The document discusses several models of communication:
1. The Lasswell model describes the basic elements of communication as the sender, message, and receiver. It also identifies the key questions of who says what through which channel to whom with what effect.
2. Shannon and Weaver's mathematical model focuses on signal transmission and introduced the concept of noise. It separates noise from the transmitter and identifies the core elements of information source, transmitter, channel, receiver, and destination.
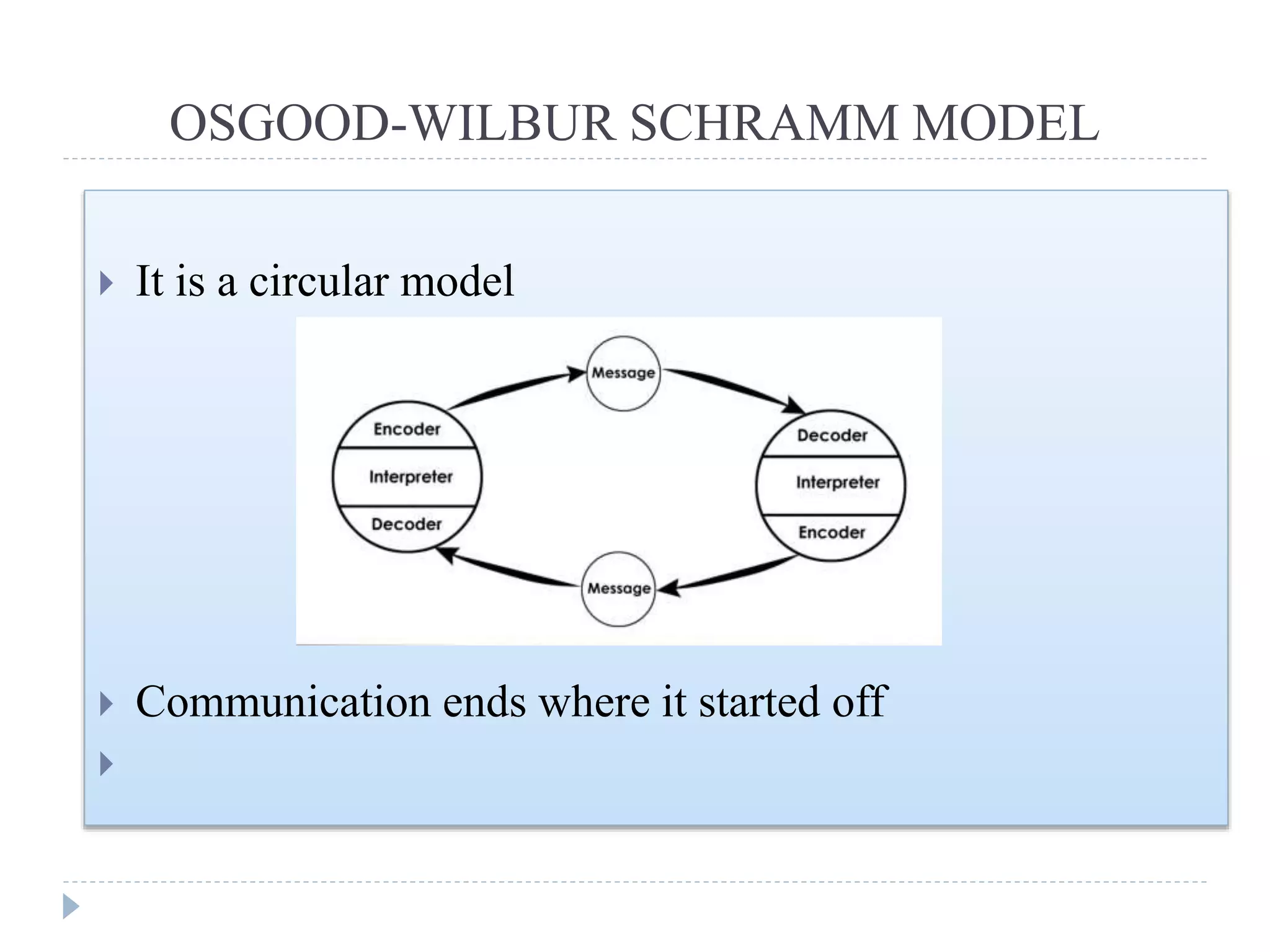
3. The Osgood-Wilbur-Schramm model presents communication as a circular process where information is shared between parties and ends where it started. It introduces the concept of semantic noise that can occur when different meanings are assigned to the same