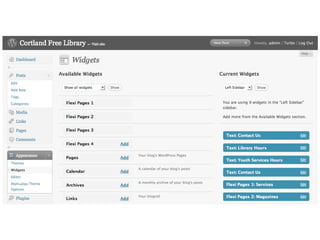
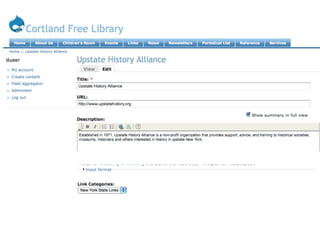
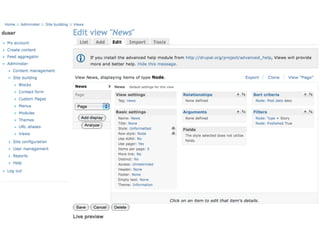
This document provides an overview of open source content management systems (CMS), focusing on WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla. It defines what an open source CMS is and explains some of the key features and components of WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla like themes, plugins/modules, pages/content types, and customization options. It also highlights some of the strengths and limitations of each system.