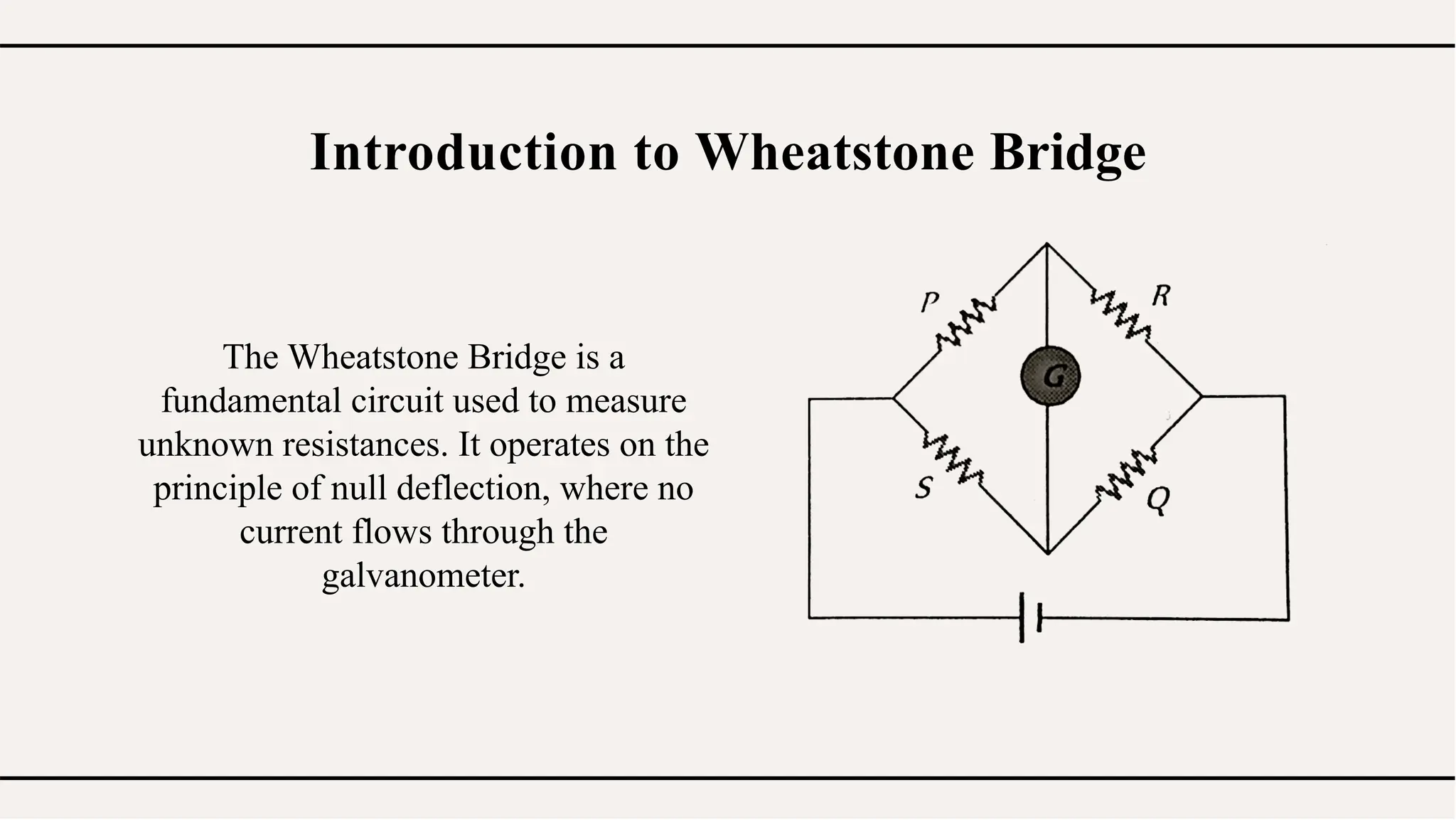
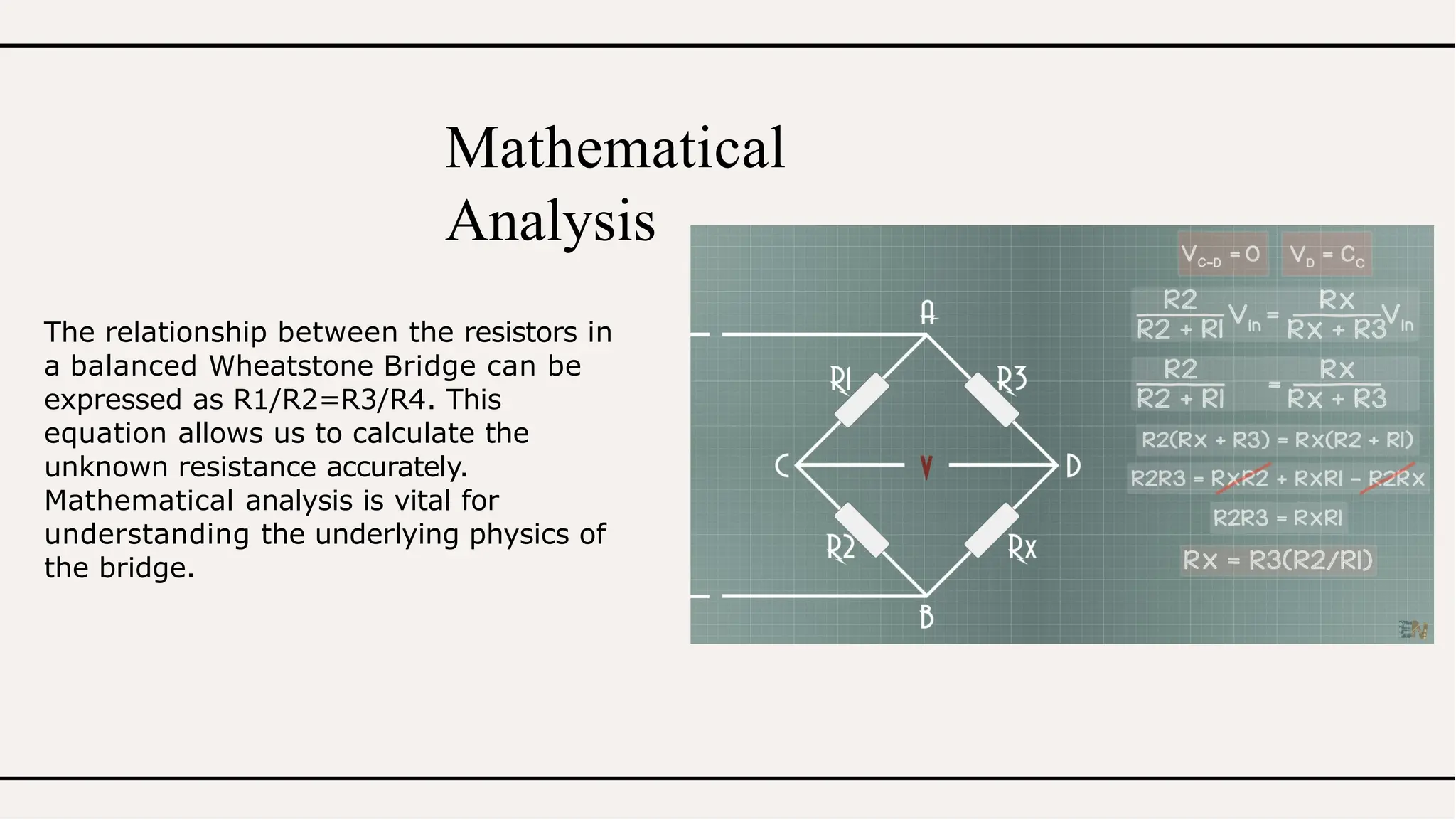
The Wheatstone bridge is a critical circuit for measuring unknown resistances based on the principle of null deflection. It operates by balancing resistors to achieve zero current across a galvanometer, allowing for precise resistance measurement while having limitations in unstable conditions and for extreme resistance values. Its applications span various fields, including strain gauges and temperature sensors, making it an essential concept in electrical engineering.