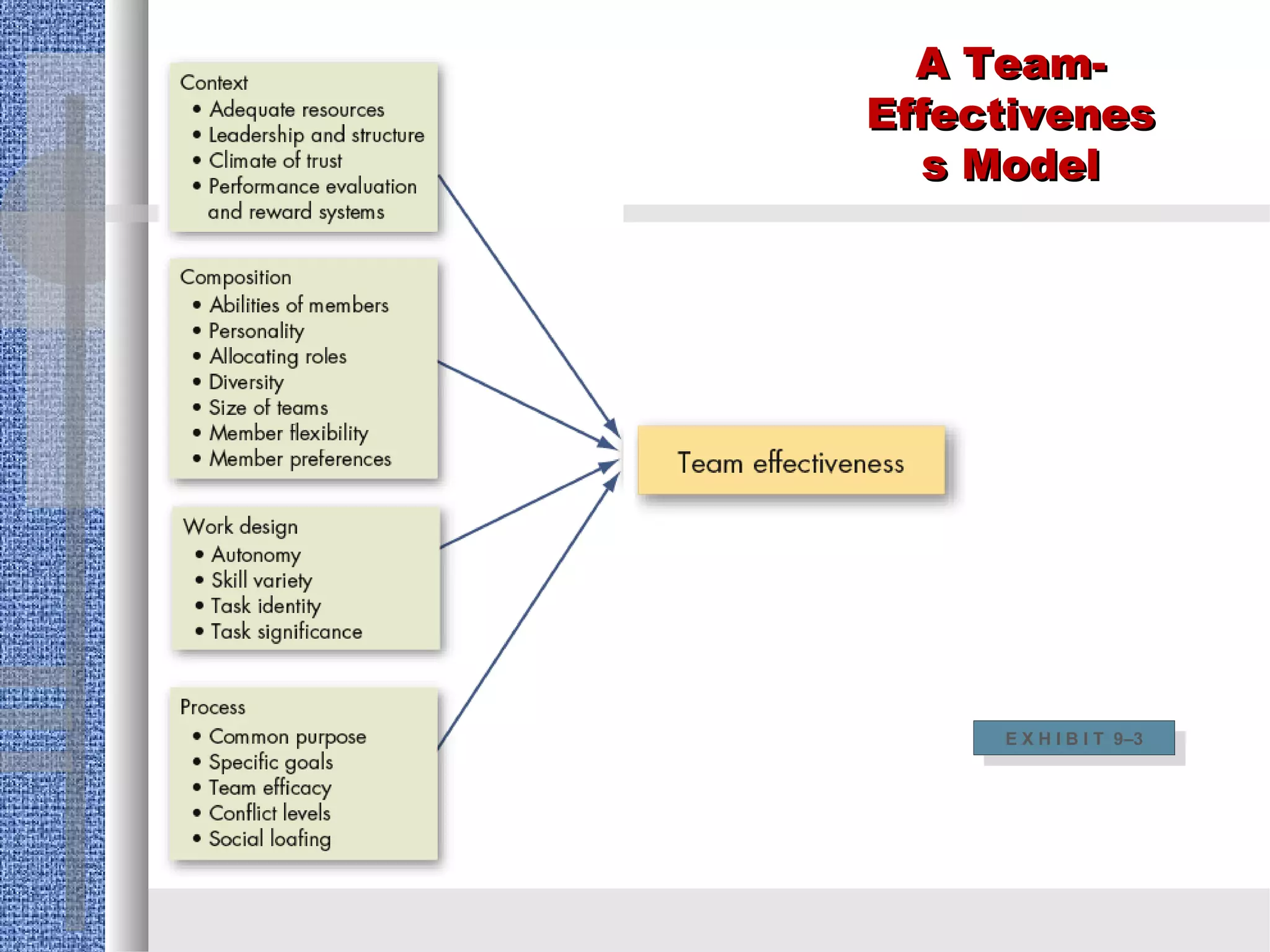
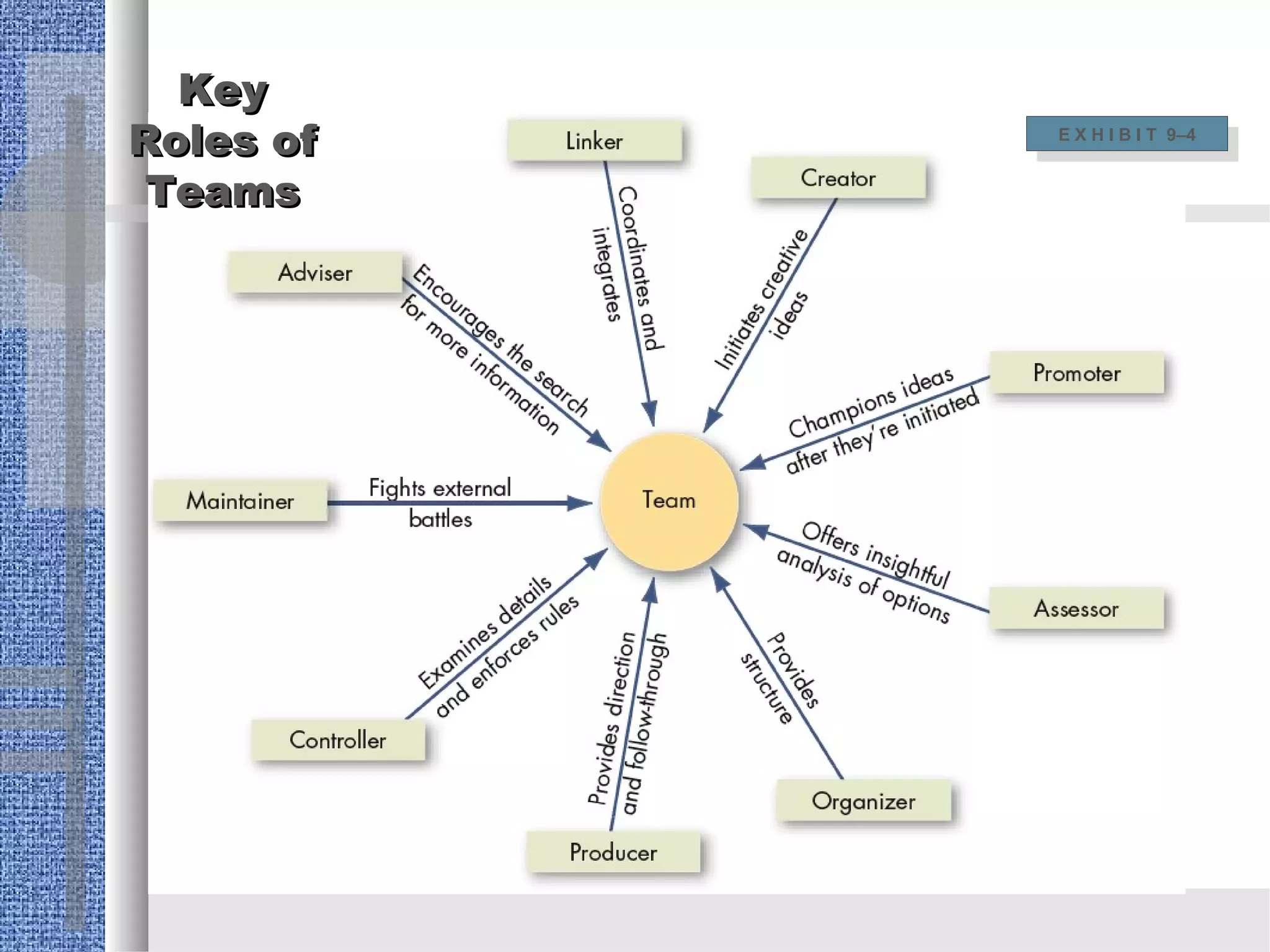
A work team consists of employees from diverse backgrounds working together on projects for a specific period of time. Teams generate synergy by coordinating individual efforts, resulting in performance greater than the sum of individual contributions. Effective teams provide benefits like improved organizational performance, innovation, and employee satisfaction. There are different types of teams like problem-solving teams, self-managed teams, and cross-functional teams comprising members from various departments. Teams are important for total quality management and can benefit from diversity but also face challenges from diversity.