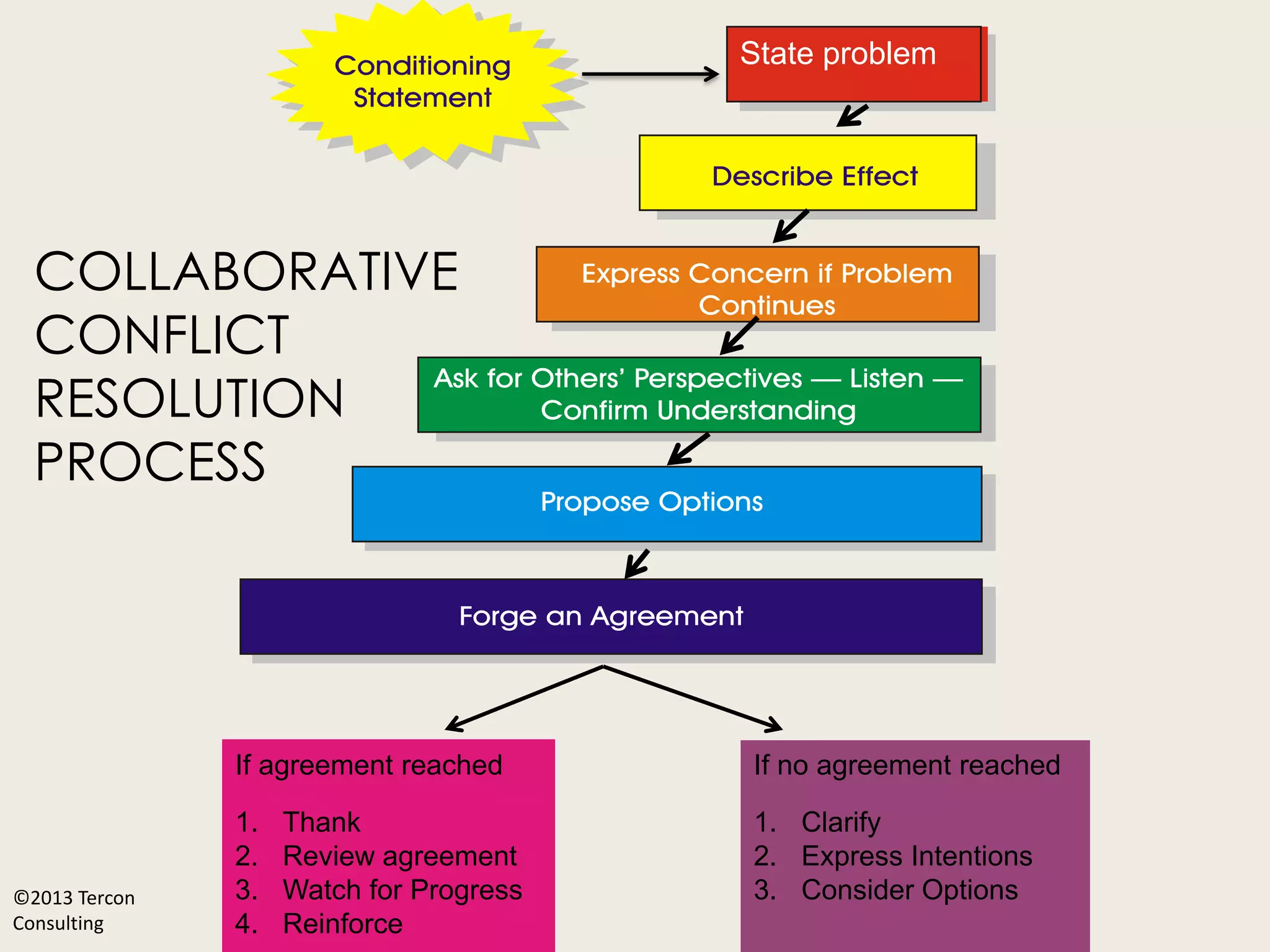
The document outlines best practices for project management, focusing on building trust and resolving conflict within teams. It includes activities aimed at understanding trust dynamics, identifying behaviors that build or erode trust, and employing a conflict resolution model. The importance of addressing unresolved conflict, its impacts, and fostering a collaborative team culture is emphasized throughout the session agenda.