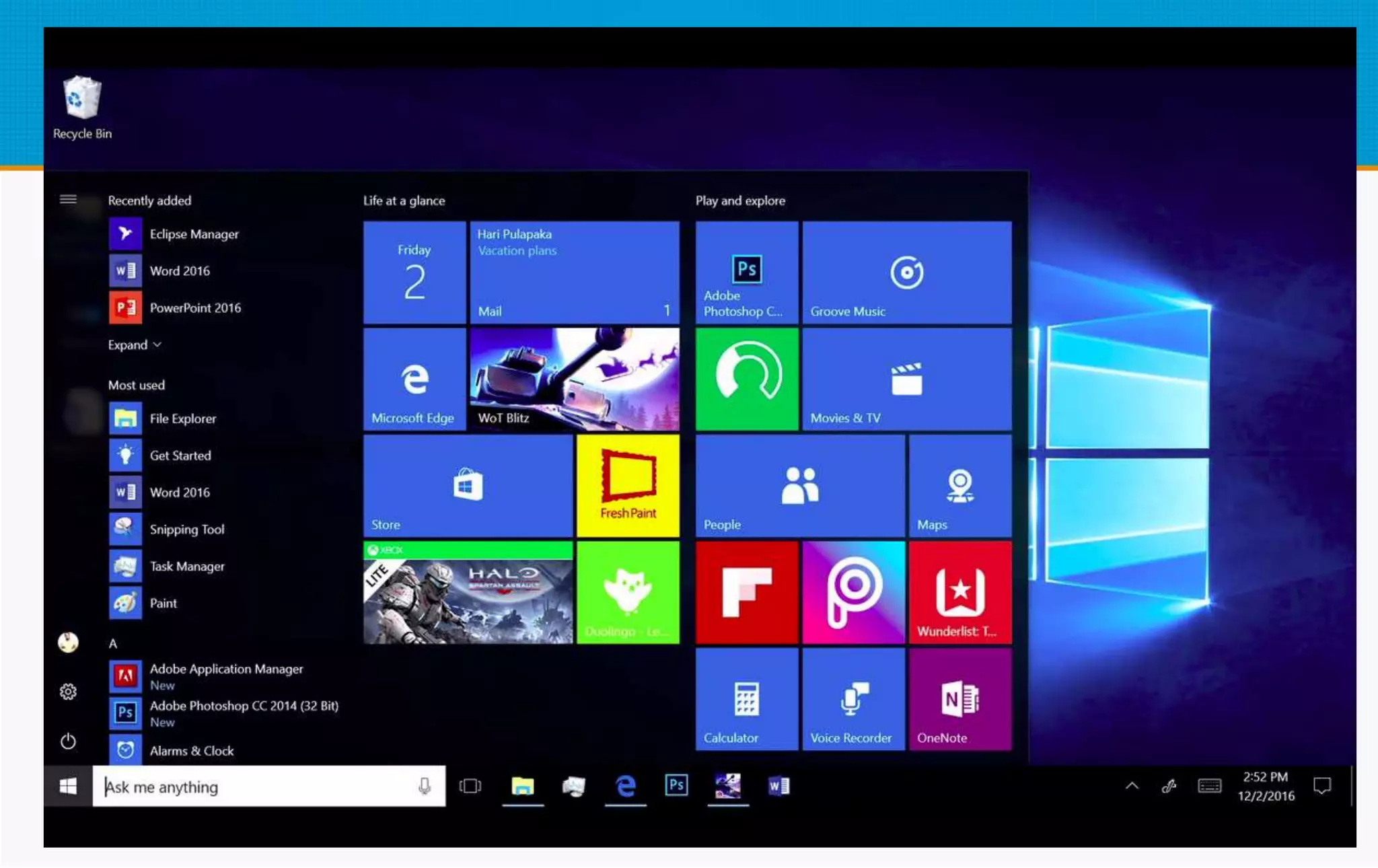
The document discusses the Microsoft Windows environment and operating system. It describes the desktop, taskbar, notification area, control panels, and user account control features of Windows. It explains that Windows is an operating system that controls computer resources and serves as an interface between hardware and software. The document also outlines the major versions of Windows released since 1985 and their new features. It describes the graphical user interface and multi-tasking capabilities of Windows.