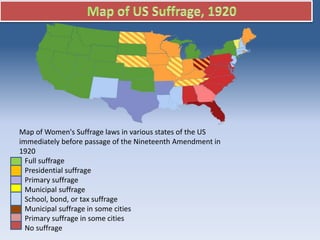
The document discusses the historical context of women's rights in the U.S., highlighting that when the Constitution was adopted, women, particularly white women, were denied voting and many other rights. Key figures such as Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, and Lucretia Mott played significant roles in advocating for women's suffrage, culminating in the passage of the 19th Amendment in 1920, which granted women the right to vote. It also outlines the formation of various women's suffrage organizations and the persistent efforts over decades to achieve legal rights for women.