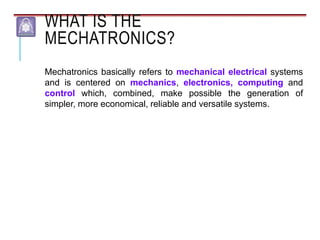
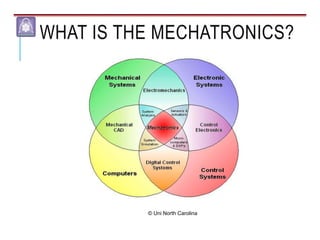
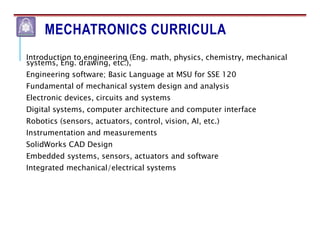
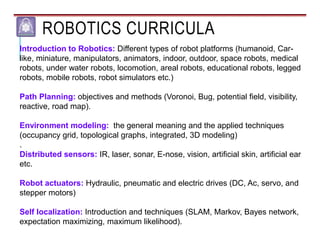
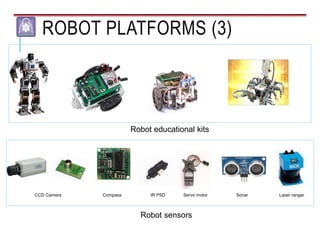
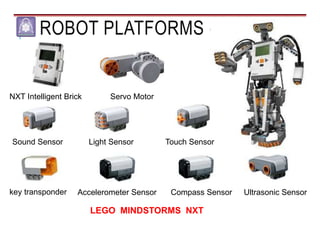
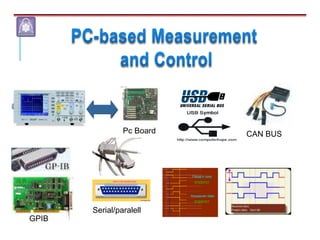
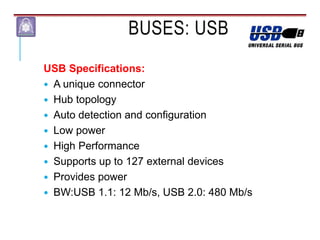
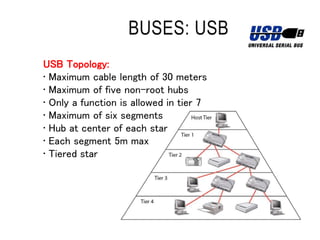
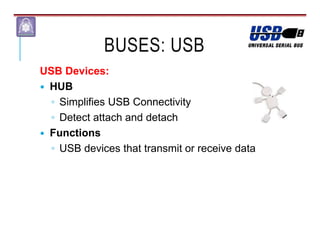
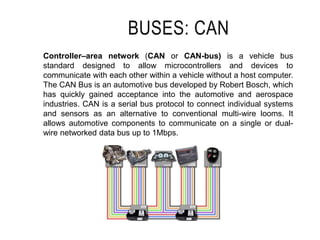
Mechatronics combines mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering to design and manufacture products. It involves integrating mechanical and electrical systems with software to create more reliable and cost-effective systems. Mechatronics curricula includes courses in engineering fundamentals, programming, electronics, robotics, and embedded systems. Labs focus on software, CAD, digital electronics, and integrating electrical and mechanical components. The field draws on disciplines like controls, robotics, automation, and computer interfaces.