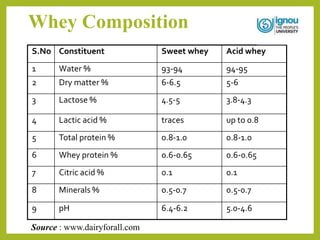
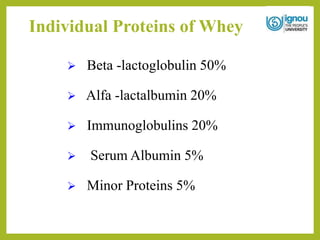
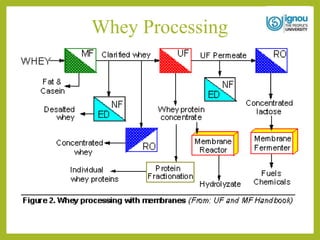
This document discusses the utilization of whey. It begins with an introduction to whey, describing it as a byproduct of cheese production that contains around half the total solids of milk. It then covers the composition of whey, current trends in its global utilization, and its various nutritional and health benefits. The document outlines different food applications of whey, including in confectionery, beverages, bakery products, infant foods, and sports nutrition. It also discusses industrial uses like whey protein concentrates and isolates. In conclusion, the document emphasizes that whey is nutritious and can be utilized in many value-added food products to reduce environmental pollution.