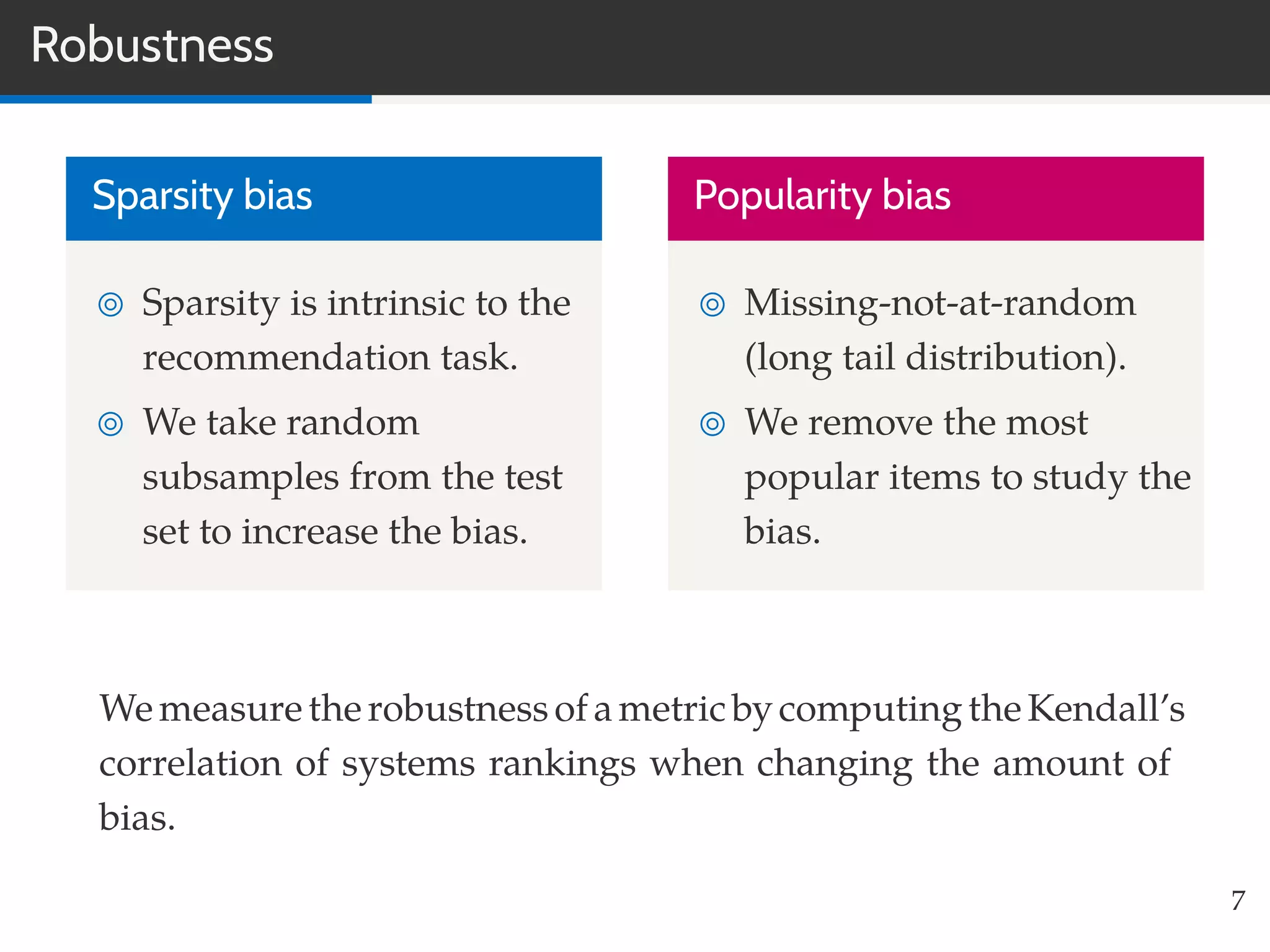
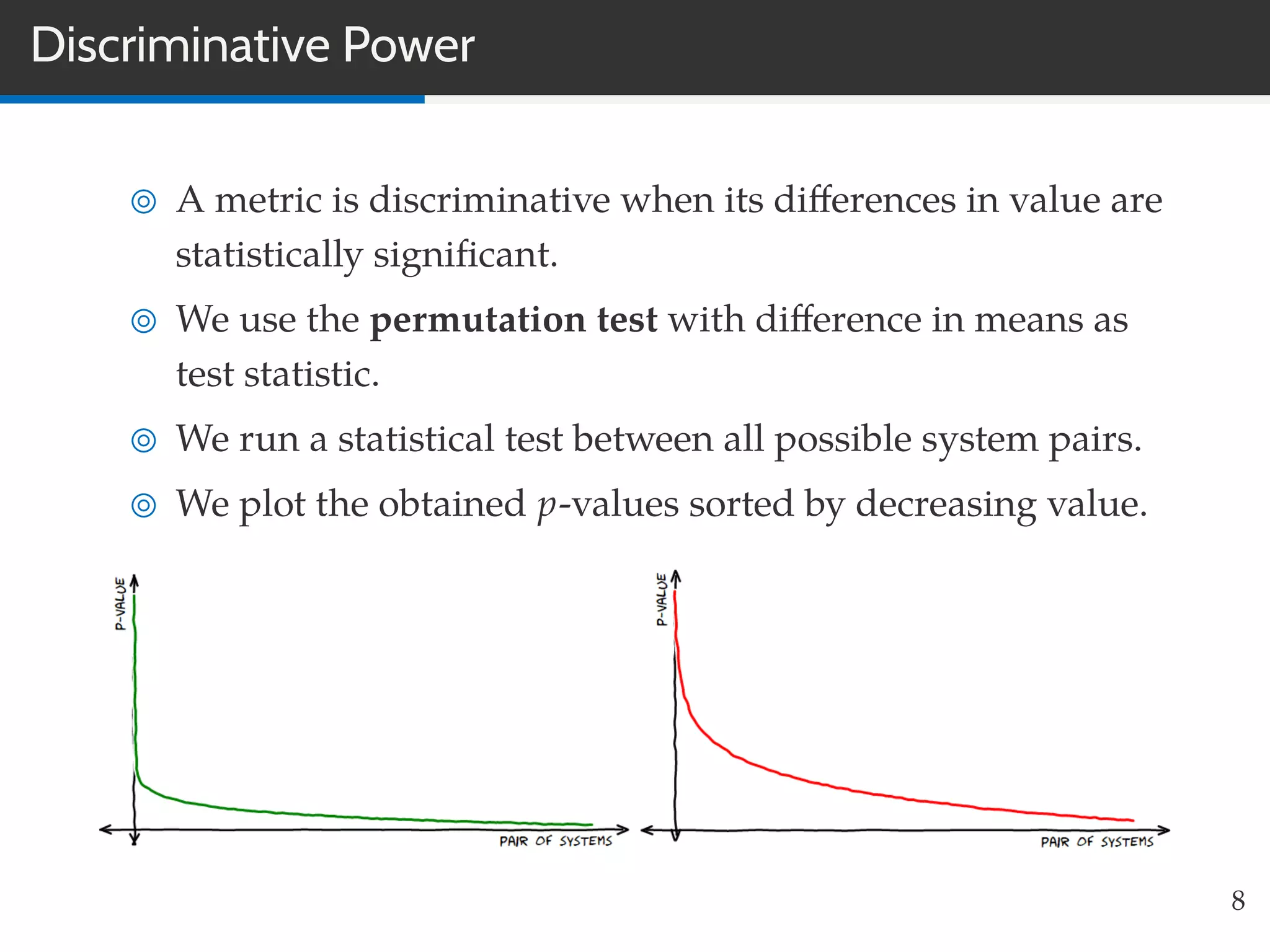
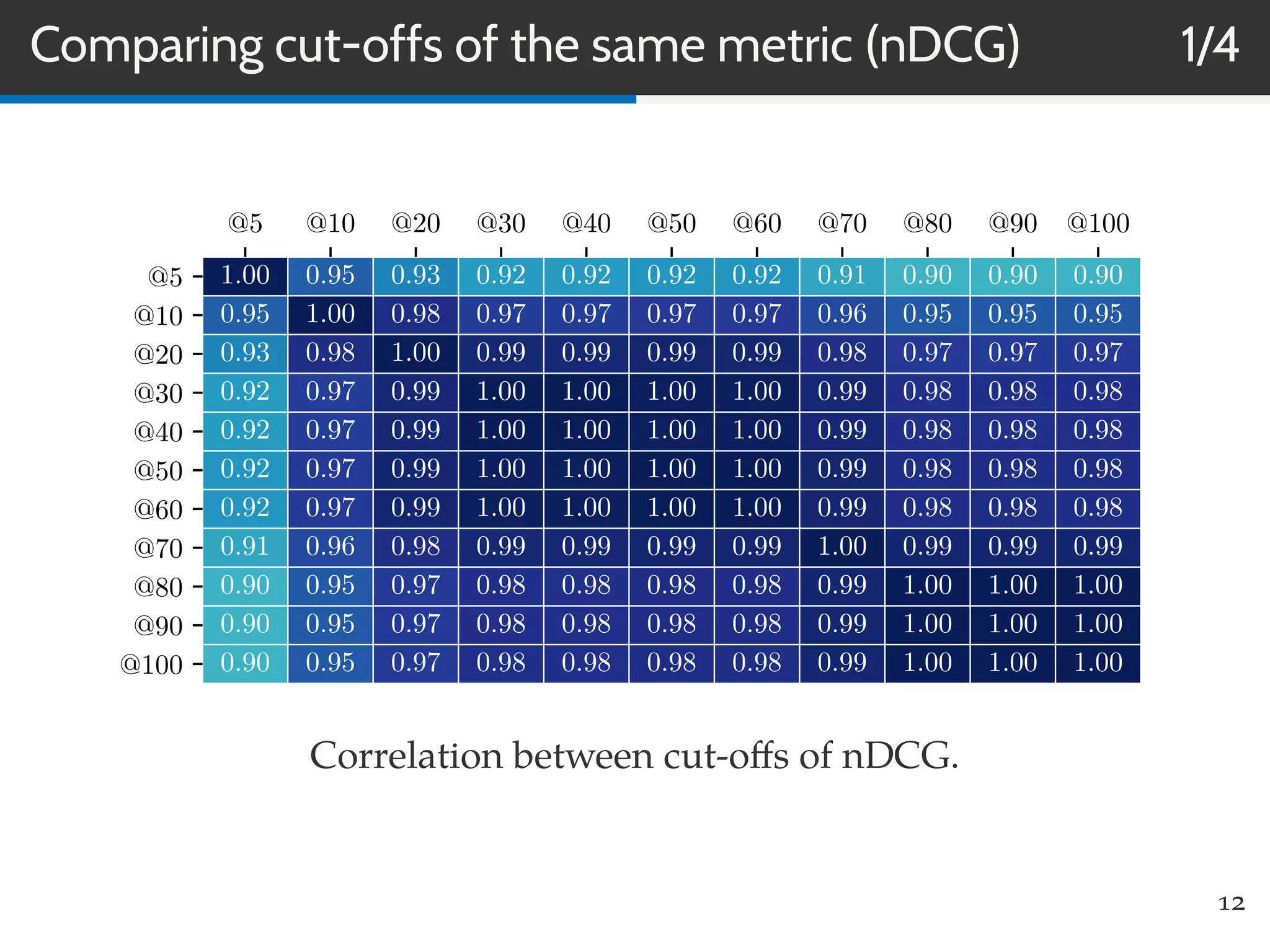
