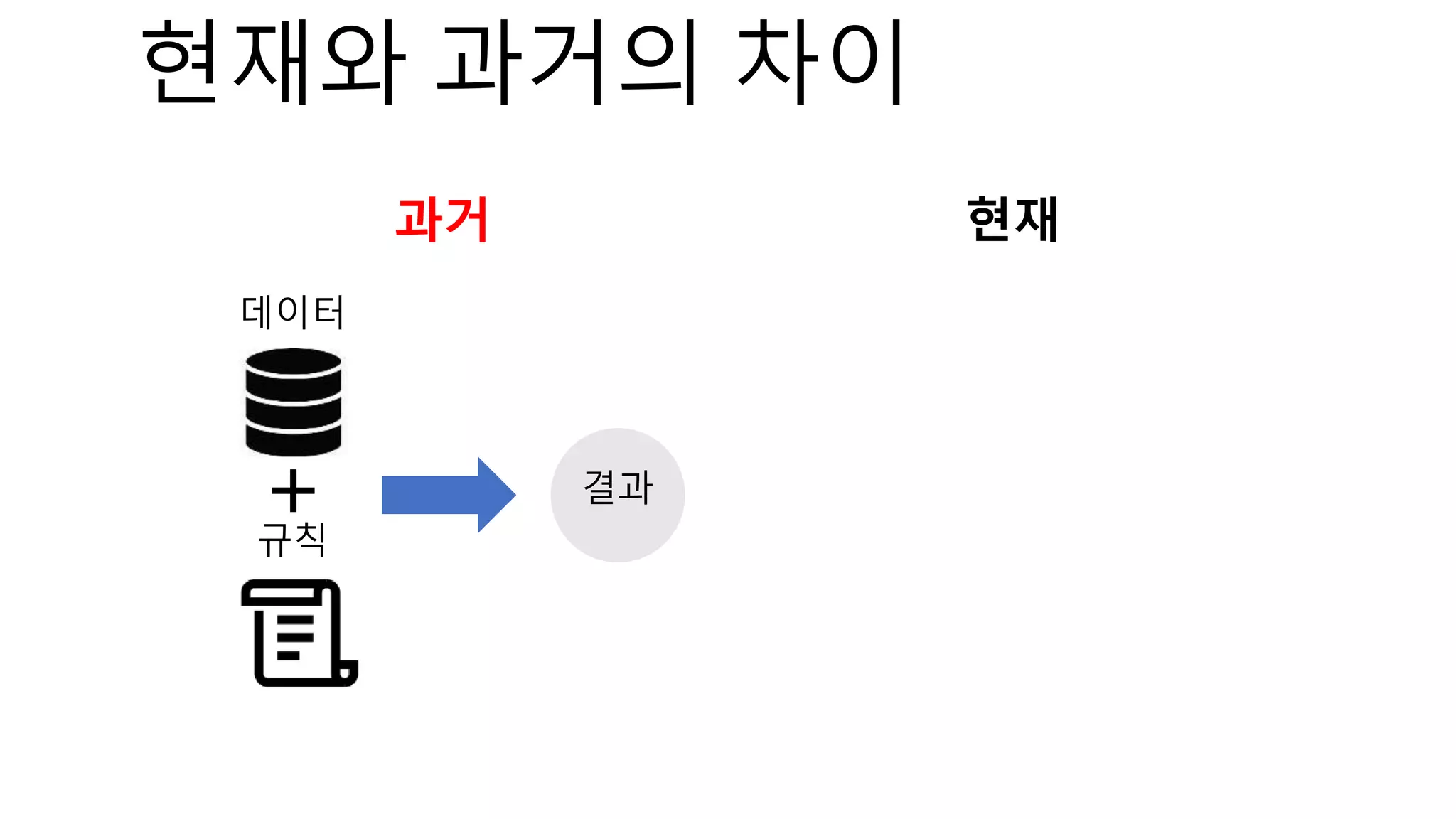
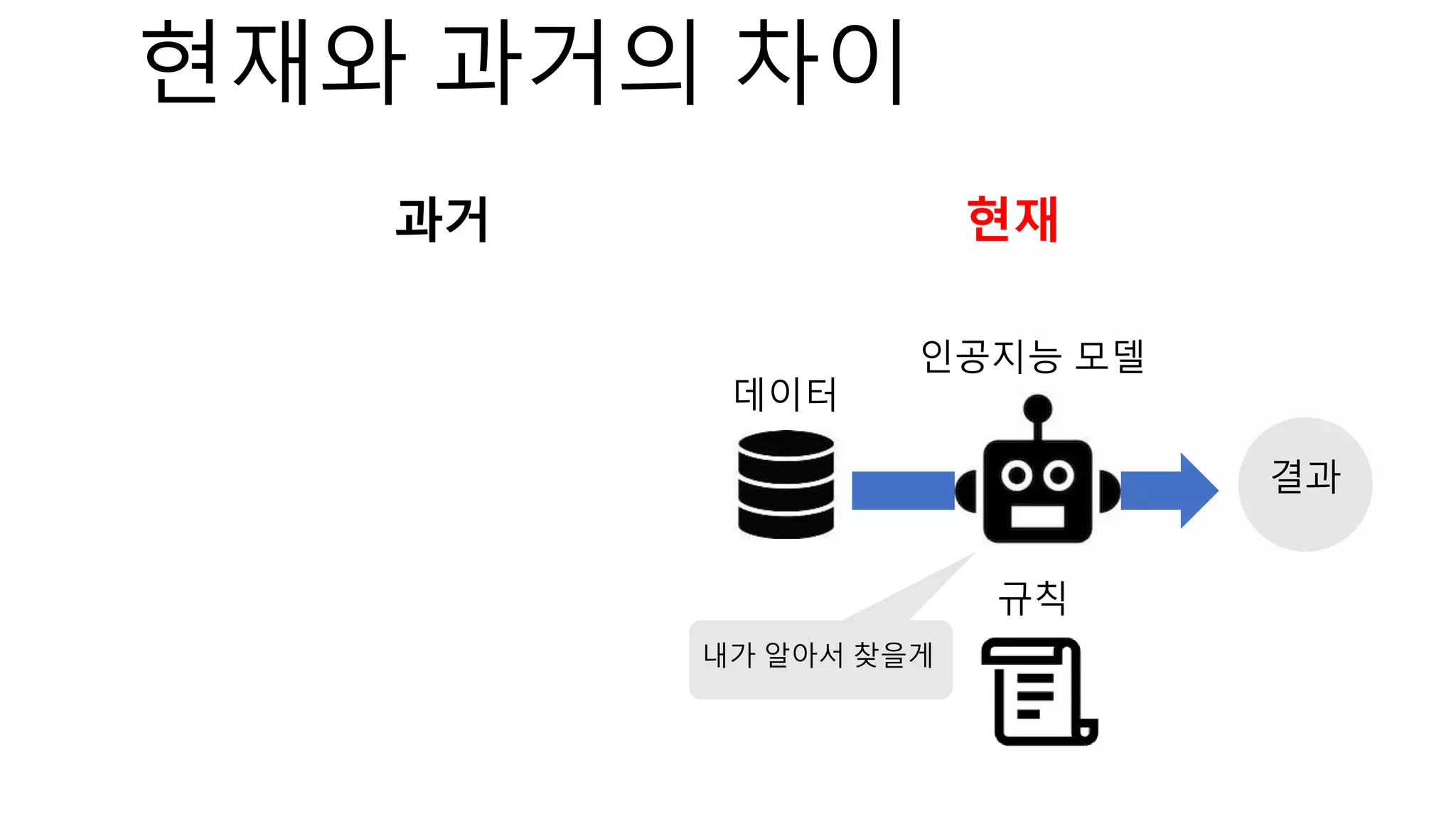
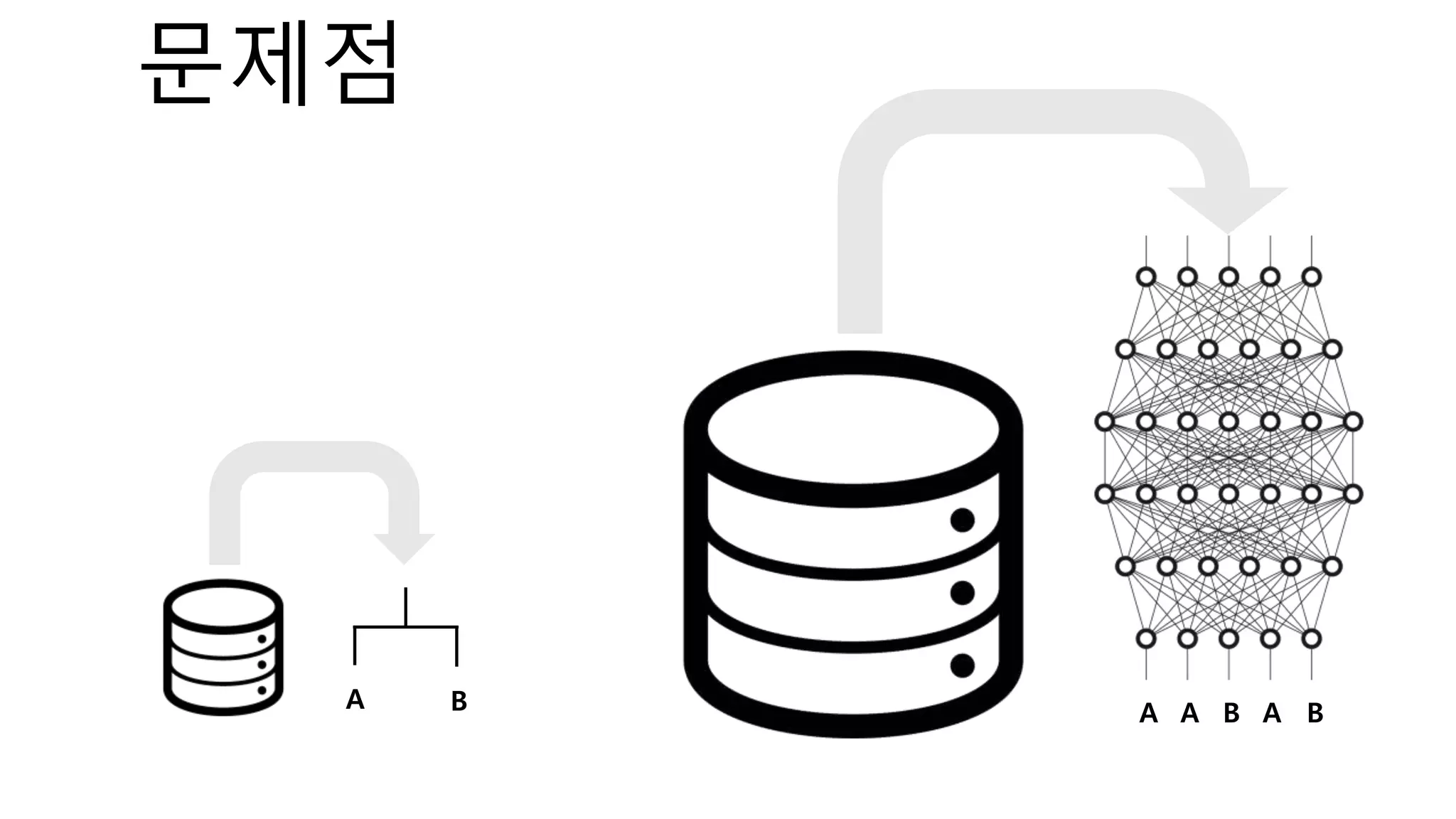
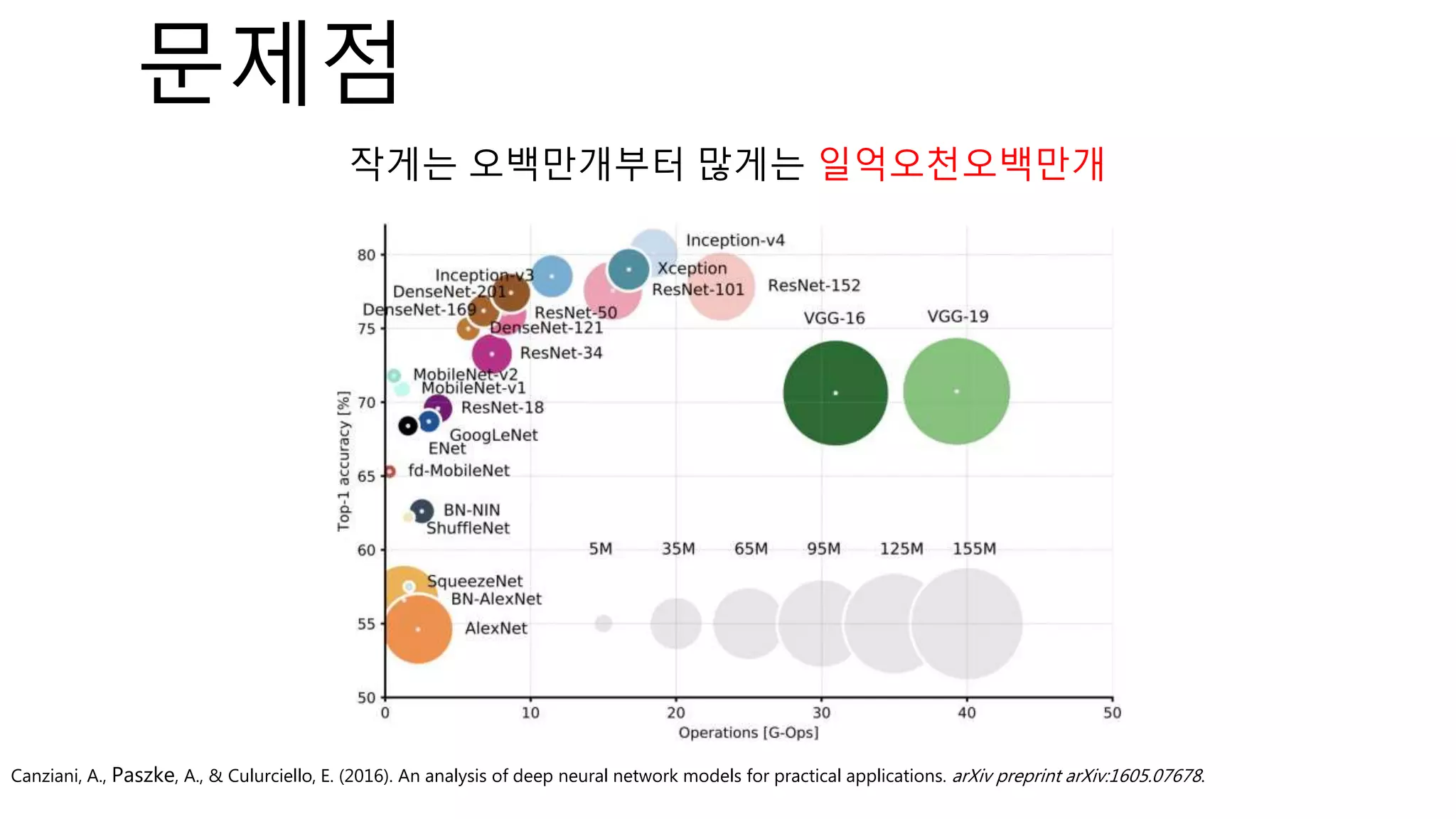
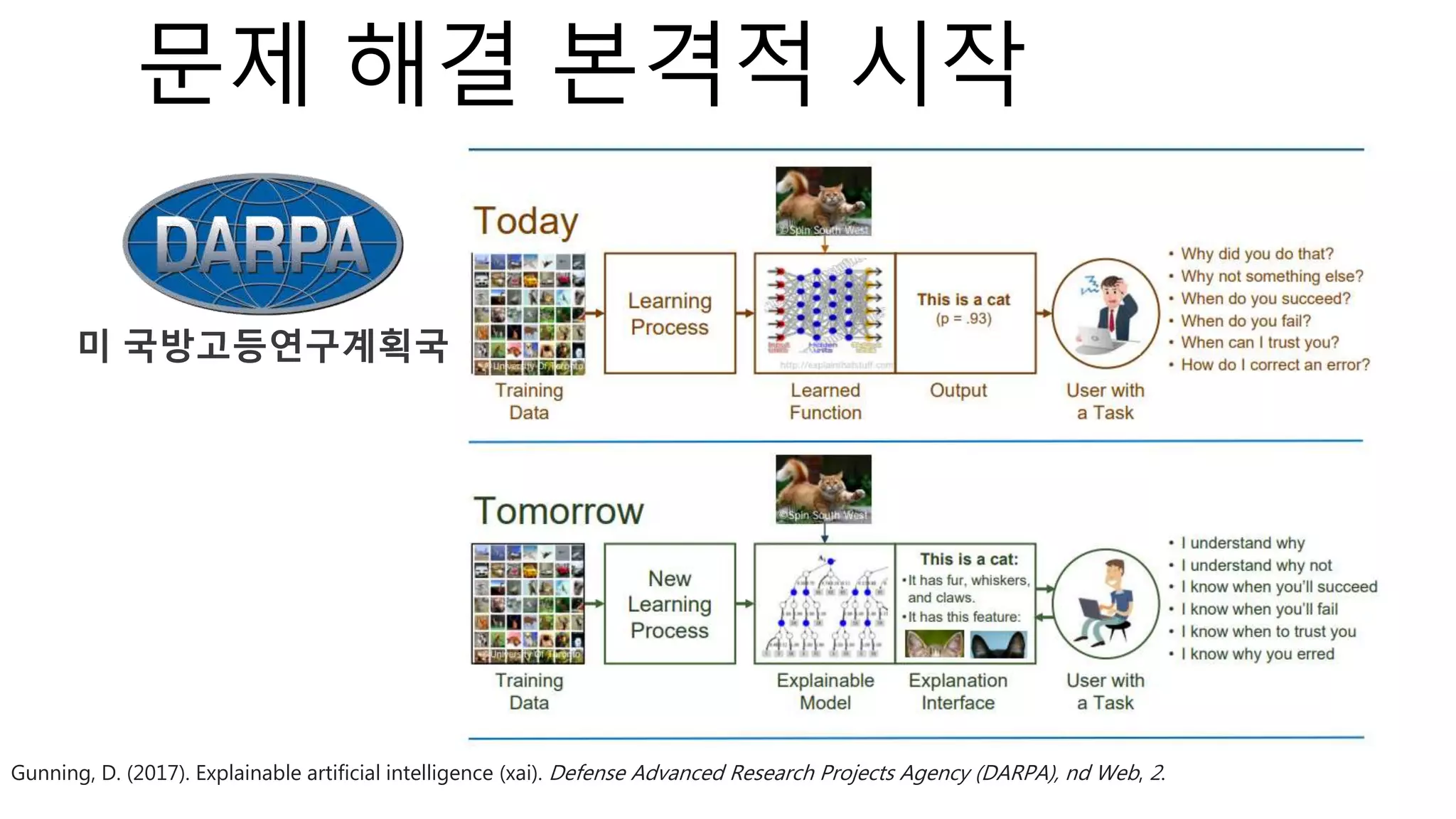
