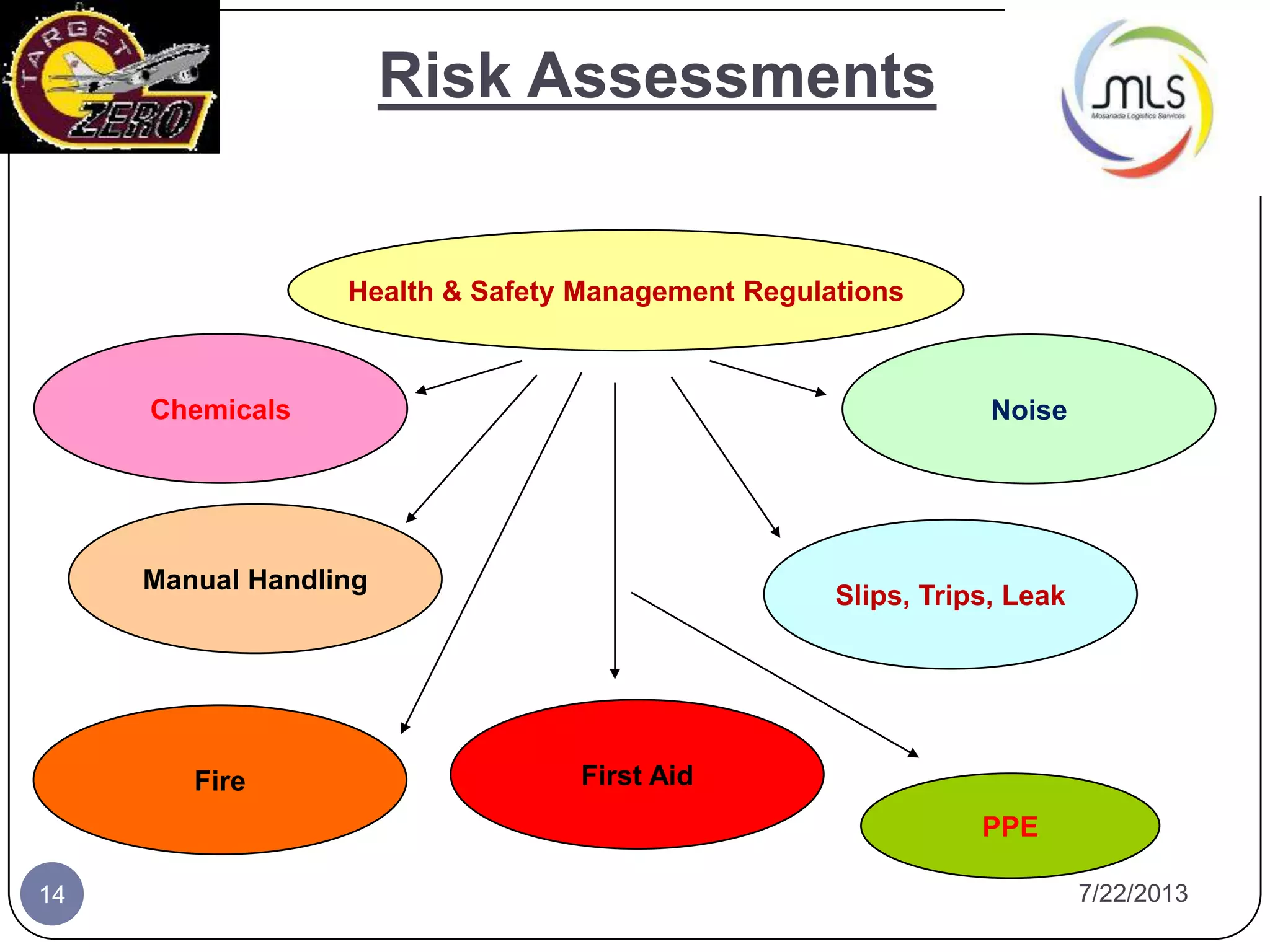
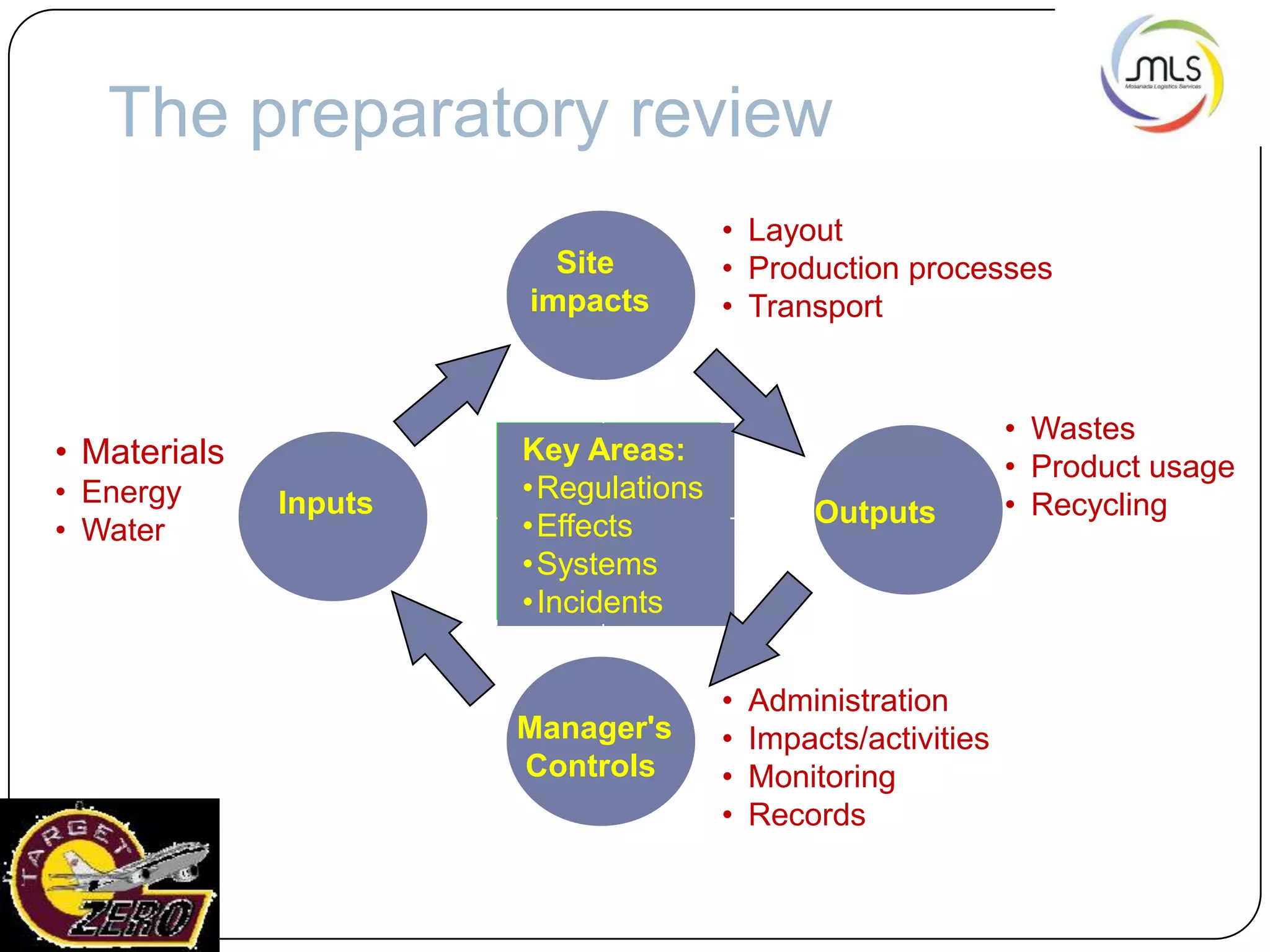