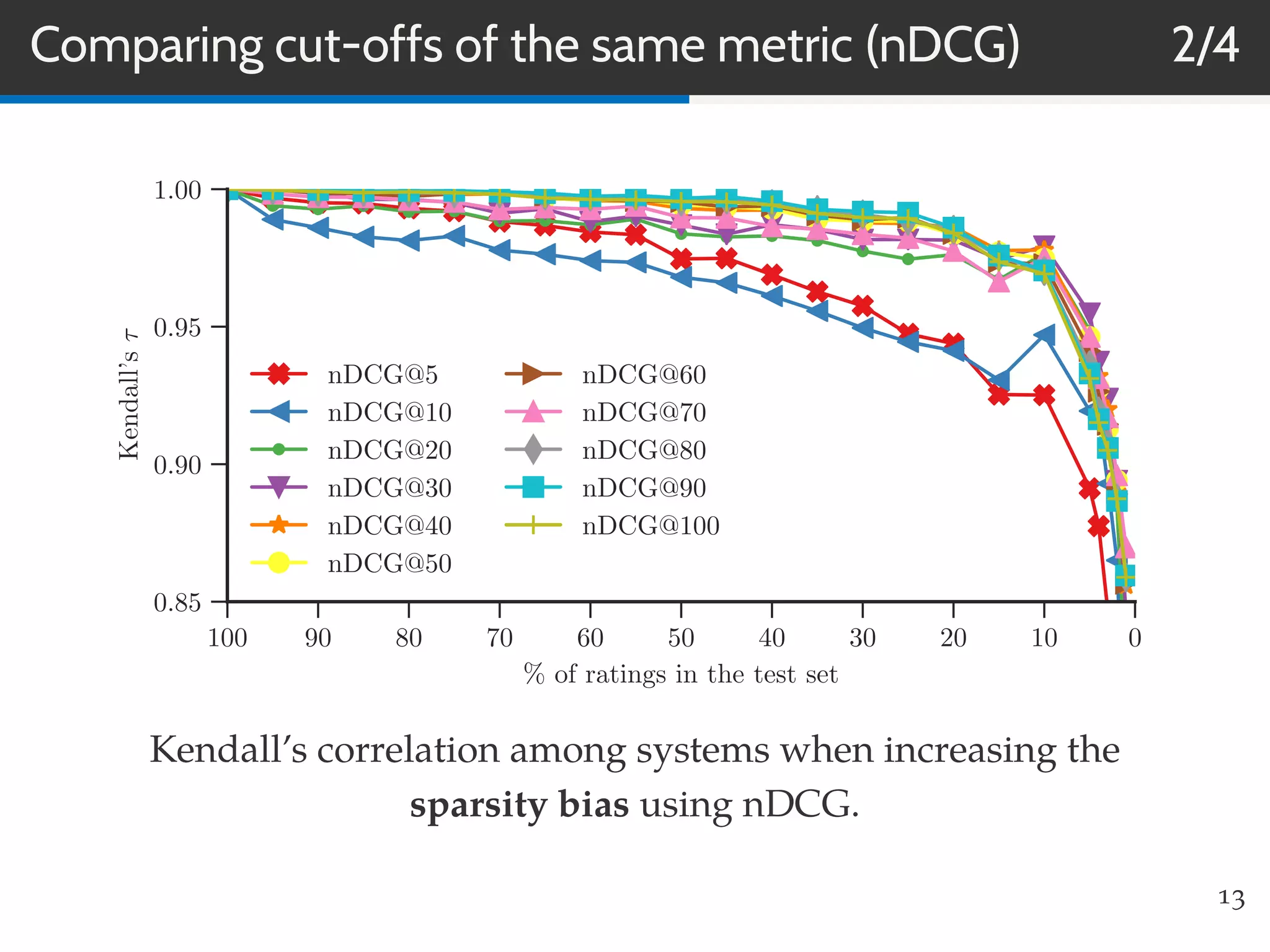
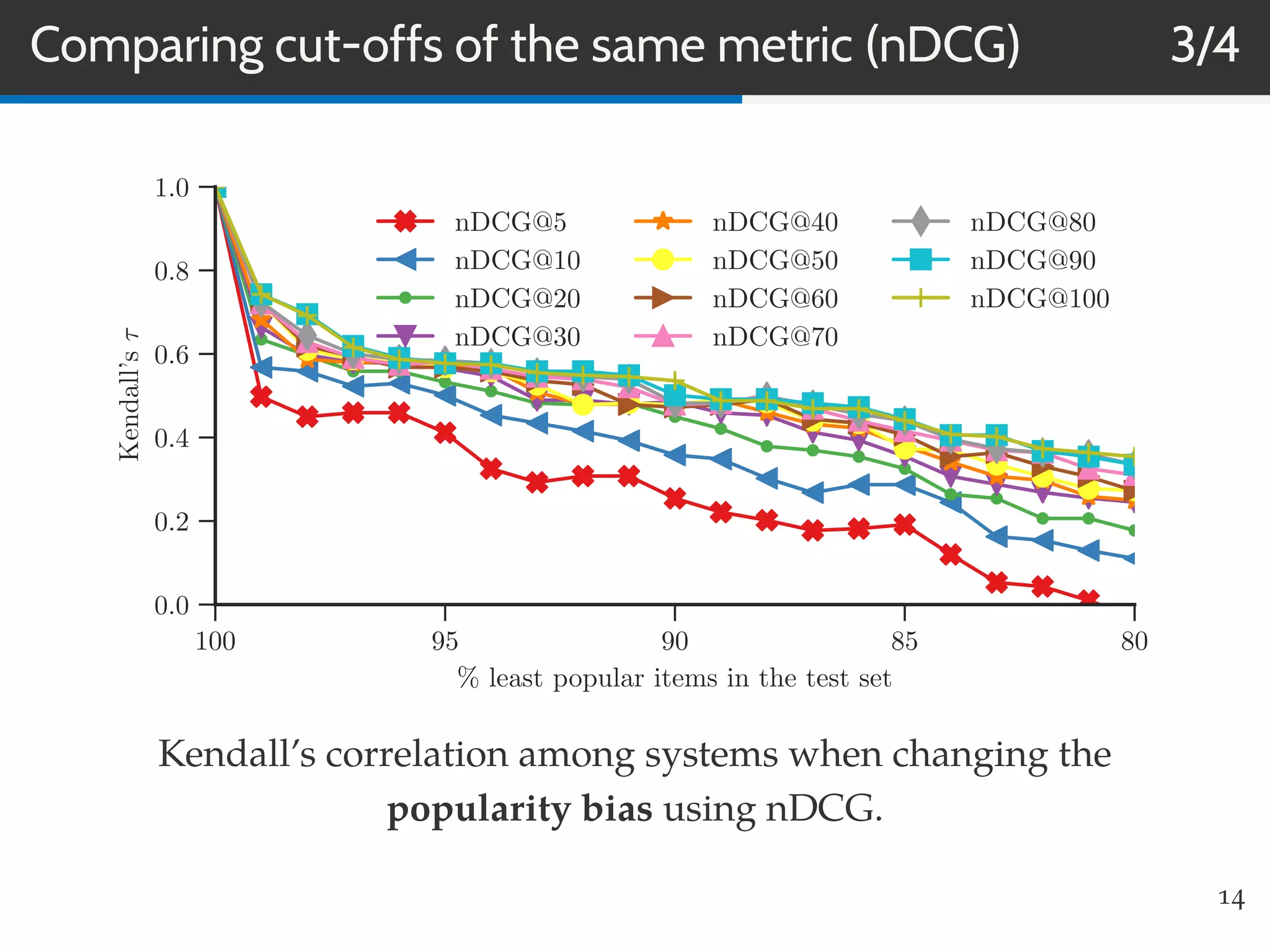
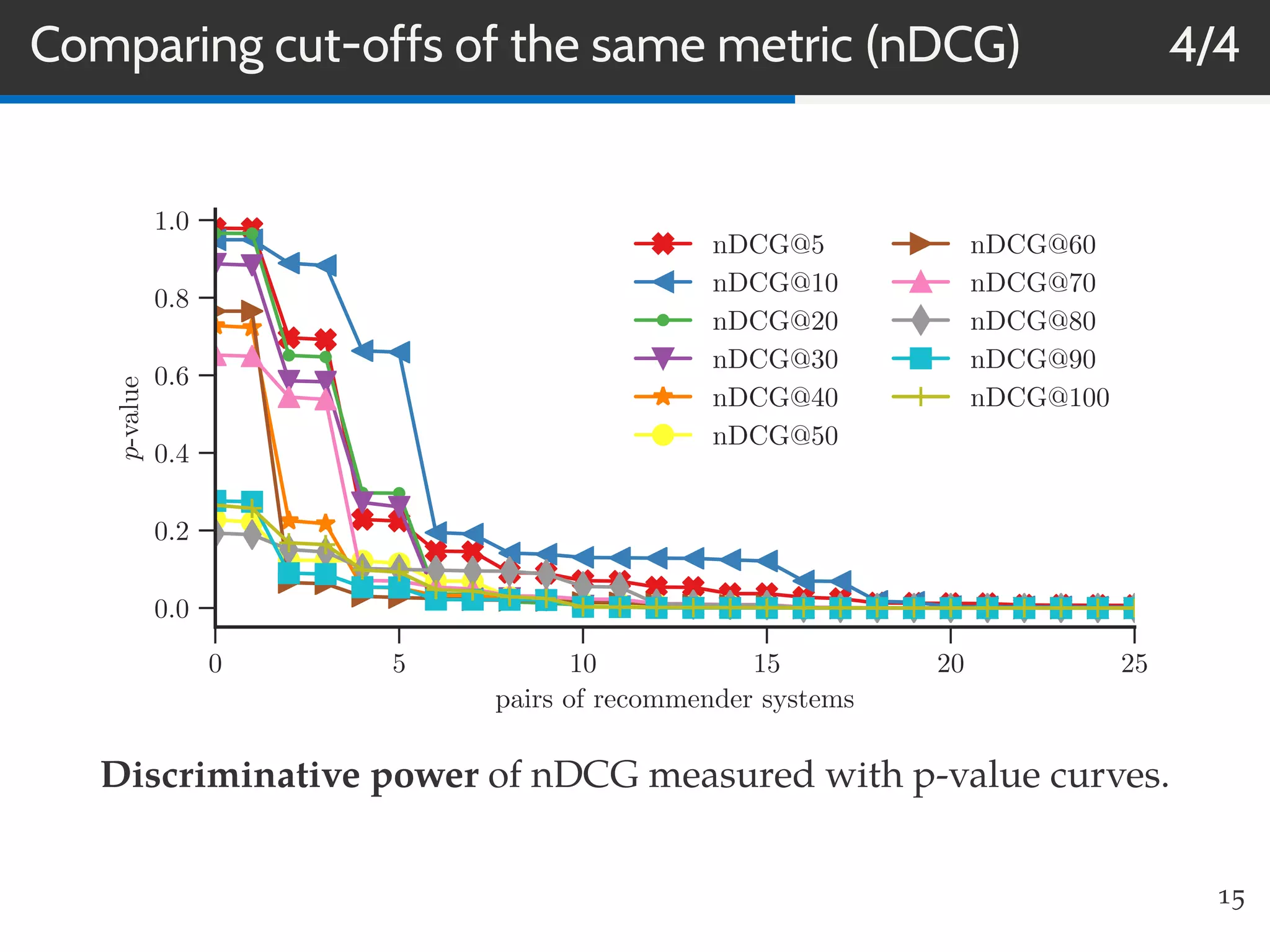
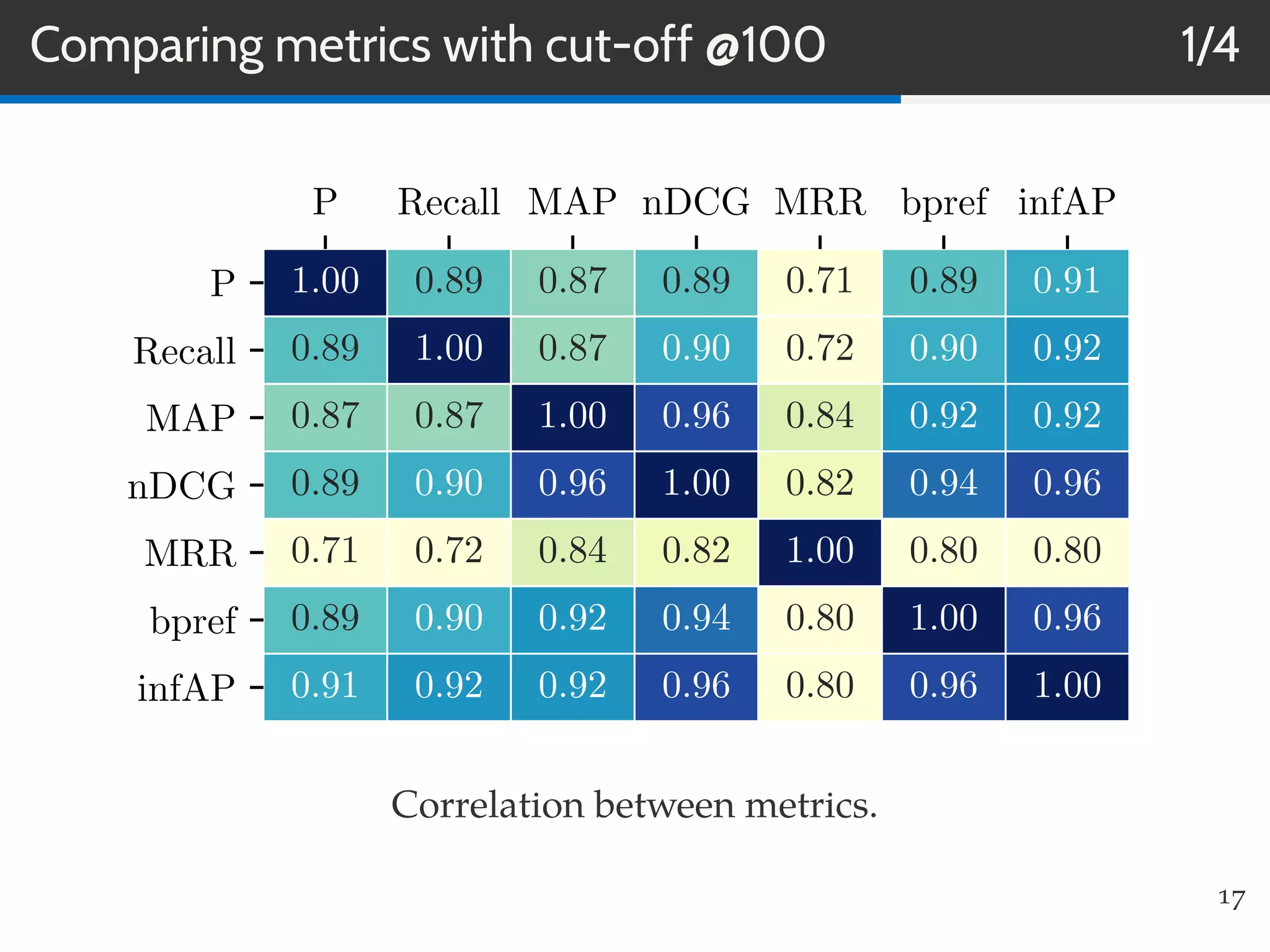
