This document discusses weight management and obesity. It covers several topics:
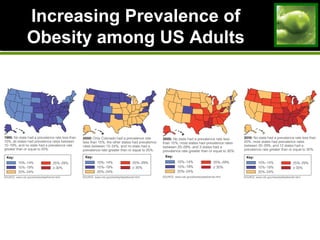
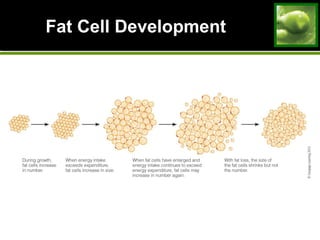
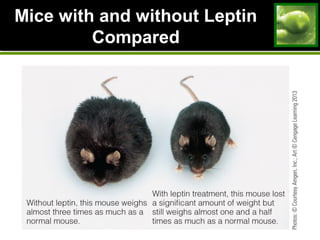
1. The increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity in the US and worldwide. Factors like genetics, environment, diet and physical activity play a role.
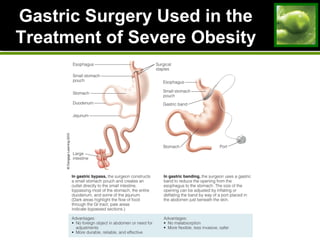
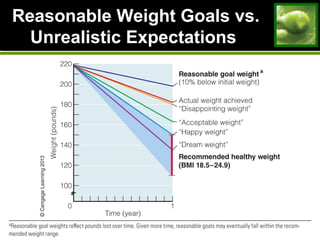
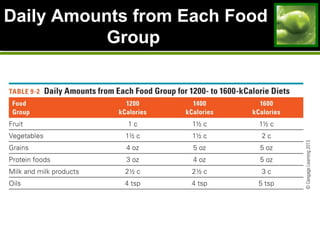
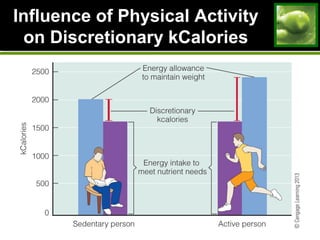
2. Strategies for weight loss and maintenance focus on modest losses through balanced diet and regular physical activity. Fad diets are not effective long-term solutions.
3. Community programs and policies aim to prevent obesity by changing environments and social norms around food and exercise.