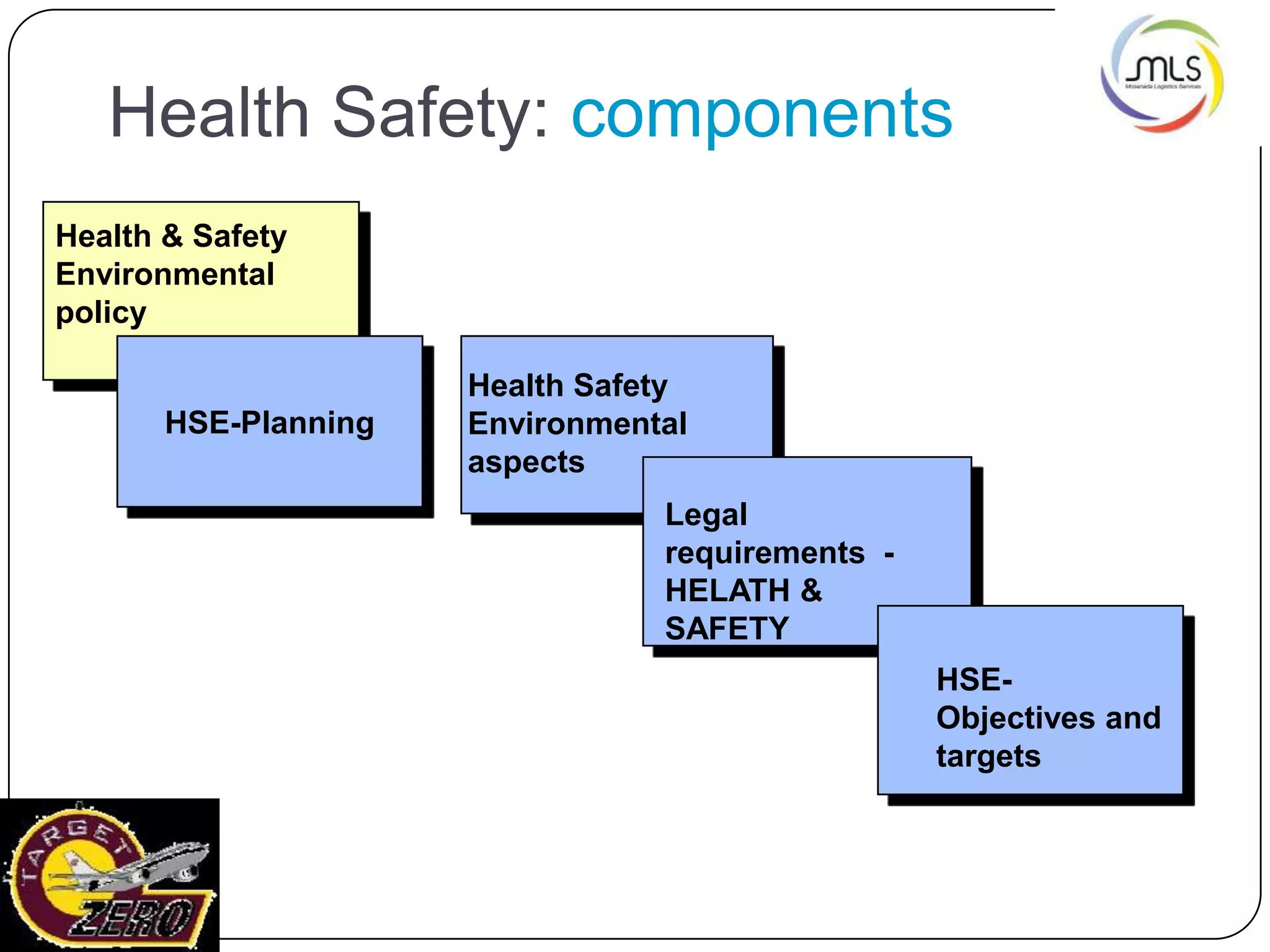
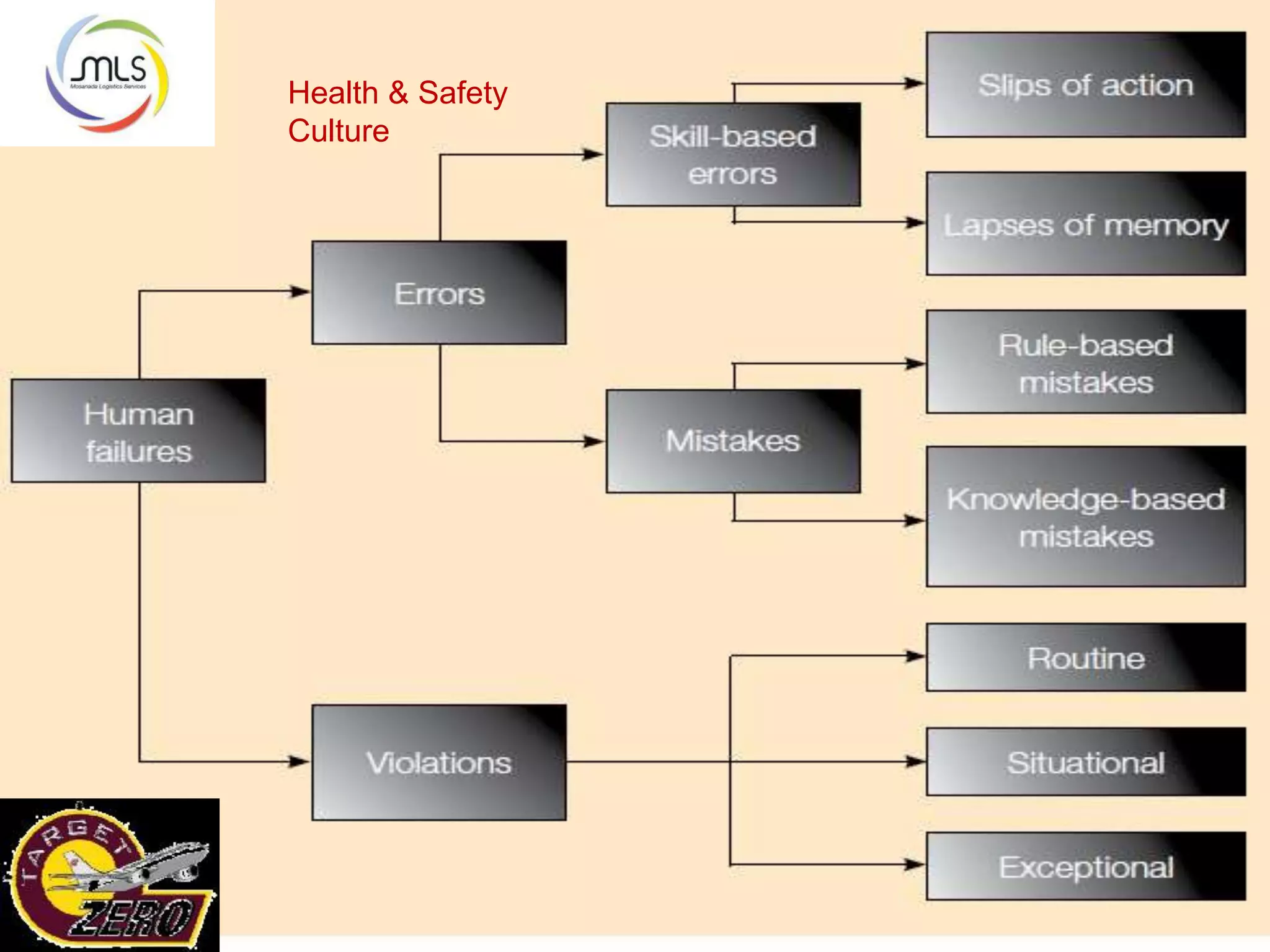
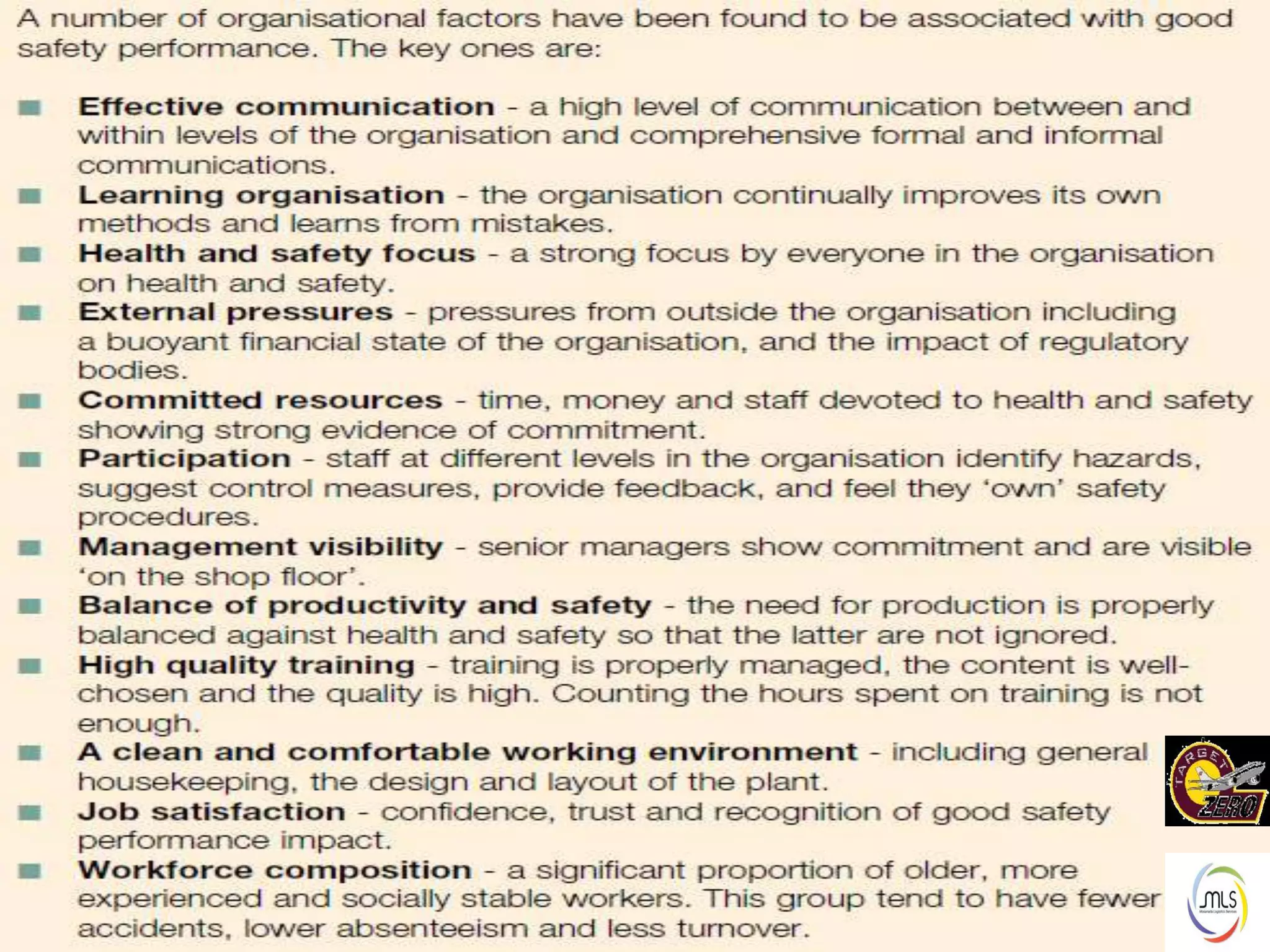
