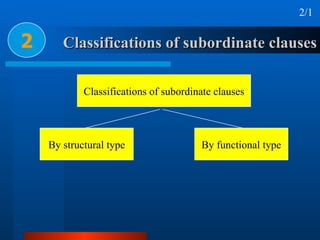
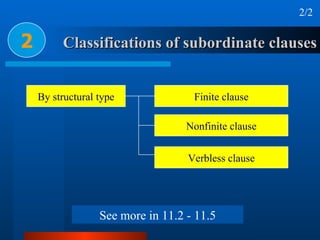
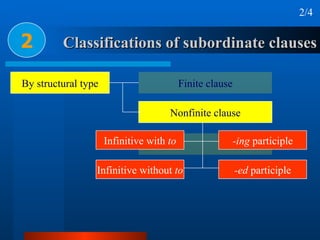
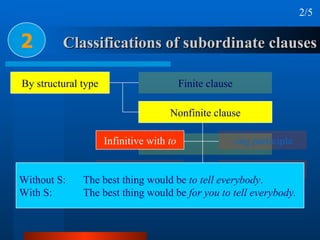
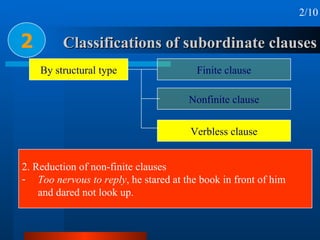
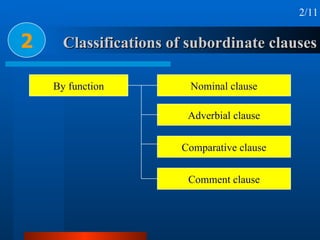
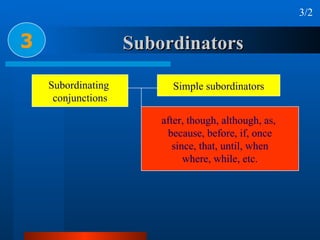
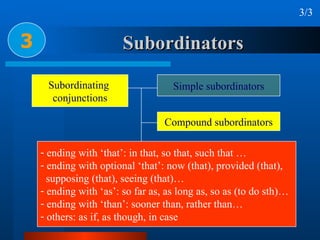
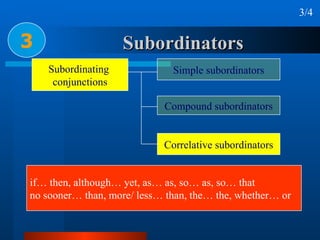
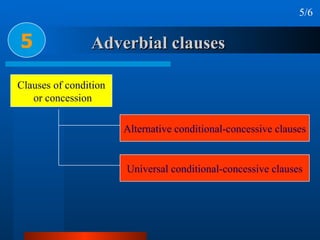
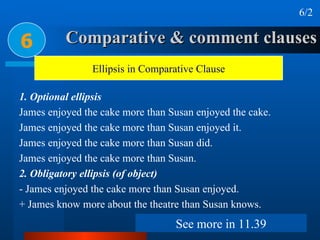
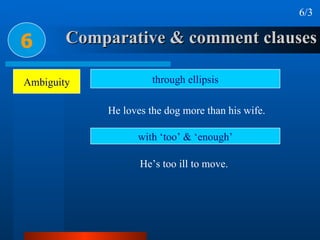
This document summarizes different types of complex sentences. It discusses subordinate clauses including nominal clauses and adverbial clauses. It covers classifications of subordinate clauses by structural type and functional type. It also describes different subordinators used to introduce subordinate clauses like conjunctions, wh-elements, and subject-operator inversion.



![Subordination 1 1/2 1 2 21 [I like John [because John likes me] ] 1 1 [superordinate/ independent/ main clause ] 2 2 [subordinate/ dependent clause] Non-symmetrical relation held between two clauses: one clause is a constituent/ part of the other Subordination i.e. one clause is Non-symmetrical relation, a constituent/ part of the other](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week9-thecomplexsentence-111118022954-phpapp02/85/Week-9-the-complex-sentence-4-320.jpg)
![Subordination 1 1/3 X- Y- Z- ( I think [ that you can do it { if you try} ] ) S V O A Z = subordinate to Y Y = subordinate to X Y & Z = dependent clauses X = independent clause Subordination Hierarchy of clauses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week9-thecomplexsentence-111118022954-phpapp02/85/Week-9-the-complex-sentence-5-320.jpg)