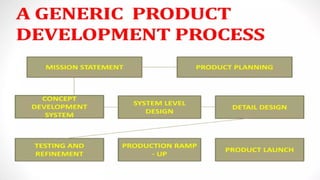
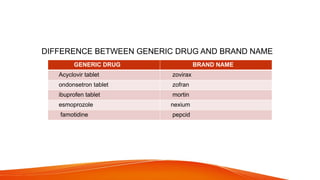
GENERIC DRUG DEVELOPMENT PROCESS, FORMULATION OF GENERIC DRUG ,STEPS OF GENERIC ,HATCH WAXMAN ACT AND AMENDMENTS , PROVISION OF ACT ,PATENT CERTIFICATES,BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF ANDA,CHEMISTRY MANUFACTURE AND CONTROLS OF ANDA,SIGNED 356H FDA ,IMPORTANCE OF ANDA,DIFFRENCE BTEWEEN BRAND NAME AND GENERIC NAME , GENERIC DEVELOPMENT PROCESS.









![PROVISION OF THE ACT
Creation of section 505 (j) ( Abbreviated new drug applicaton [ANDA] )
Selection 505(j) established the ANDA approval process
The timing of an ANDA approval depends in part on patent protection for the innovator
drug .
NDA must include any patent that claims the drug or a method of using the drug for a
claim of patent infringement could reasonably be asserted .
On approval of NDA , FDA publishes patent information of drug in orange book.
An NDA applicant was submit the information for each patent :
a) patent no and date on which patent will expire
b) Type of patent,drug product ,method of use, name of the patent owner must be specified.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genericdrugdevelopmentprocess-250430063153-b063ff64/85/GENERIC-DRUG-PRODUCT-DEVELOPMENT-PROCESS-10-320.jpg)