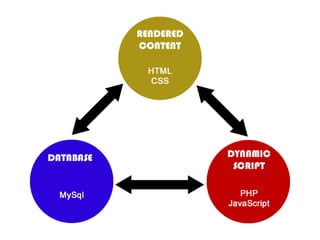
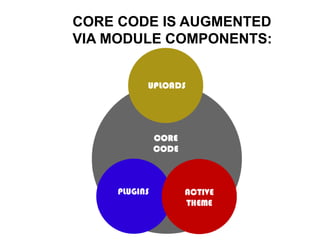
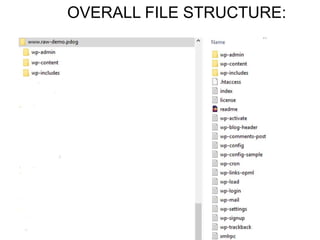
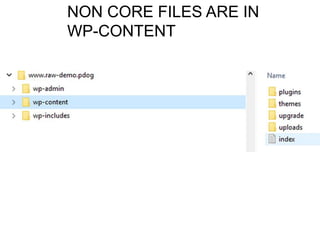
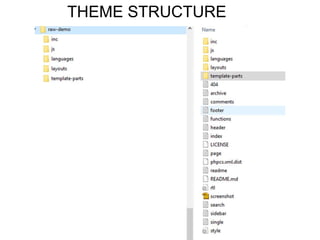
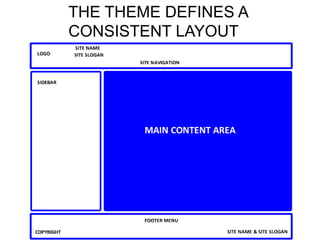
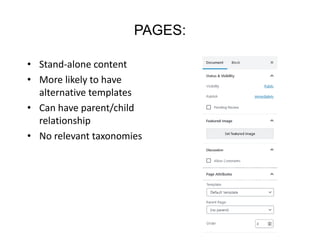
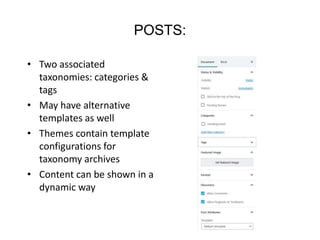
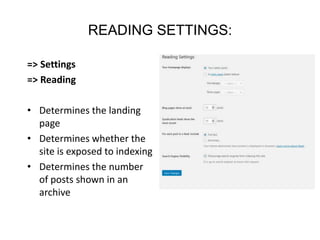
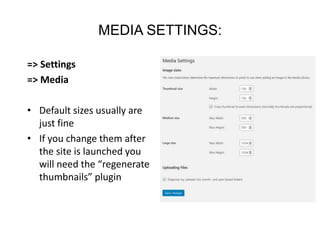
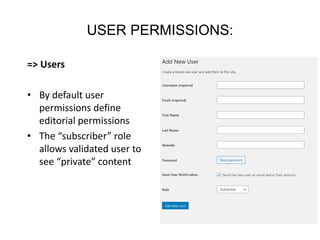
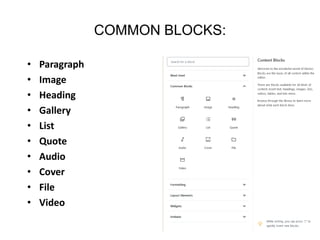
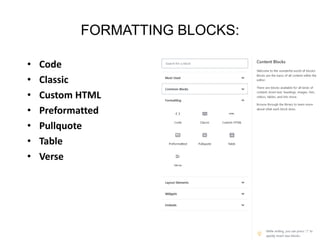
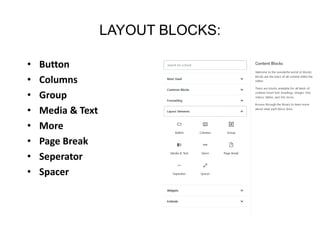
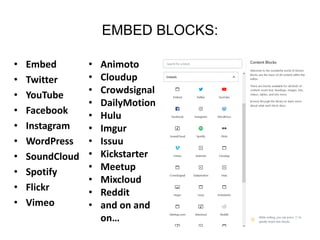
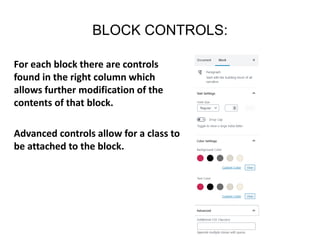
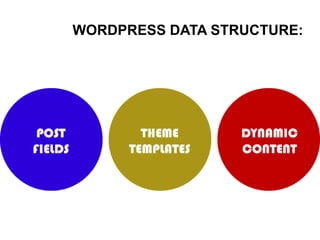
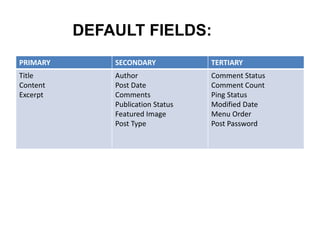
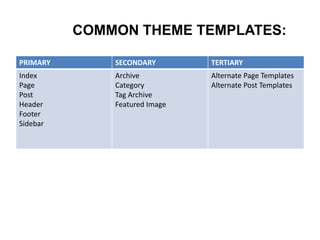
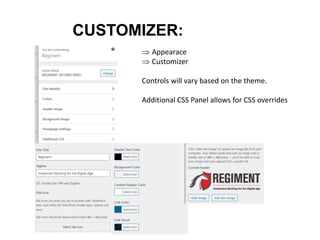
This document provides an overview of building and maintaining WordPress sites. It discusses WordPress fundamentals like posts, pages, taxonomies, menus, widgets, and custom fields. It also covers themes, plugins, and common issues like plugin bloat and unoptimized images. The document recommends plugins and themes to use and provides tips for customizing WordPress through the customizer and child themes.