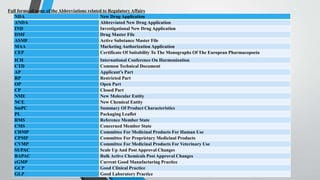
Regulatory affairs professionals act as the interface between the pharmaceutical industry and drug regulatory authorities. Their main goals are to protect human health, ensure drug safety and quality, and ensure accurate product information. Key roles include liaising with regulatory agencies, preparing regulatory submissions, and advising on regulatory requirements and guidelines. An investigational new drug (IND) application is filed with regulatory agencies to legally test an experimental drug in humans after preclinical testing. A new drug application (NDA) is filed to obtain approval to market a new drug, while an abbreviated new drug application (ANDA) is filed for generic drug approval based on demonstrating bioequivalence to an existing drug. Drug master files and active substance master files provide confidential manufacturing