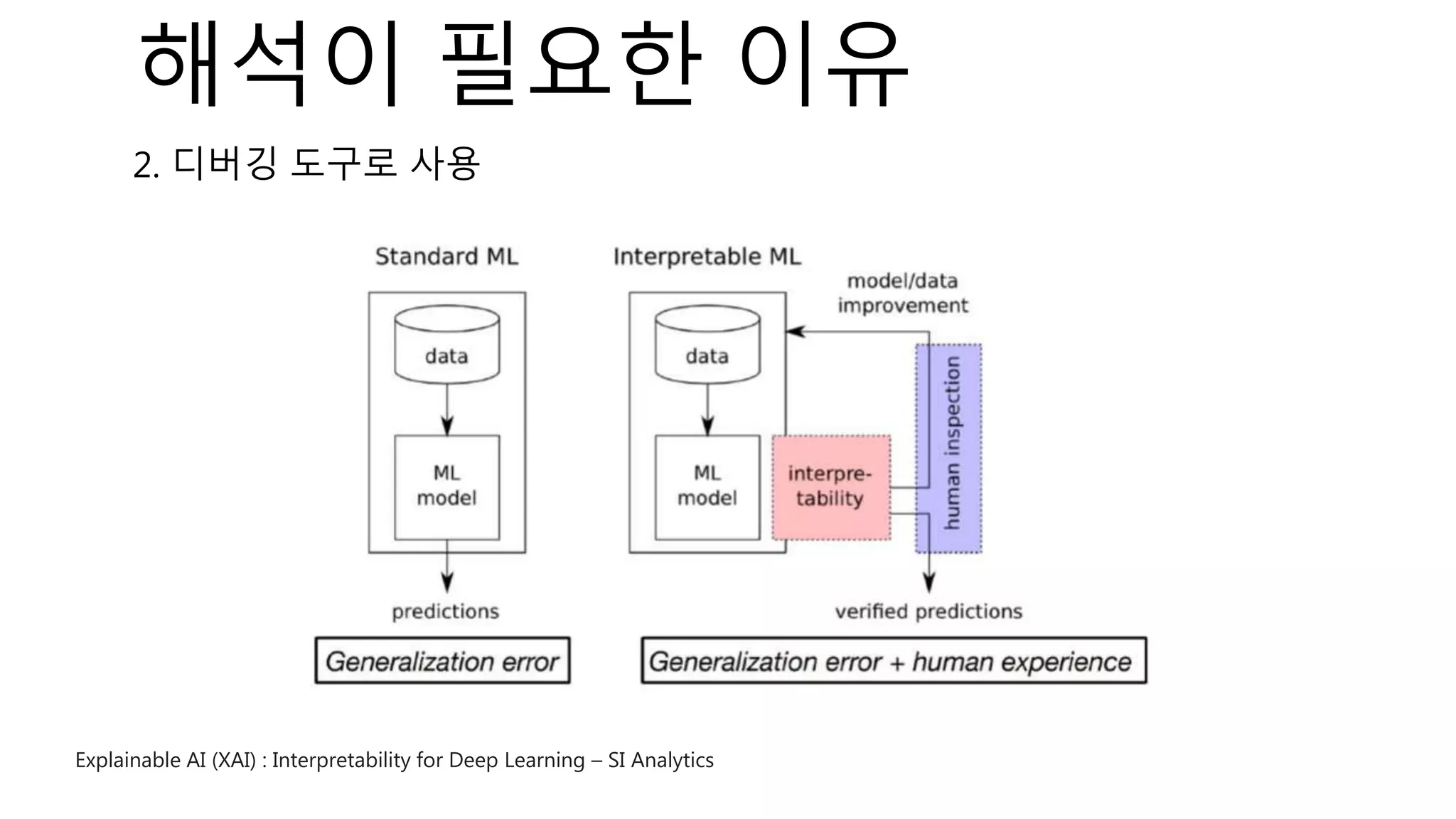
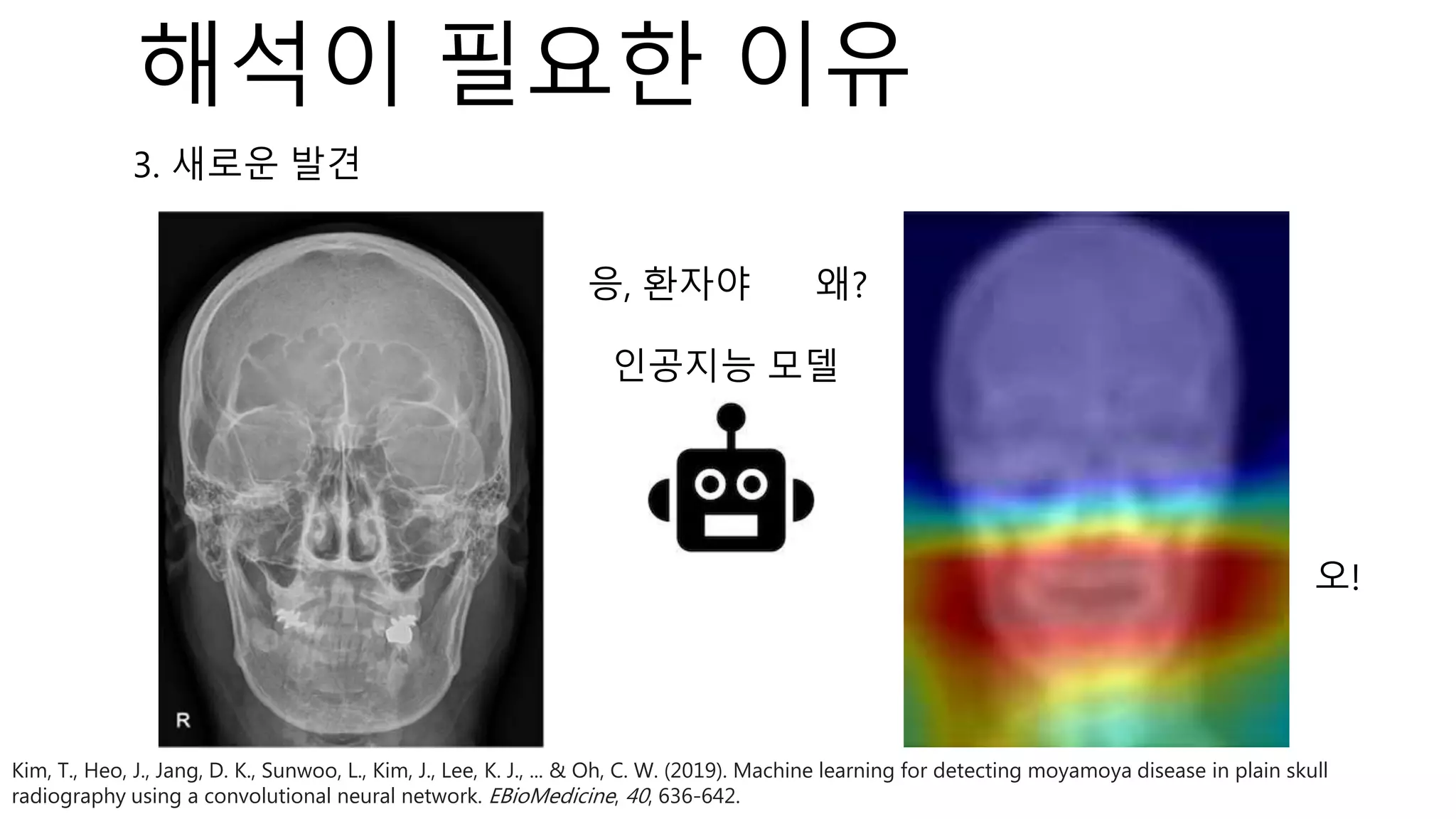
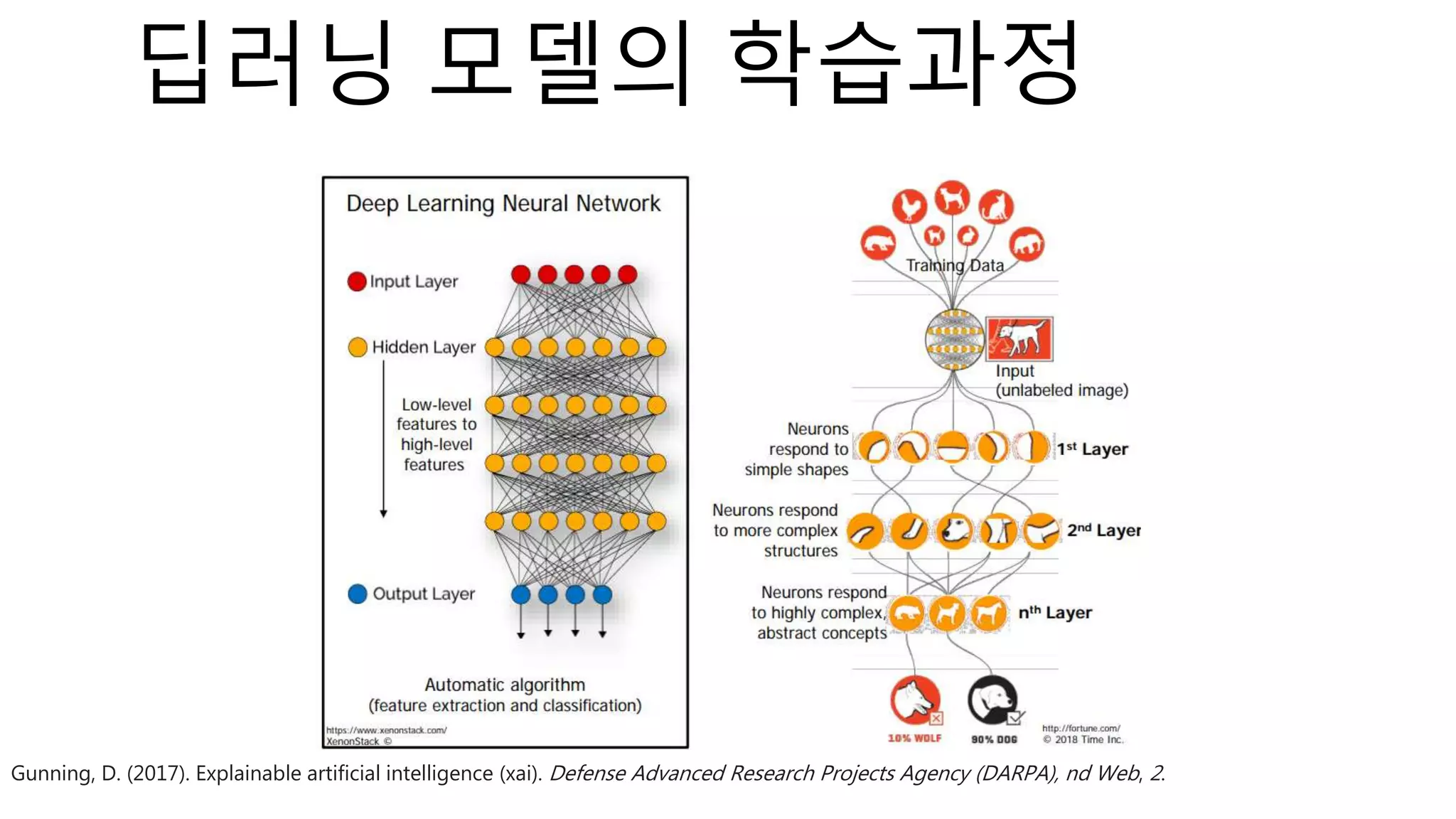
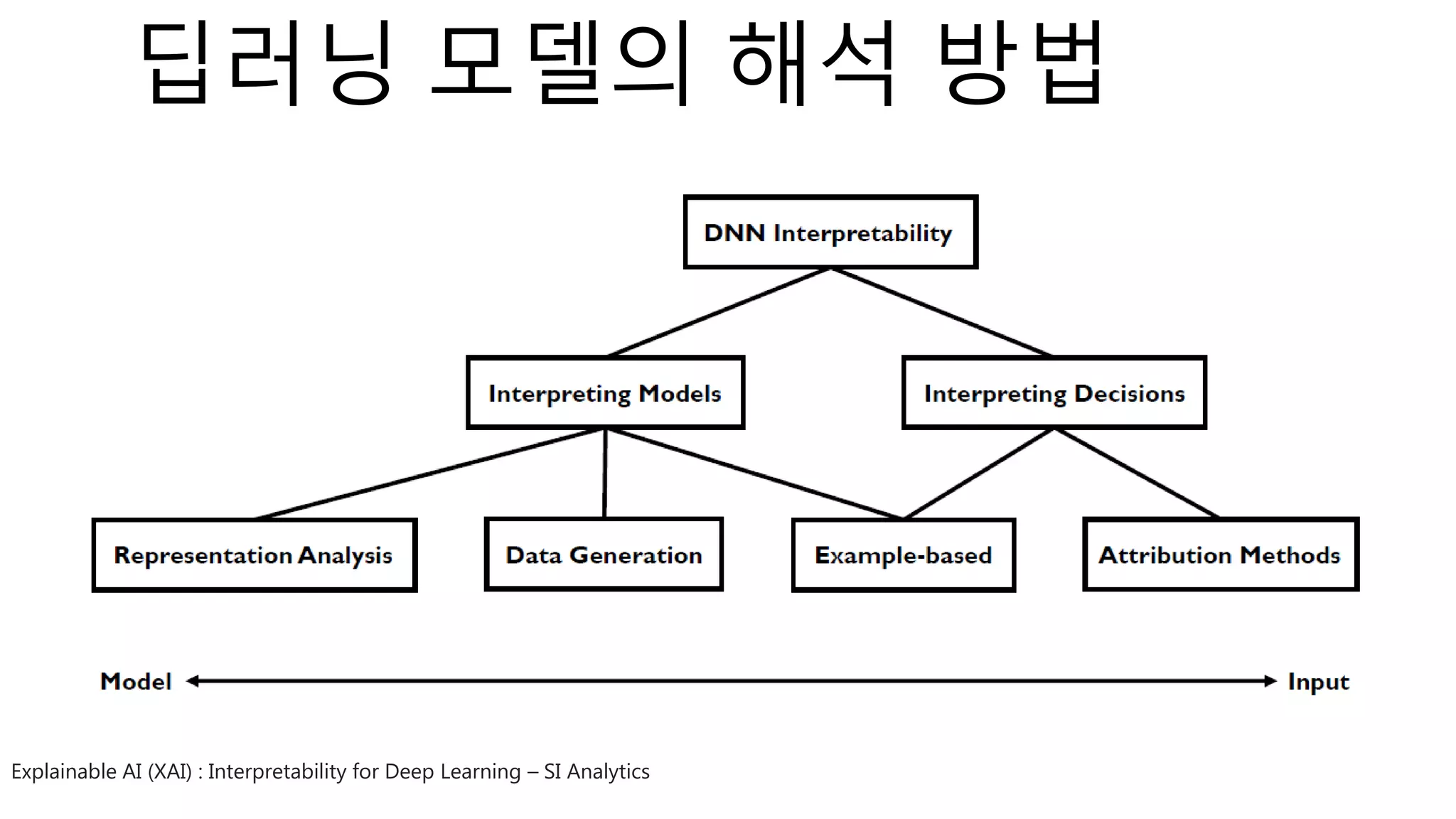
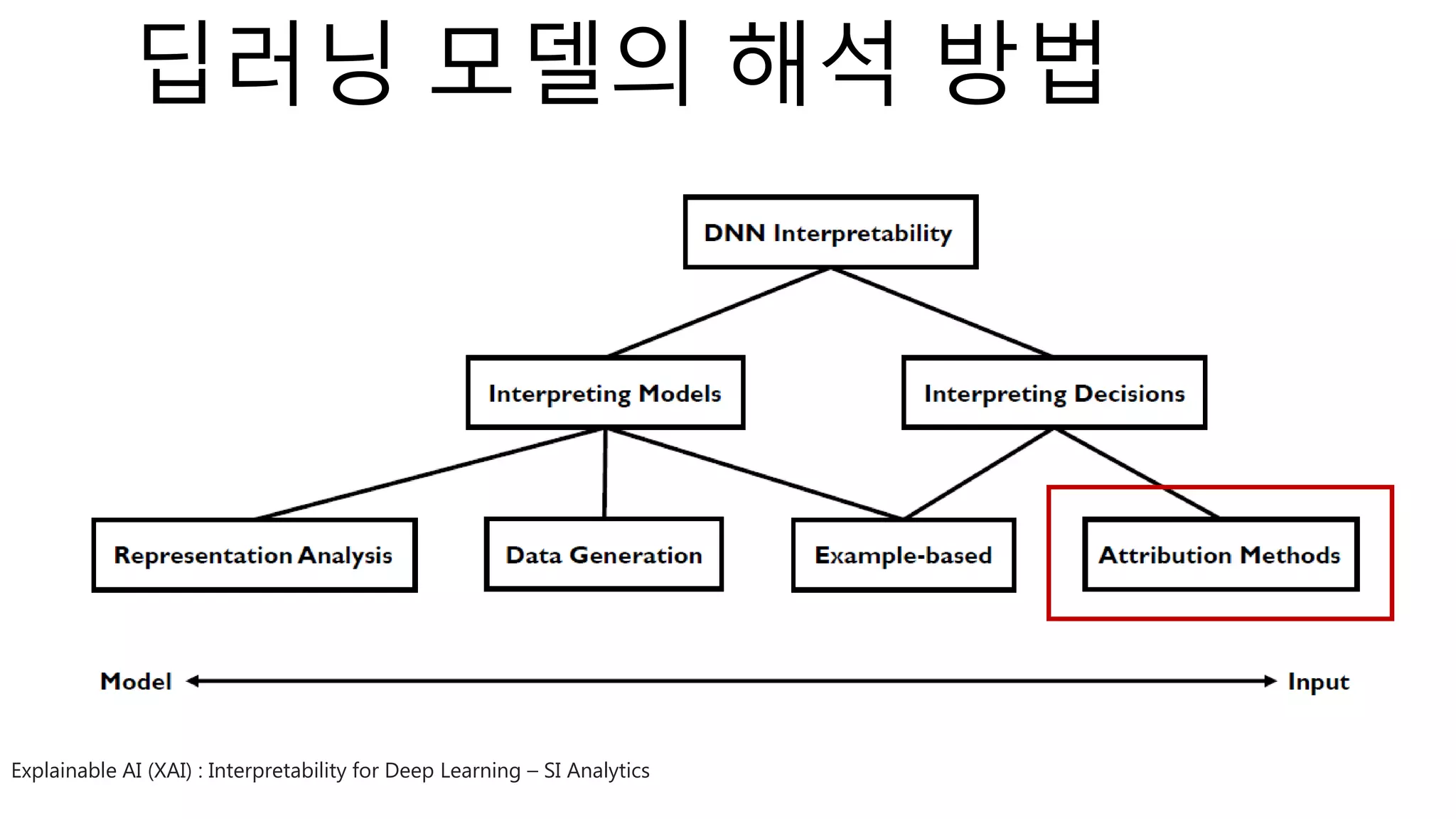
