Embed presentation
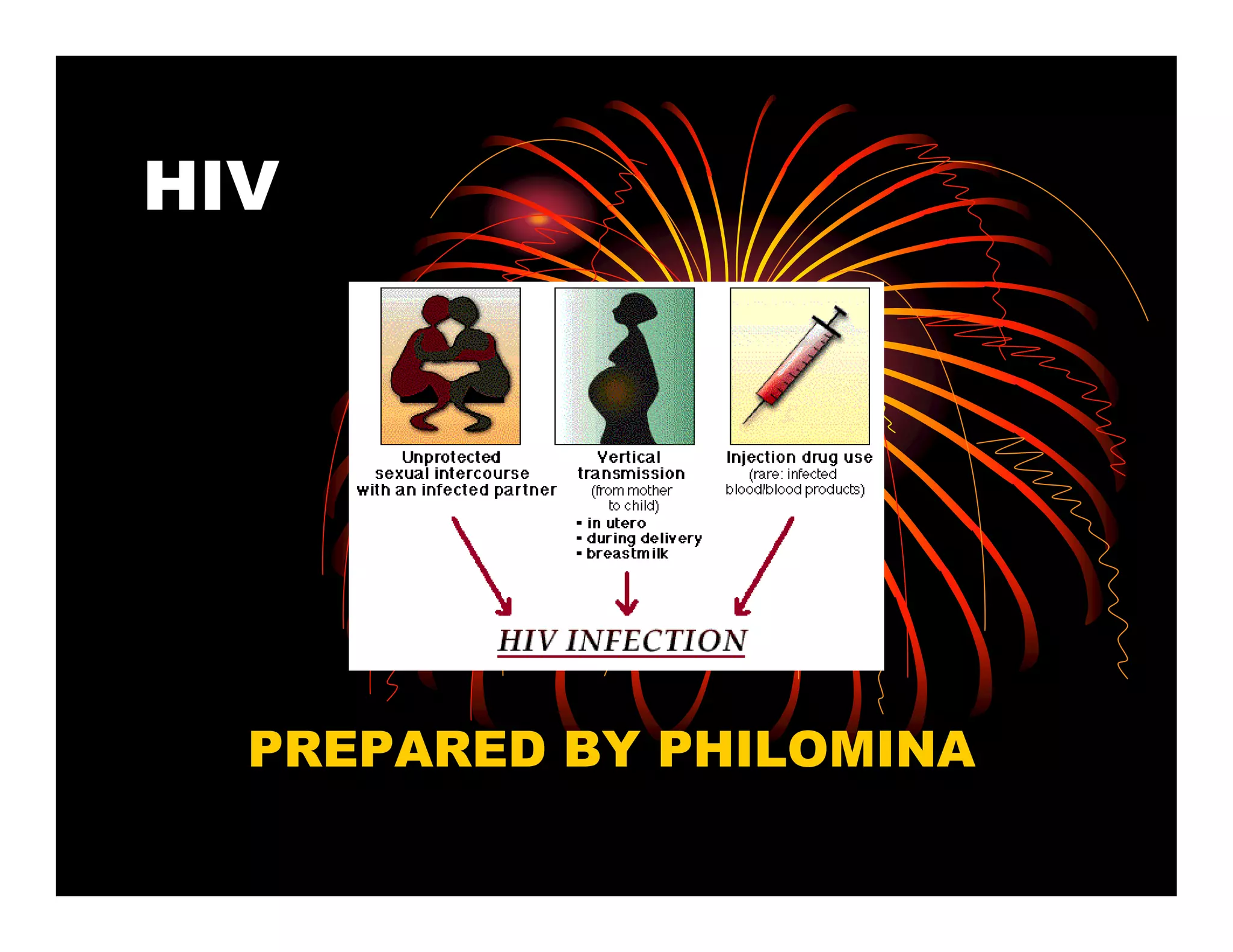













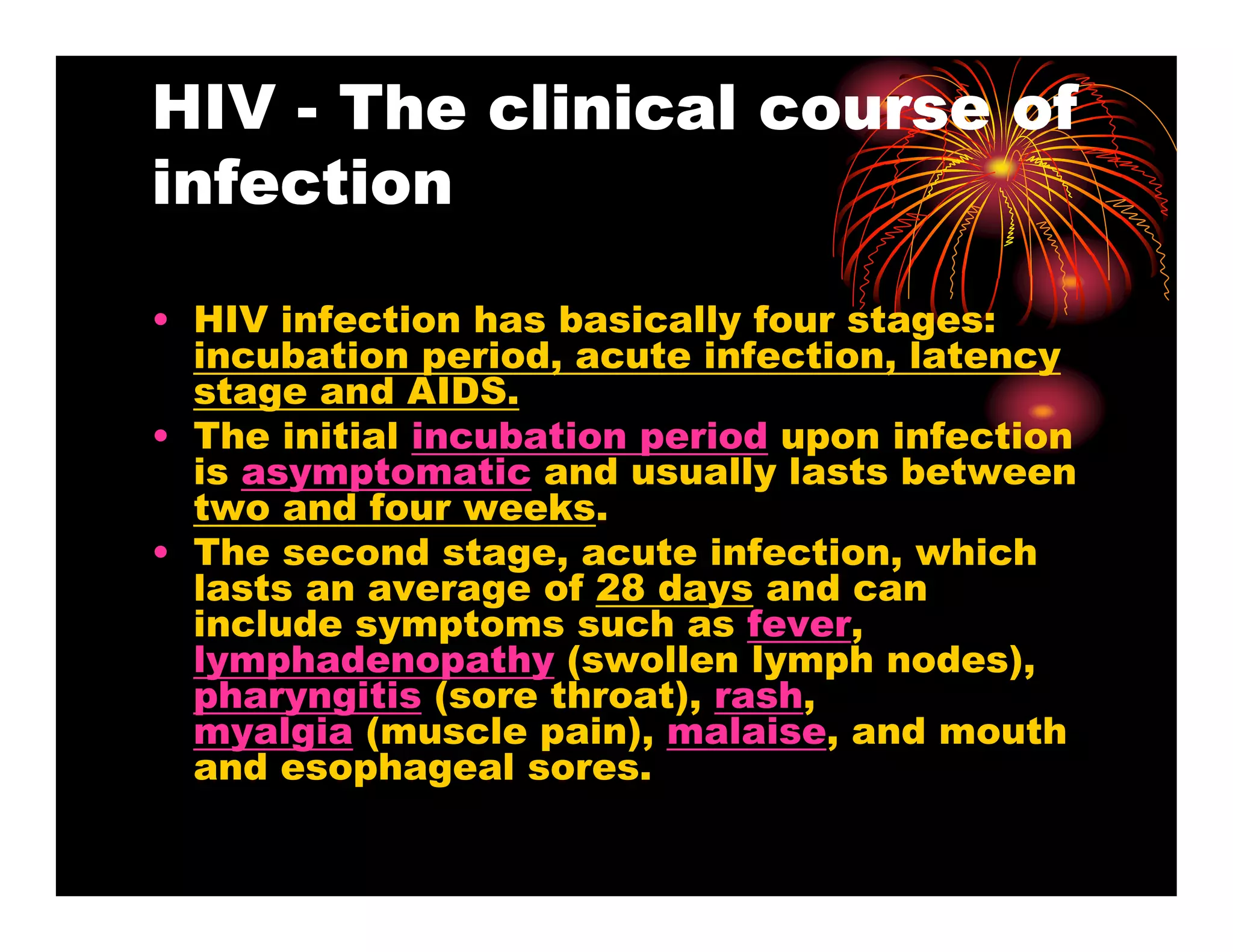
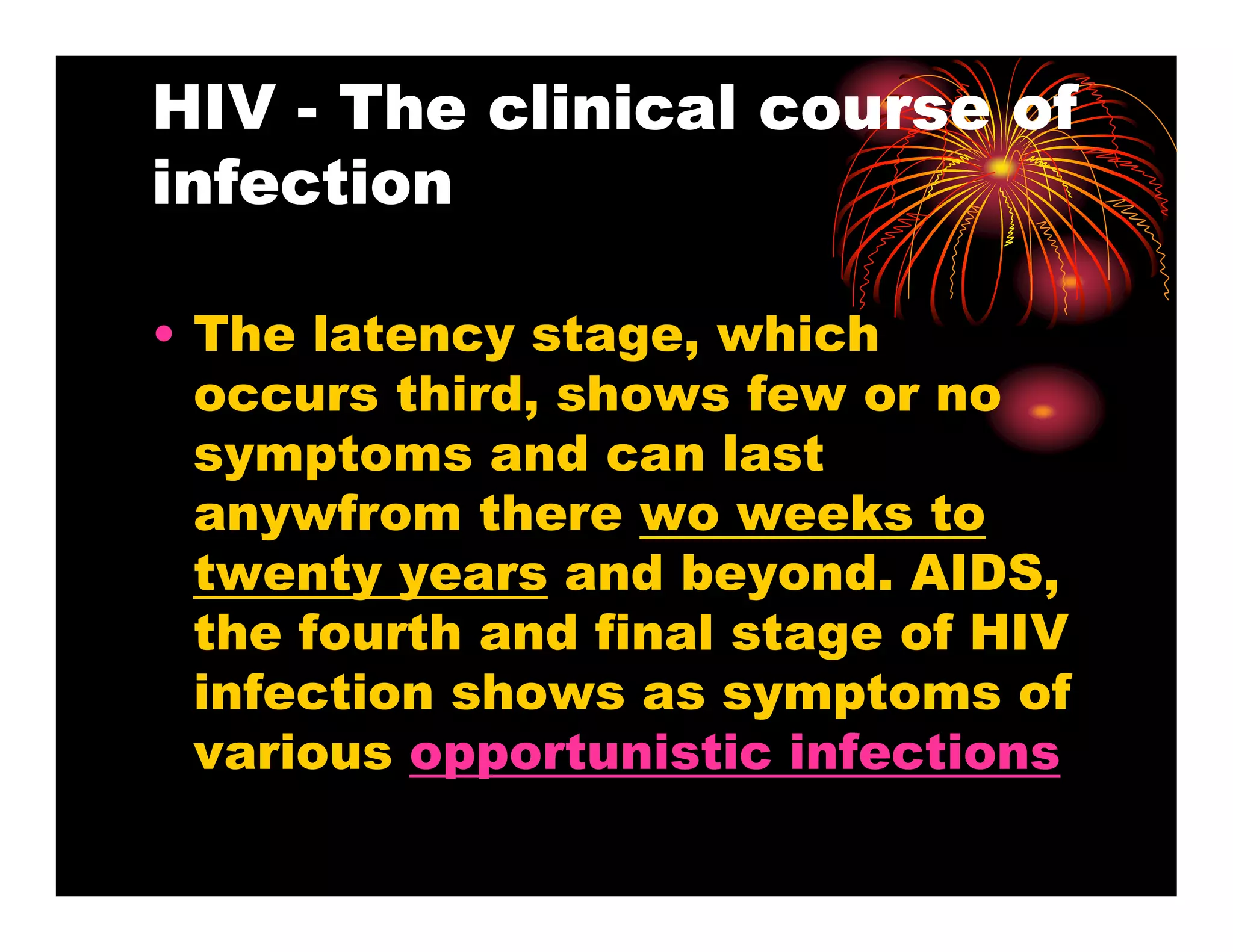



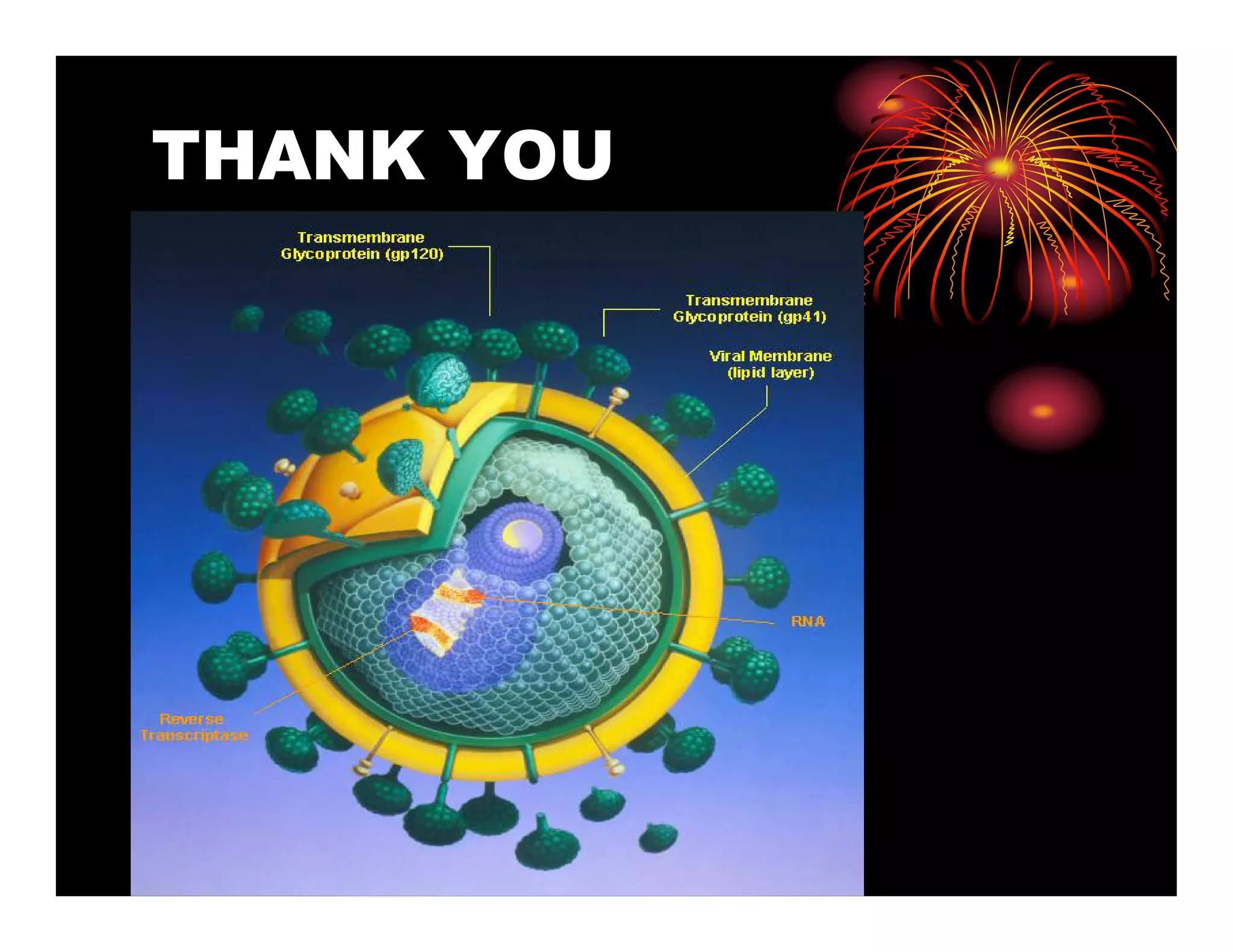
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). HIV primarily infects helper T cells in the immune system, which causes the immune system to fail over time. There are two types of HIV that infect humans - HIV-1, which is more prevalent and virulent, and HIV-2, which is less so. HIV is most commonly transmitted through unprotected sex, contaminated needles, or from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding. While there is no vaccine or cure for HIV/AIDS, antiretroviral treatment can effectively suppress the virus and allow those infected to live longer, healthier lives.



















