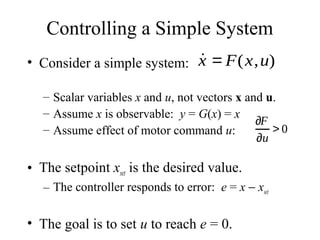
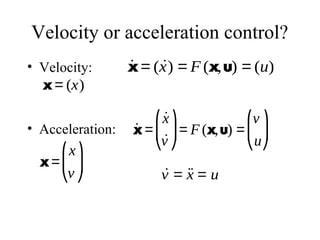
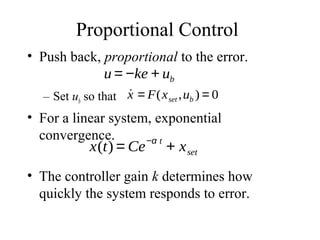
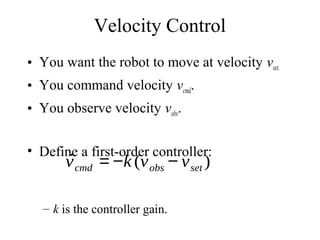
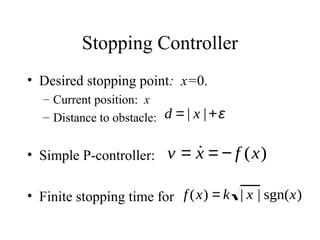
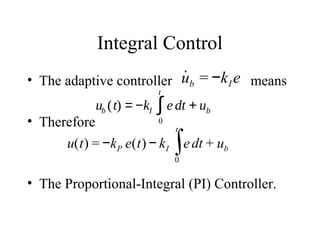
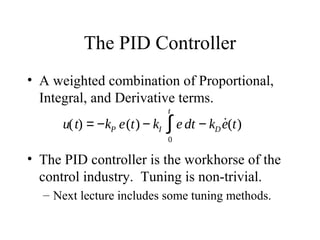
This lecture introduces basic concepts in control systems including proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) control. Proportional control uses feedback of the error to determine the control input proportional to the error. Integral control adds an integral term that eliminates steady-state error caused by disturbances. Derivative control adds a damping term proportional to the rate of change of error. Together, proportional, integral and derivative control form the widely used PID controller. The lecture also discusses velocity control, stopping control, adaptive control and different types of controllers including feedback and feedforward control.