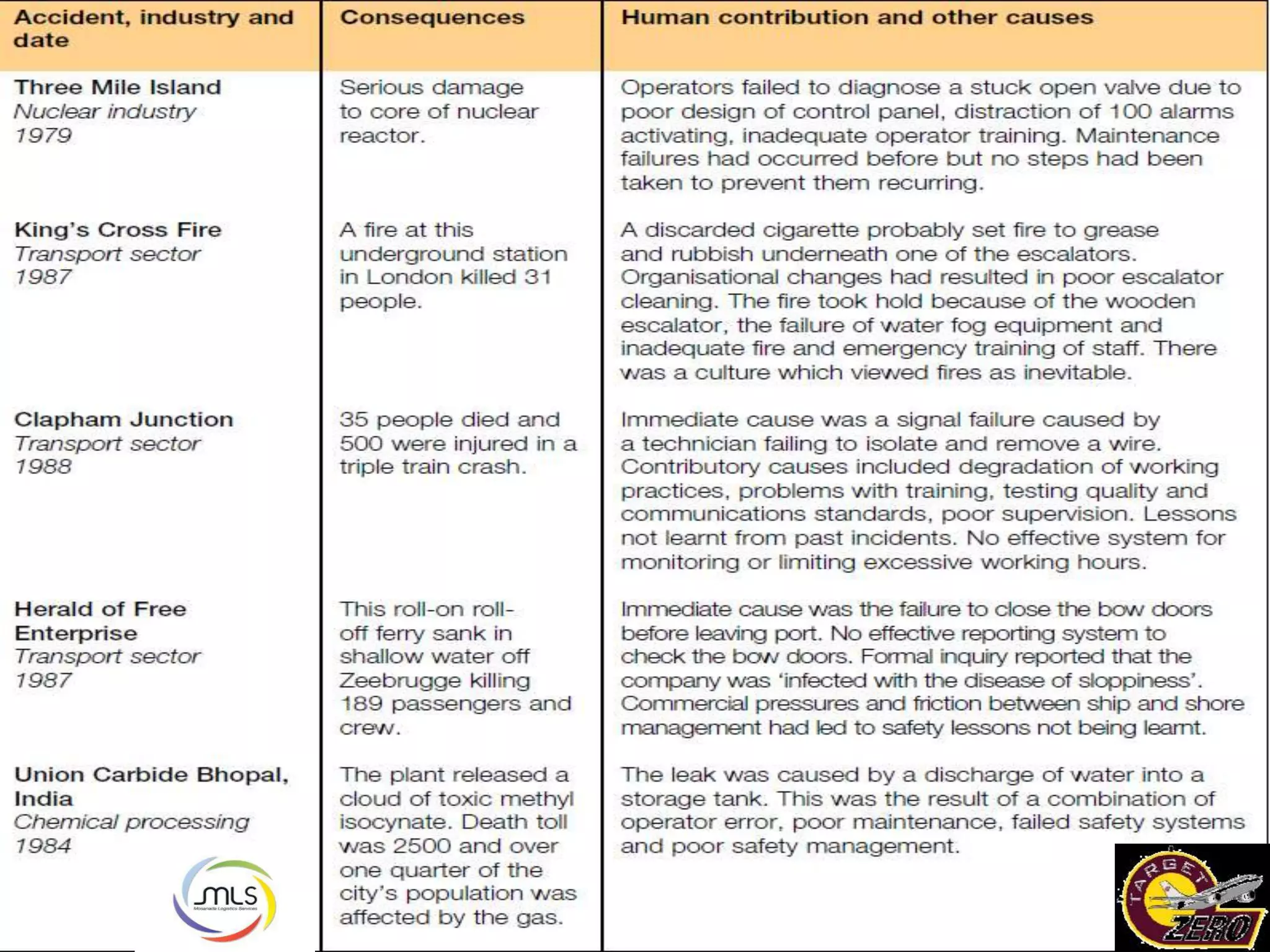
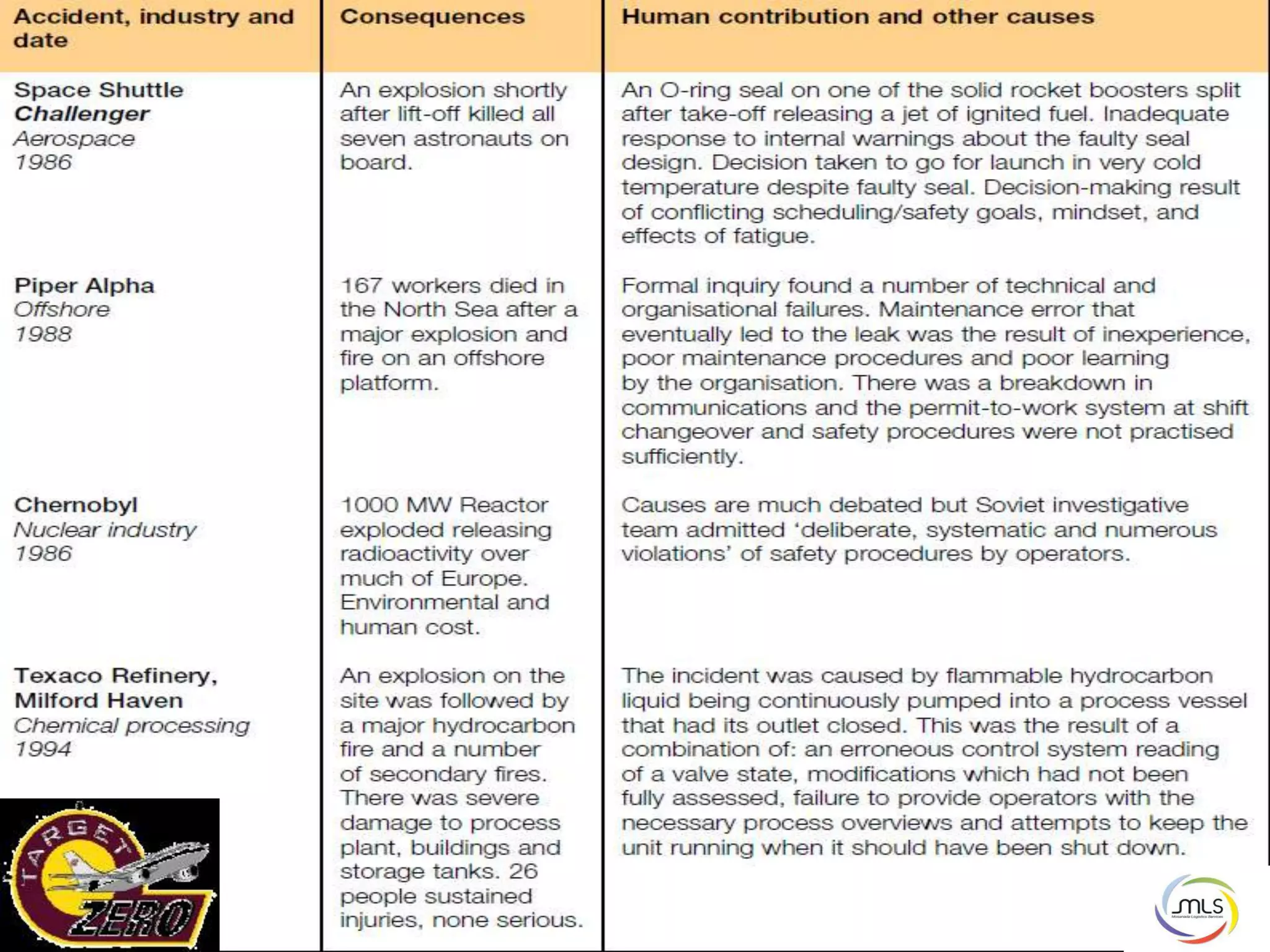