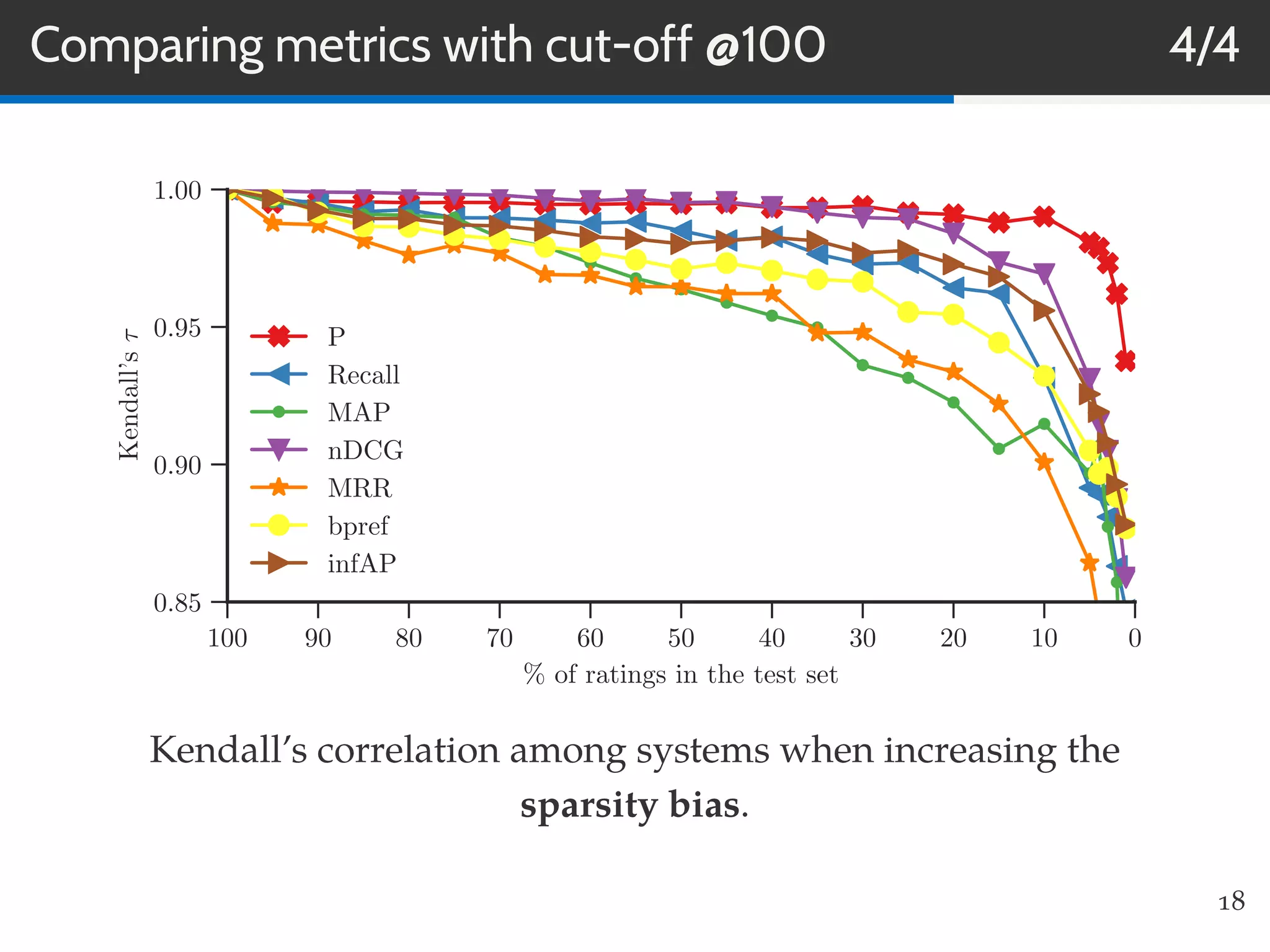
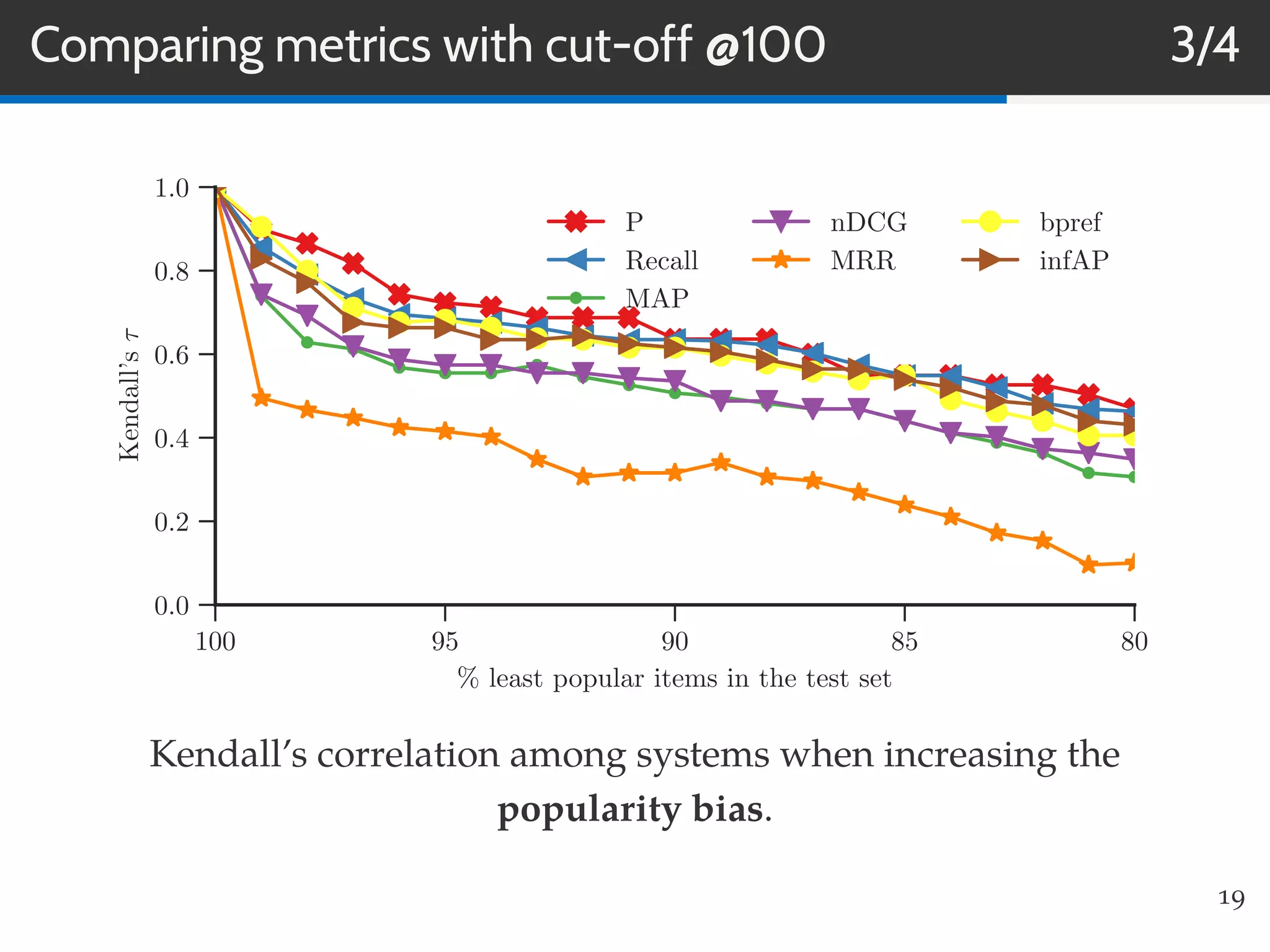
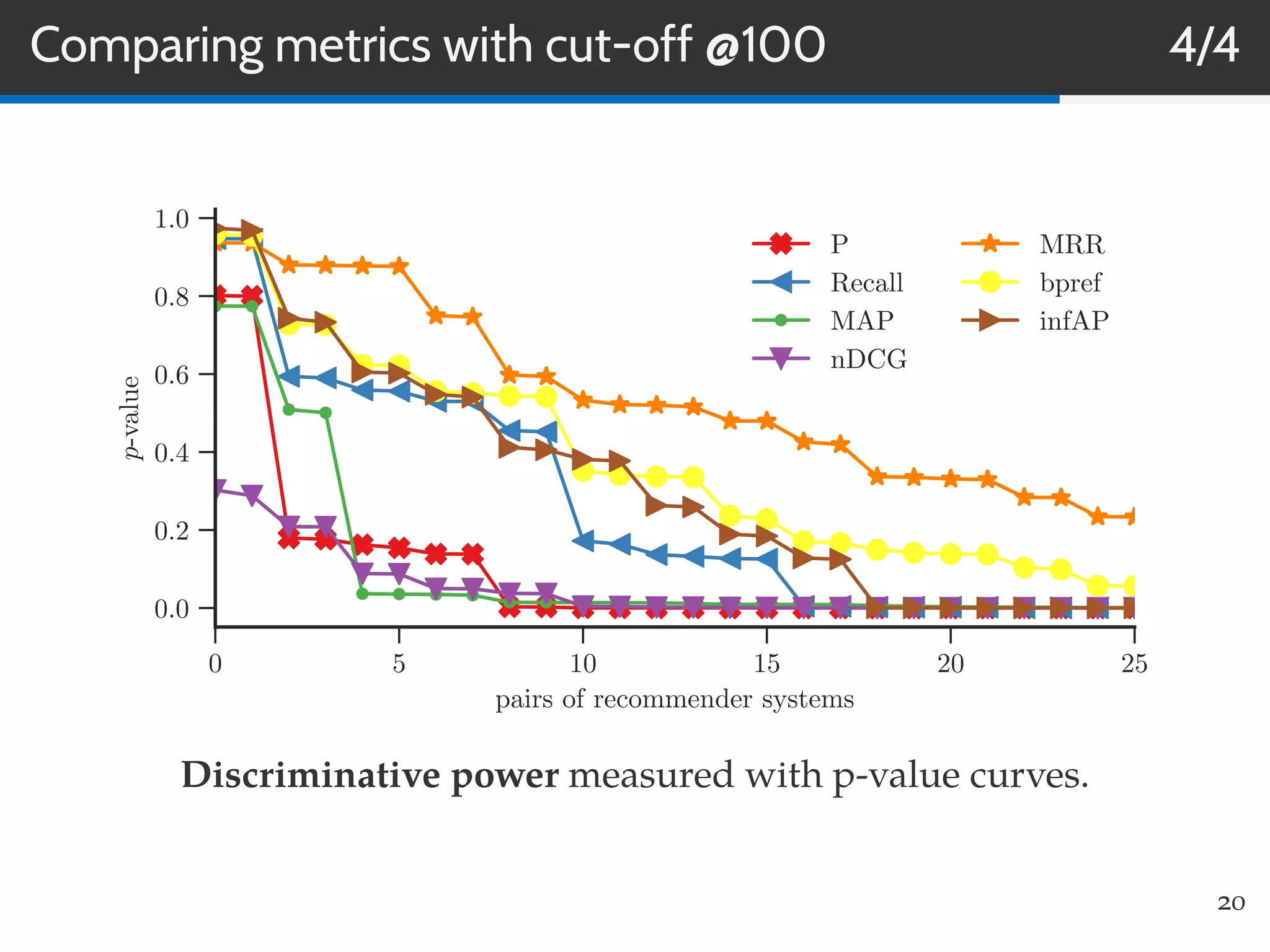
This document summarizes research on evaluating the robustness and discriminative power of information retrieval (IR) metrics for top-N recommendation. The researchers studied how various IR metrics like precision, recall, MAP, nDCG, MRR and bpref behave under different conditions like increased sparsity or popularity bias. They found that deeper cut-offs of metrics offer greater robustness and discriminative power than shallow cut-offs. Precision provided high robustness to biases and good discriminative power, while nDCG had the best discriminative power and robustness to sparsity bias. Future work could explore other metrics like diversity, use different evaluation methodologies, and employ temporal data splits.