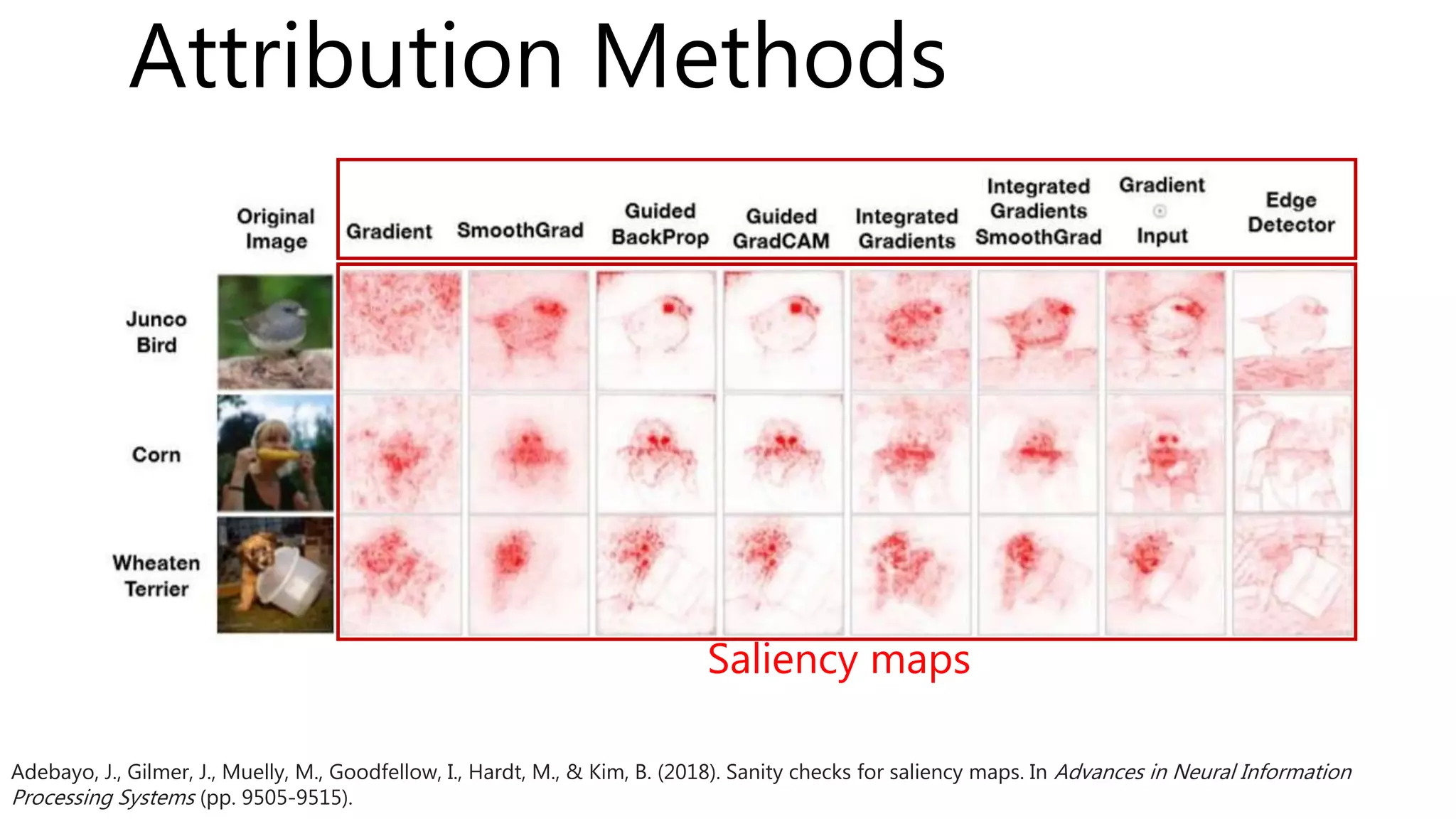
The document introduces a computer vision XAI project. It discusses implementing several attribution and attention methods on classification models for MNIST and CIFAR10 datasets, including Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), Class Activation Map (CAM), and Residual Attention Network (RAN). Over 400 training runs will be performed to evaluate the different methods on base models and retrained models with salient regions removed or kept. The project files are organized to load data, define models, and visualize saliency maps and evaluation results.




















