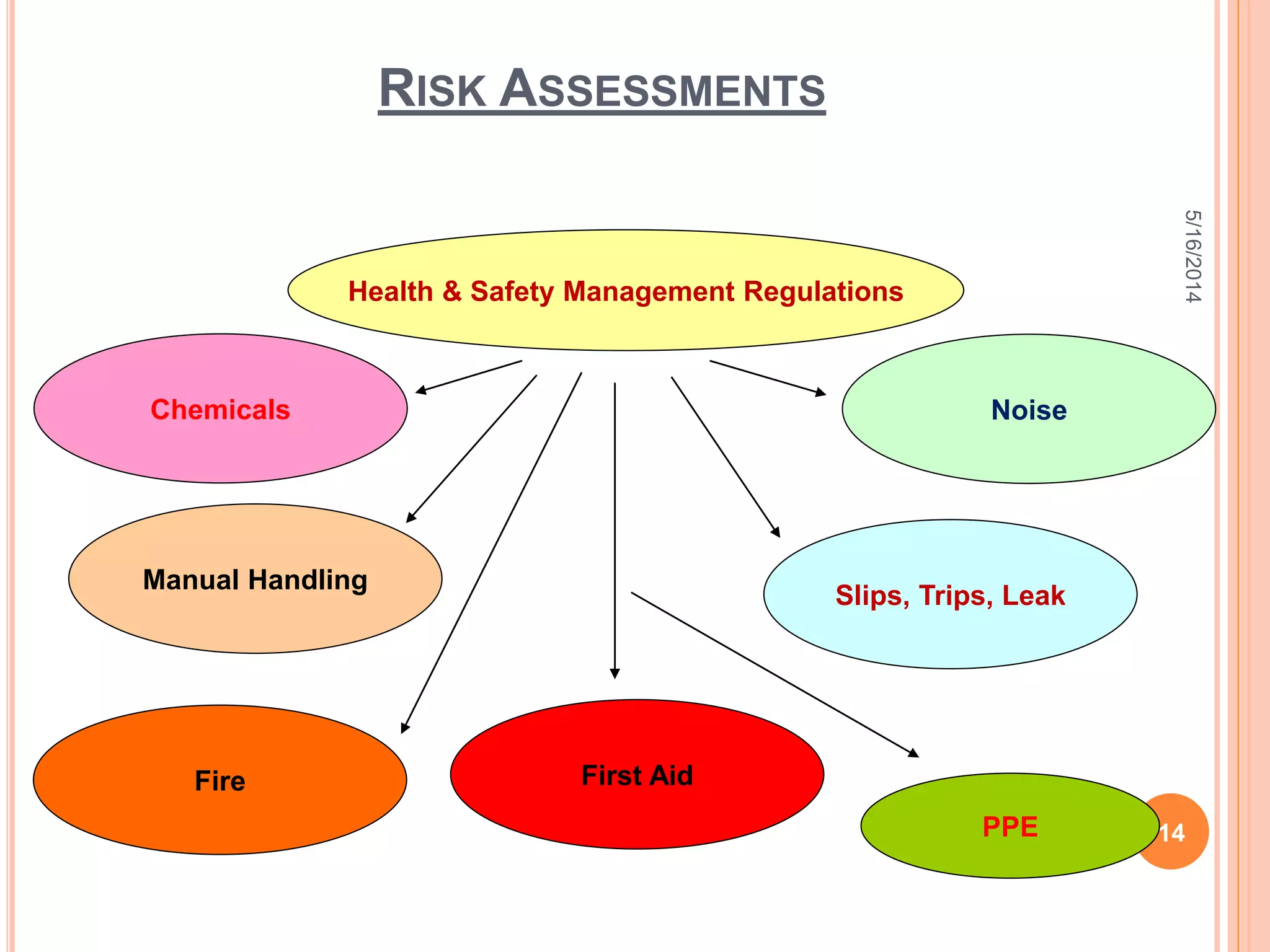
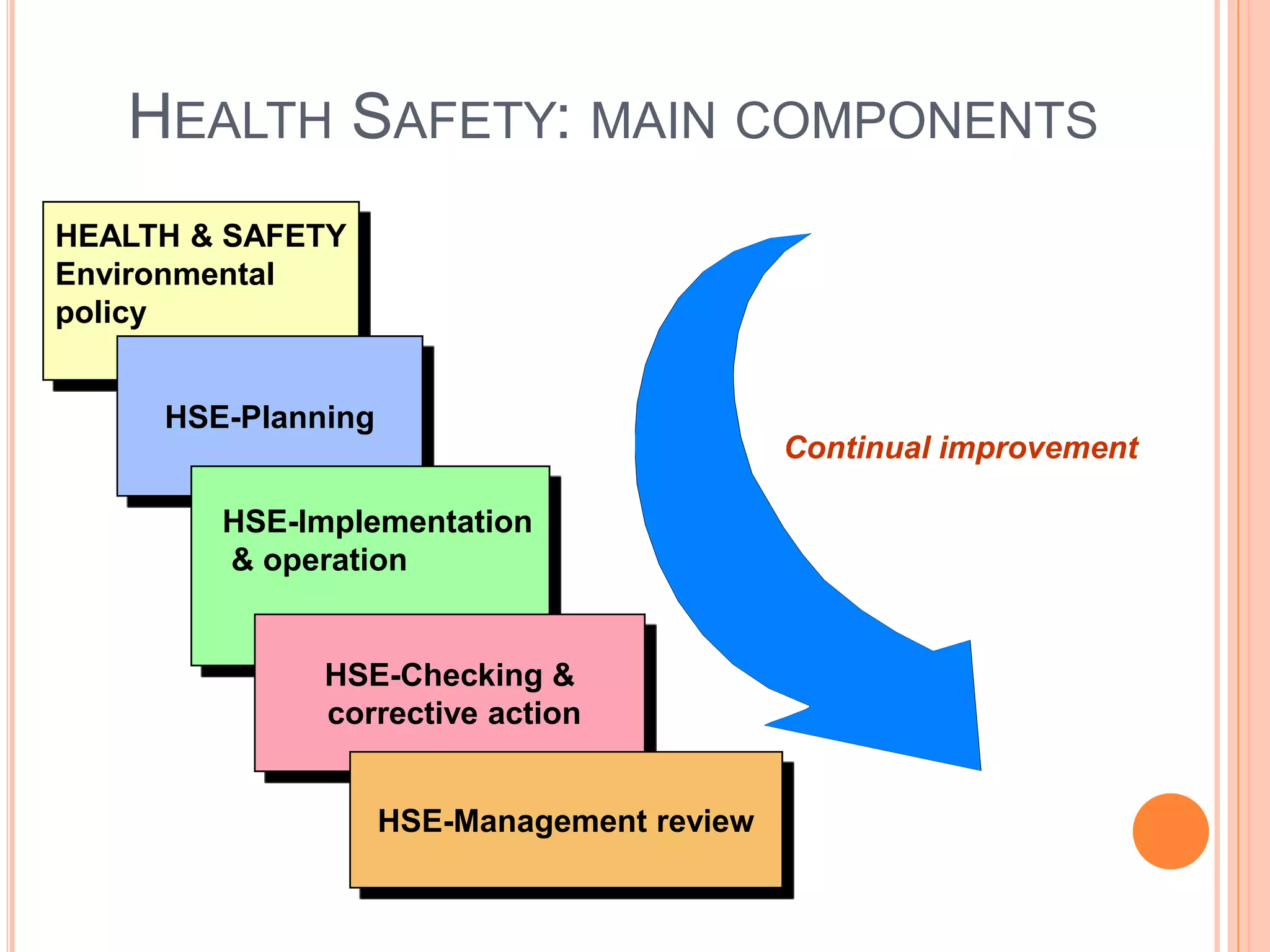
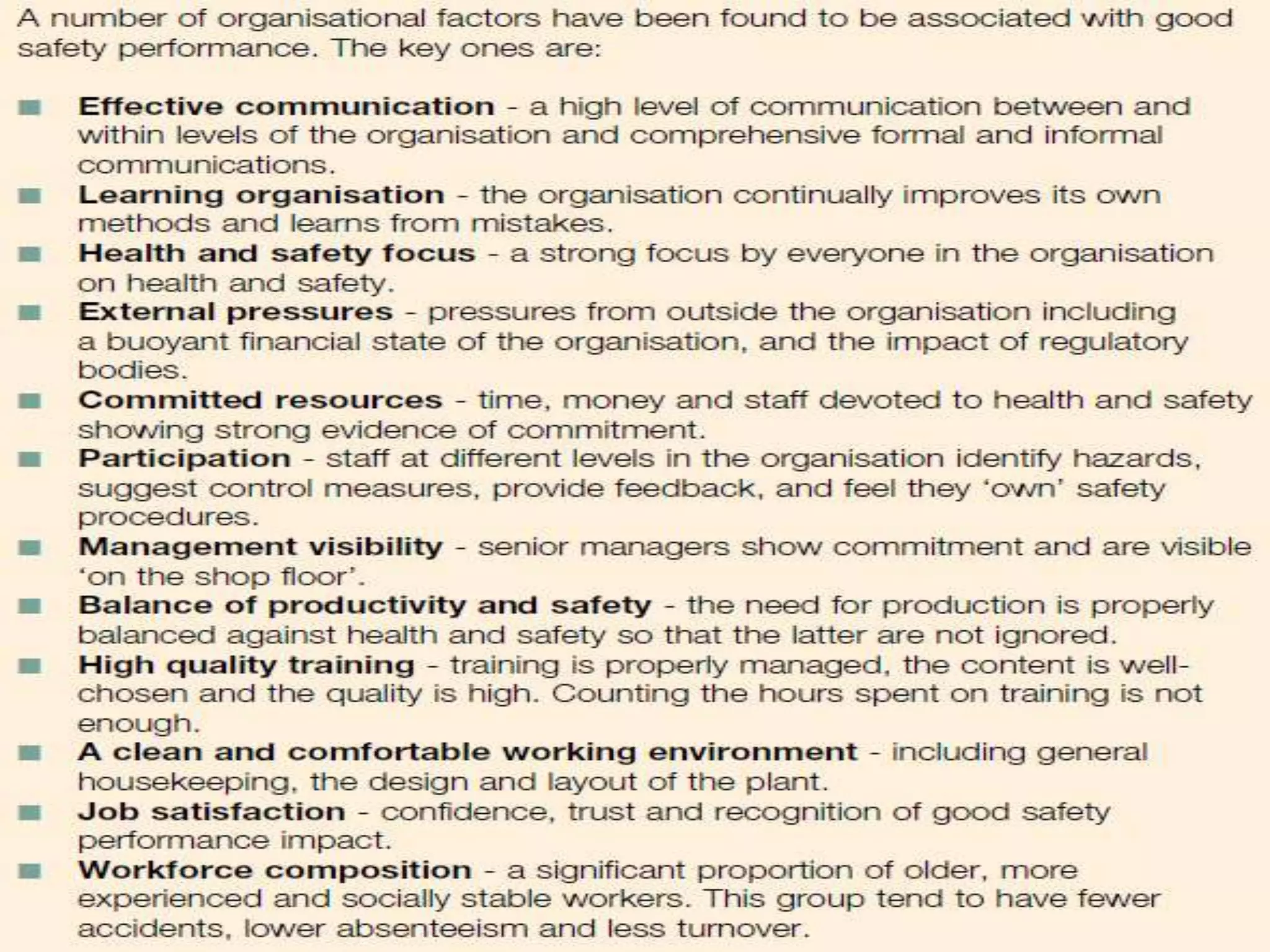
The document discusses environmental health and safety awareness. It covers topics like signage, risk assessments, hazards, risks, health risks, safety task analysis, a health and safety management system, and ISO 14001 components. Risk assessments are used to reduce accidents through planning, organization, control, monitoring and review. Hazards are things that have potential to cause harm, while risks are the likelihood of hazards causing harm. A health and safety management system includes a policy, planning, implementation, checking and corrective action, and management reviews.