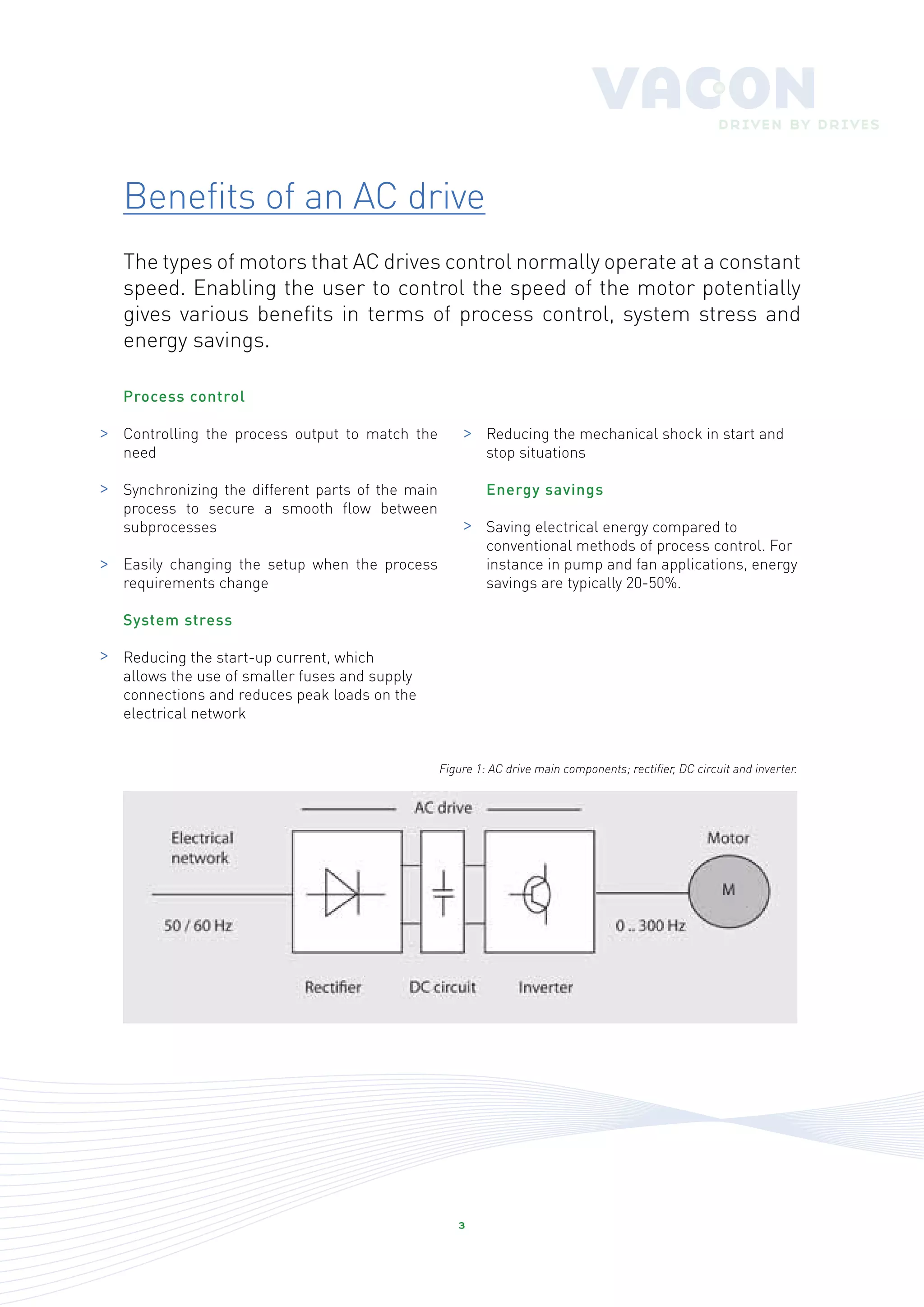
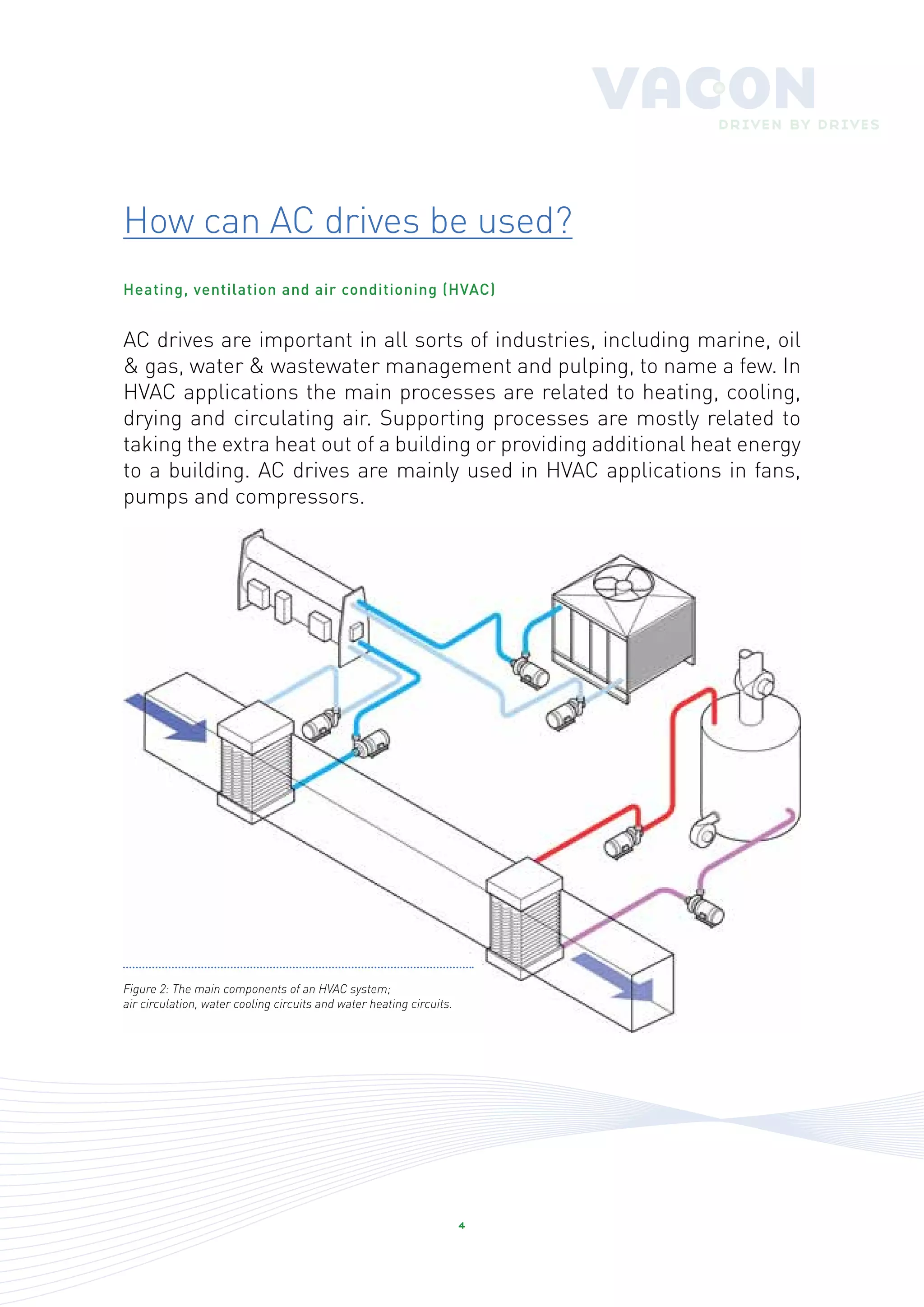
An AC drive is a device that controls the speed of an electrical motor by varying the frequency of the electrical supply, which allows for enhanced process control, energy savings, and reduced mechanical stress. These drives are commonly used in various industries, particularly HVAC applications, to manage the performance of fans, pumps, and compressors efficiently. With significant potential for energy savings, it is essential to consider the lifetime costs of HVAC systems, where energy expenses dominate.