![⁃ Dataset : 2개
⁃ Model : 1개 + 3개 (attention methods)
⁃ Attribution Method : 7개 + 2개(Random/Conv Output) + 3개(ensembles)
⁃ ROAR / KAR [ratio 0.1~0.9] : 9번 x 2
우리집 전기세,,,
그래픽카드 주데요,,,
학습계획
모델을 학습해야하는 횟수
( (1 x 9 x 18) + (3 x 1 x 18) + 4 ) x 2 =
Base Model
Attribution
Methods
Attention
Methods
ROAR/KAR Models
Datasets
440번](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whiteboxprv5-200210152225/75/White-box-in-Computer-Vision-48-2048.jpg)


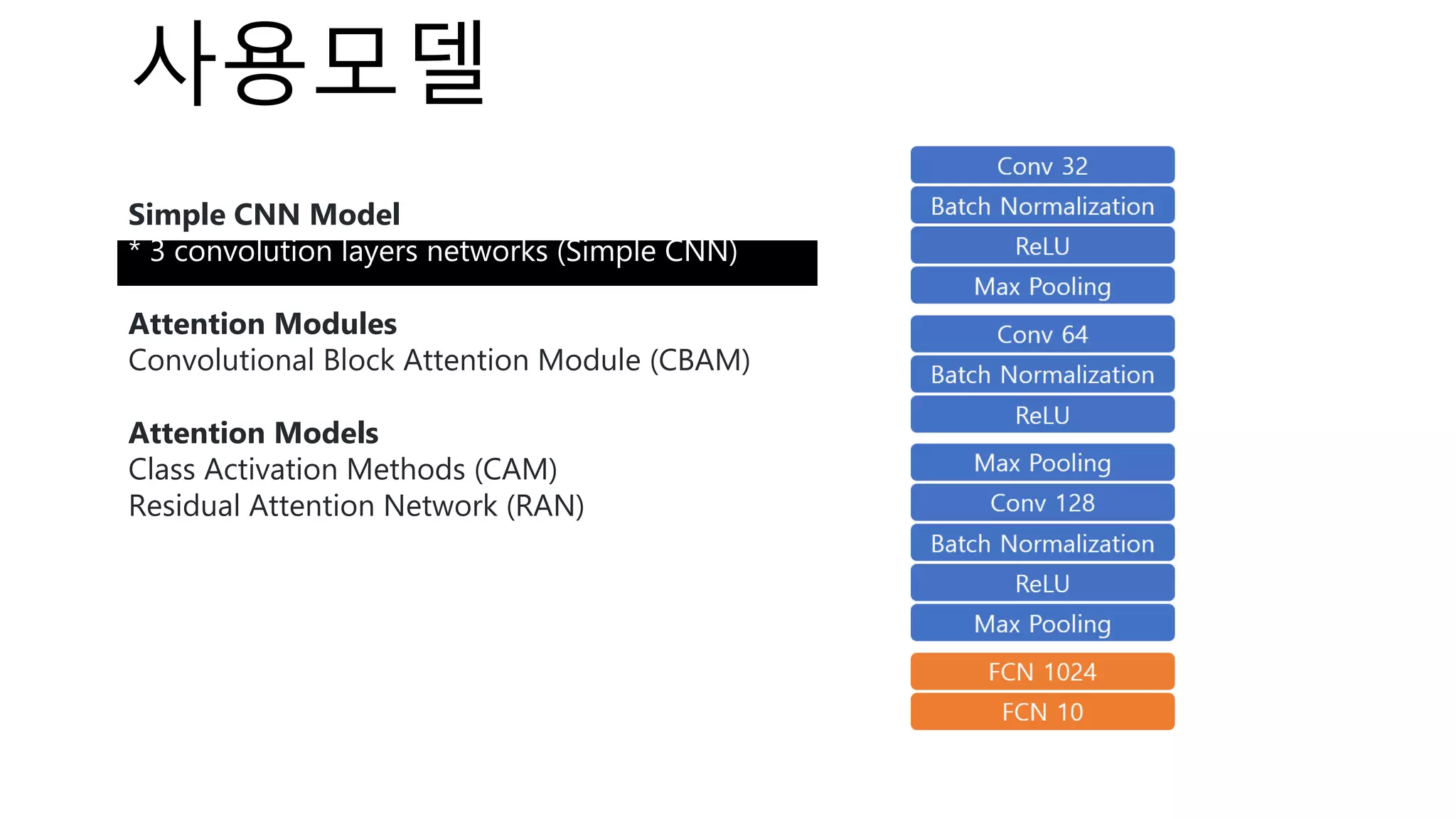
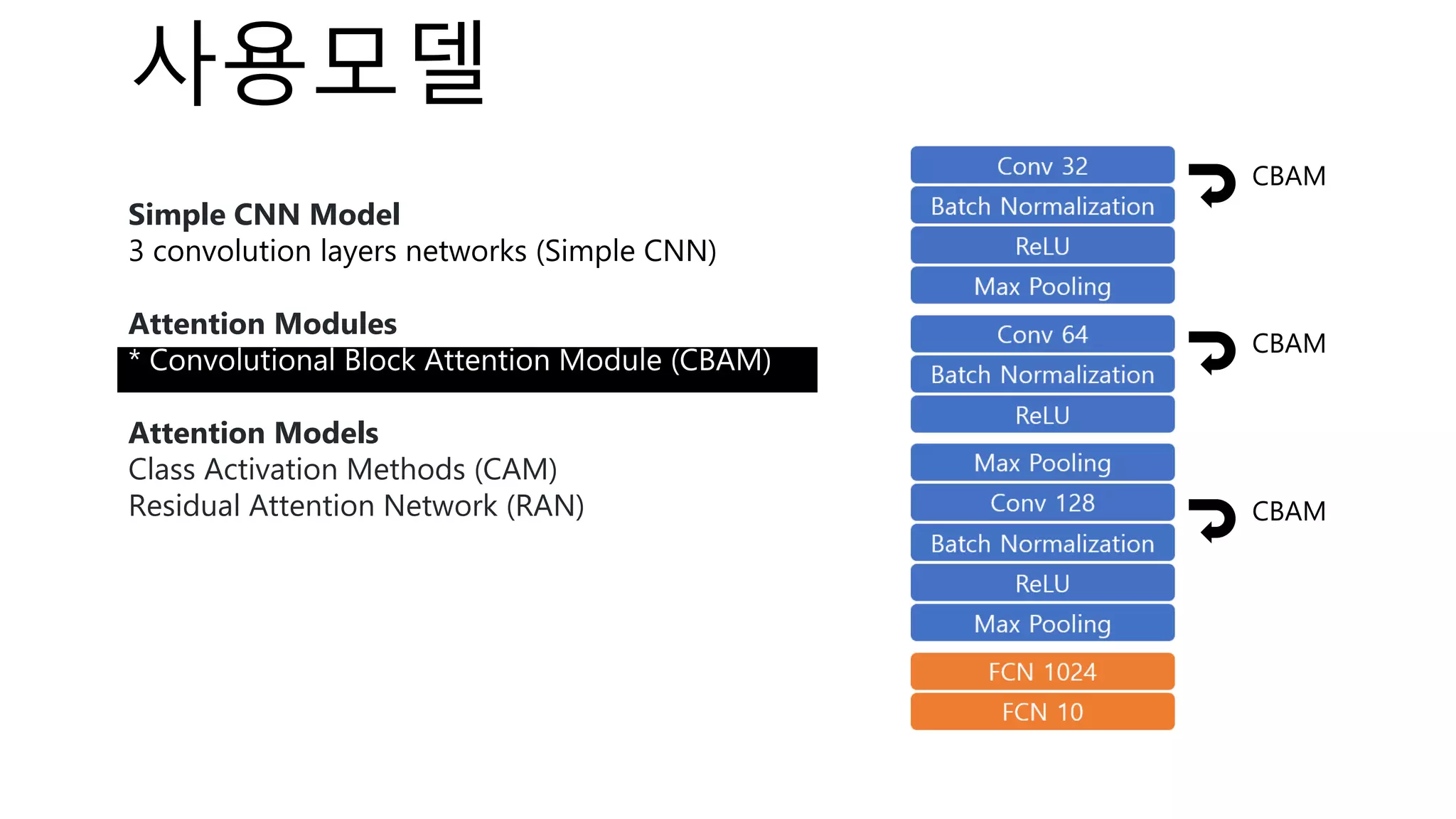
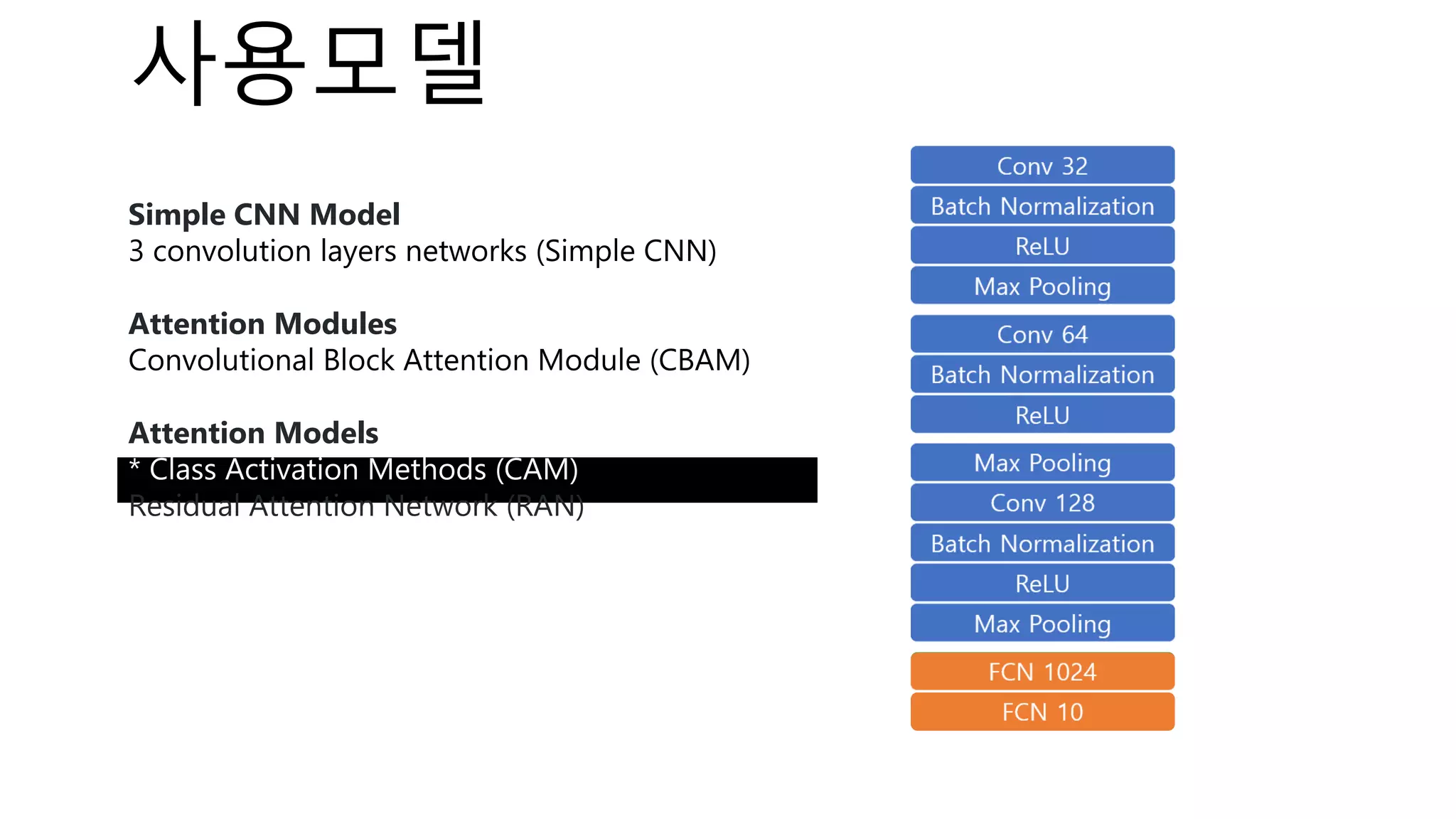
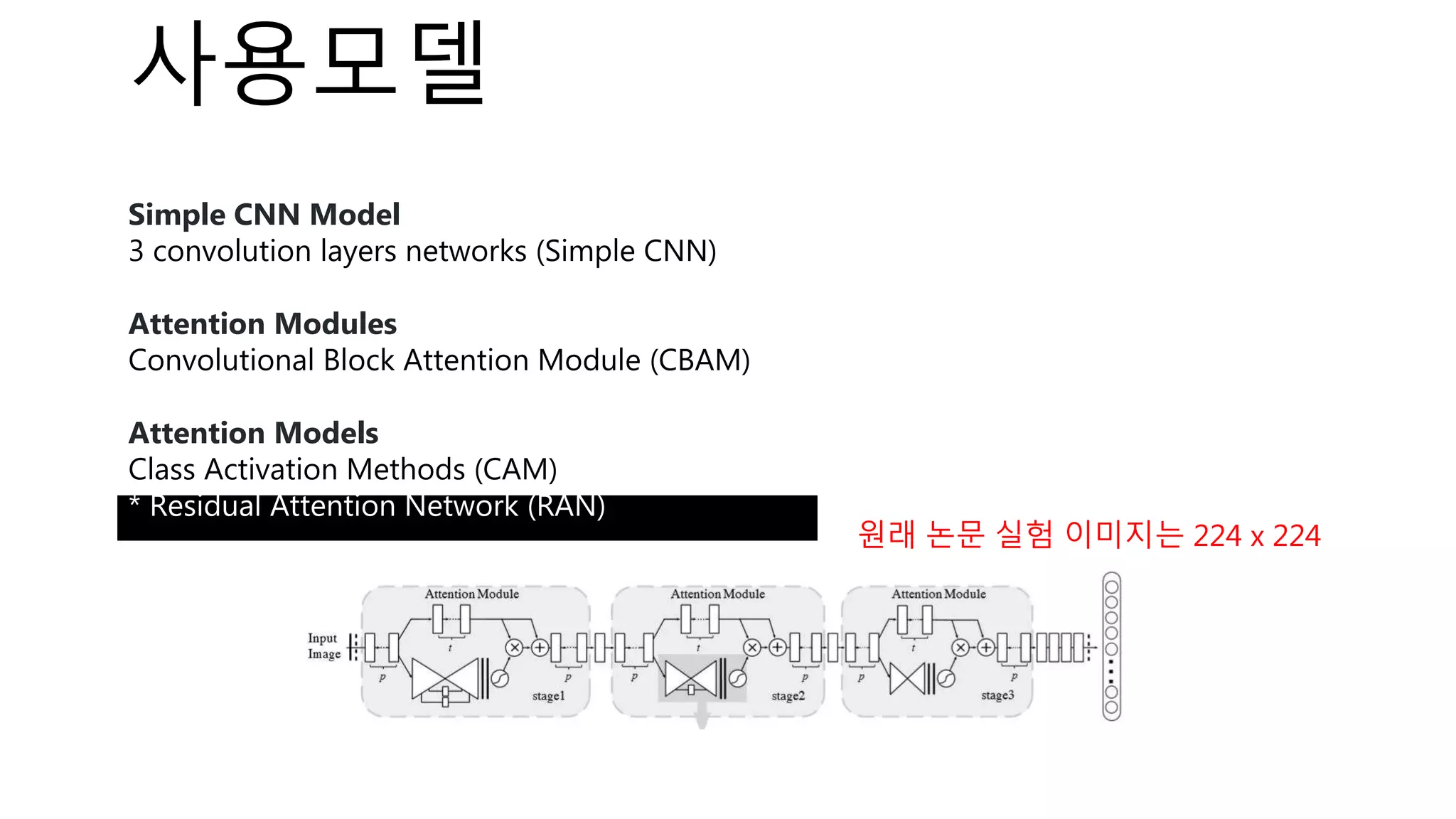
![파라미터설정
Details
- Epochs
- MNIST models train 30 epochs.
- CIFAR10 models train 100 epochs.
