Alfred Wegener first proposed the theory of continental drift in 1915, hypothesizing that 200 million years ago the continents were joined together in a supercontinent called Pangaea. Pangaea began breaking apart in the late Triassic period, forming the continents of Gondwanaland and Laurasia separated by the Tethys Sea. By the end of the Cretaceous period the continents had separated into their modern positions. Wegener published his theory of continental drift and the existence of Pangaea in his 1915 book.













































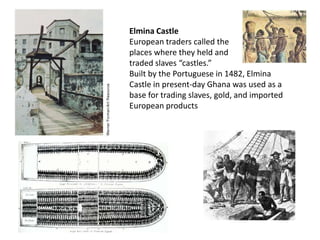


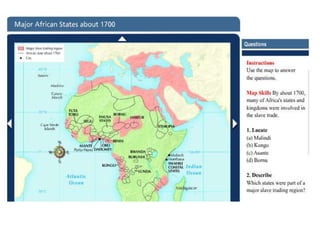

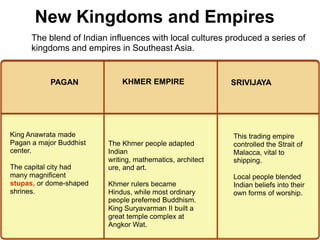
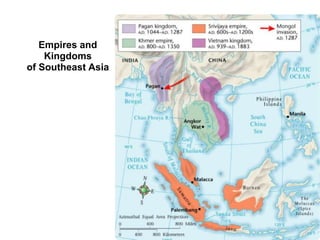


![In 1511, a Portuguese fleet
commanded by Afonso de Albuquerque
dropped anchor off Malacca, a rich
Islamic trading port that controlled the
sea route linking India, Southeast a Portuguese rifle
Asia, and China. The fleet remained at
anchor for several weeks before
opening fire. According to a Malaysian
account:
“The cannon balls came like rain. And
the noise of the cannon was as the
noise of thunder in the heavens and the
flashes of fire of their guns were like
flashes of lightning in the sky: and the
noise of their matchlocks [guns] was
like that of groundnuts [peanuts]
popping in the frying pan.”
—From the Malay Annals
Commander Afonso de Albuquerque](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whiich3-120924092534-phpapp01/85/Whiich3-73-320.jpg)