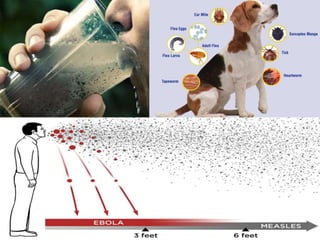
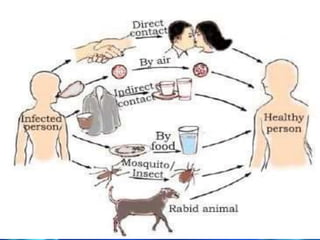
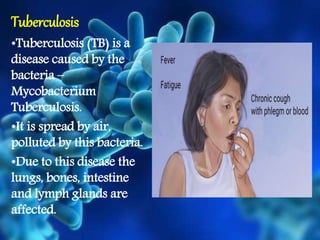
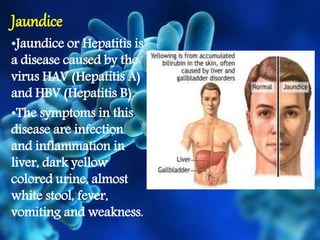
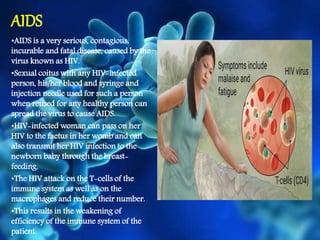
The document discusses health and disease, emphasizing the importance of various bodily activities and factors affecting health, such as nutrition, public cleanliness, and financial stability. It categorizes diseases into acute and chronic, explains infectious and non-infectious diseases, and details specific diseases like typhoid, tuberculosis, jaundice, AIDS, and swine flu, including their causes and symptoms. It also outlines principles of treatment, focusing on managing infectious diseases through medication, public sanitation, and preventive measures like vaccination.