- Optimizer: SGD(learning rate=0.01)
- Batch size: 128
- Loss function: cross entropy
python main.py --train --target=['mnist','cifar10'] --attention=['CAM','CBAM','RAN','WARN']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whiteboxprv5-200210152225/75/White-box-in-Computer-Vision-56-2048.jpg)

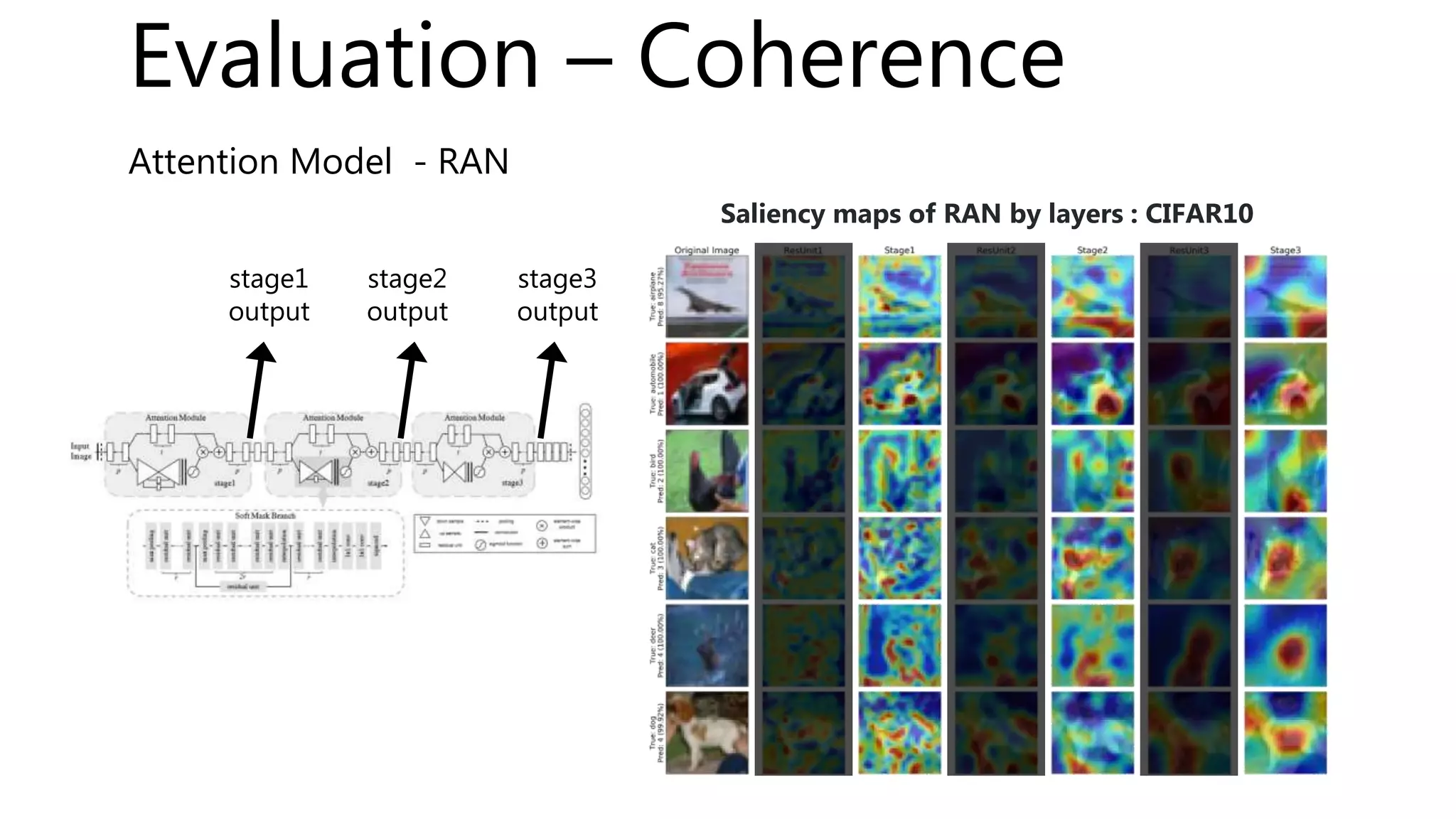
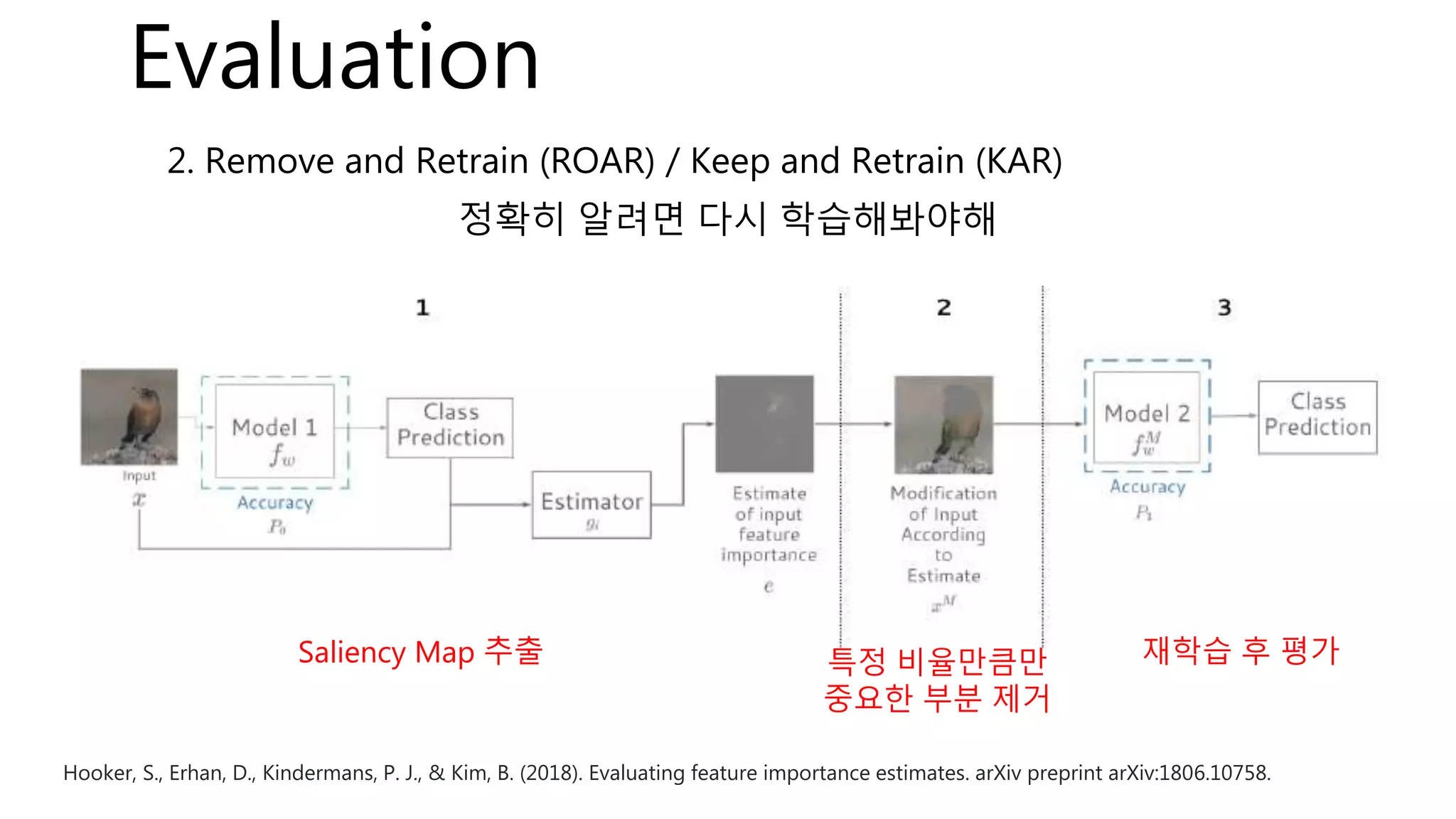
![Evaluation – Selectivity
* iteration : 50
python main.py --eval=selectivity --target=['mnist','cifar10'] --method=['VGB','IB','DeconvNet','IG','GB','GC','GBGC']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whiteboxprv5-200210152225/75/White-box-in-Computer-Vision-63-2048.jpg)
![Evaluation – ROAR / KAR
python main.py --eval=['ROAR','KAR'] --target=['mnist','cifar10’] –attention=[‘CAM’,’CBAM’,’RAN’,’WARN’]
--method=['VGB','IB','DeconvNet','IG','GB','GC','GBGC’,’CO’,’RANDOM’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whiteboxprv5-200210152225/75/White-box-in-Computer-Vision-64-2048.jpg)