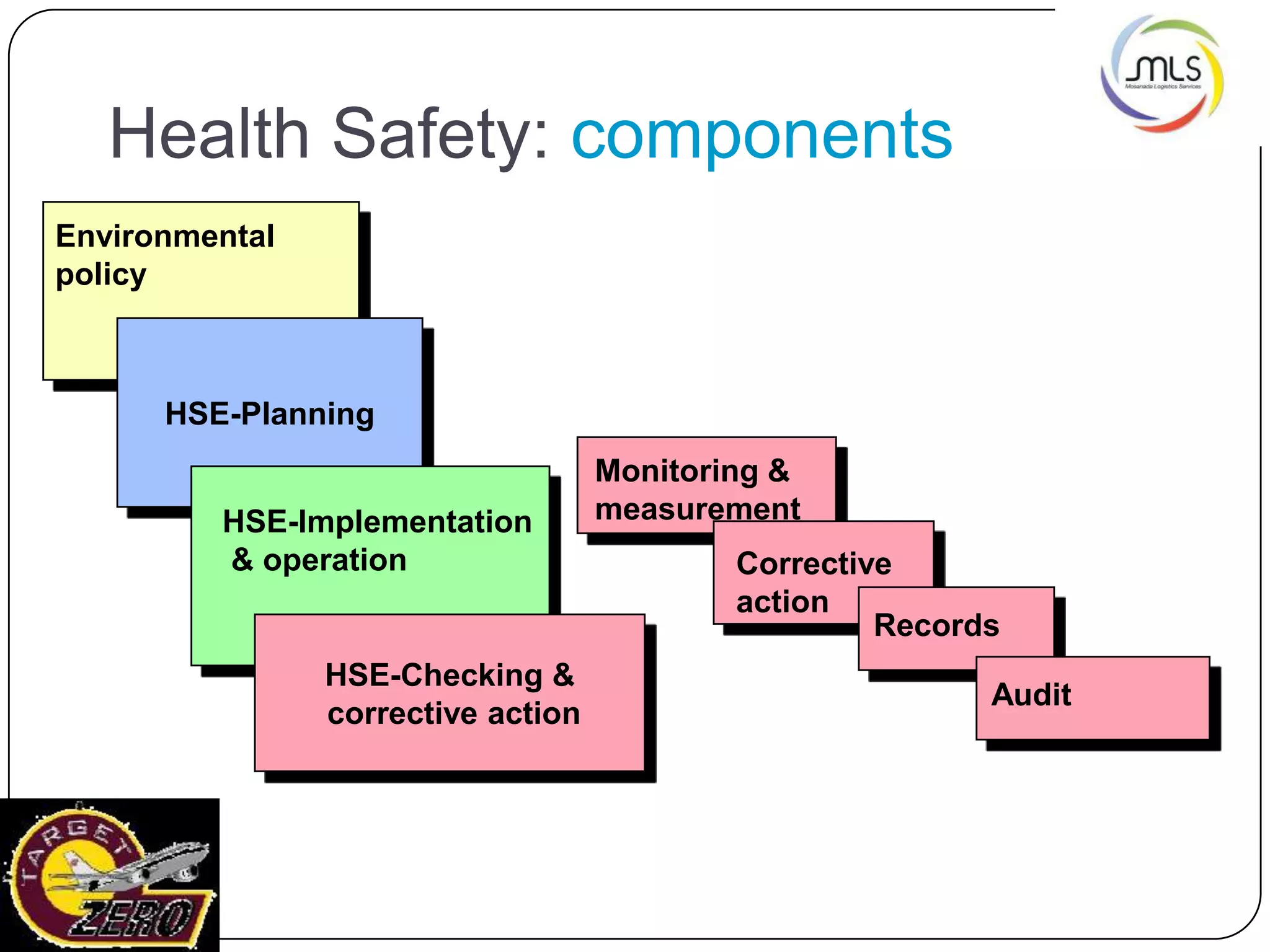
The document discusses the key components of an Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) management system based on ISO 14001 standards. It covers developing an EHS policy, planning objectives and processes, implementation through training and documentation, monitoring performance, conducting audits and reviews, and continually improving the system. The overall goal is to prevent risks, comply with regulations, and promote a strong safety culture.