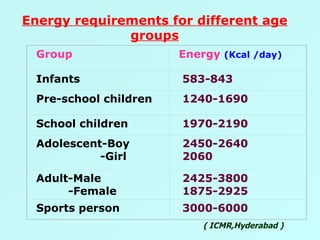
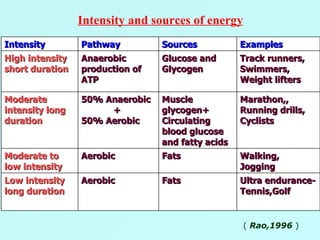
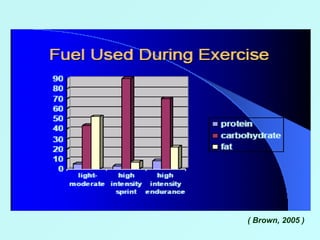
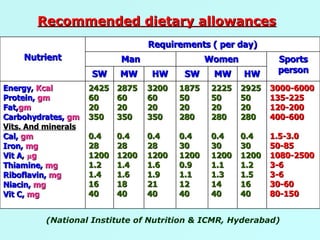
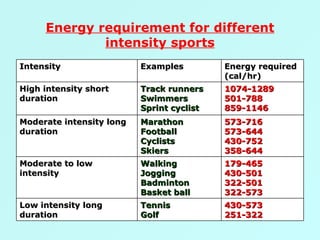
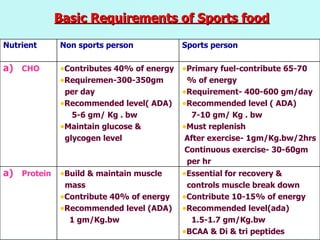
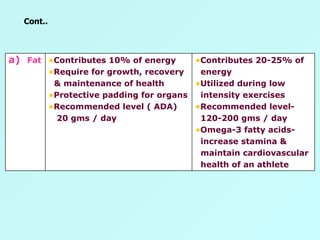
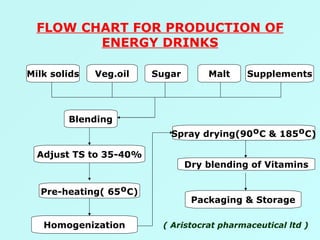
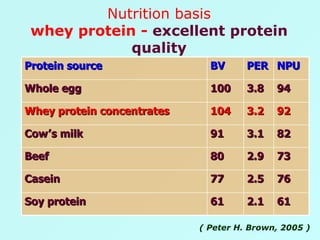
The document discusses sports food and nutrition requirements for athletes. It covers the basics of sports nutrition including macronutrients, micronutrients, hydration, and classifications of sports foods such as sports drinks, energy drinks, and milk products. Recommendations are provided on food intake before, during, and after exercise for optimal performance and recovery.